1, Foreword
article Kubernetes production practice series 15: Architecture and working principle of Kubernetes Ingress Nginx This paper describes the working principle of Ingress Nginx, and introduces the practice of Ingress in the production environment.
First of all, it needs to be clear that the Ingress Nginx of the production environment is not directly external. In front of it, there are internal network LB/Kong / external network LB and other components. To reach the Ingress Nginx, all we need to do is to select the route for the domain name and path.
Reprinted from https://blog.csdn.net/cloudvtech
2, Deployment
2.1 deployment application
Because the Kubernetets cluster we deployed in AWS uses Calico CNI, we deployed Ingress Nginx in the following way:
https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/blob/master/docs/deploy/baremetal.md
The configuration file of ingress nginx needs to be deployed in advance is as follows:
apiVersion: v1
data:
compute-full-forwarded-for: "true"
forwarded-for-header: X-Forwarded-For
upstream-keepalive-connections: "110"
use-forwarded-headers: "true"
worker-processes: "4"
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
name: nginx-configuration
namespace: ingress-nginx
Here, it is specified that when Nginx is started, four worker s are used, and keepalive is 110 seconds
Before deploying Ingress Nginx, select several nodes and label them. These nodes will be added to LB and the Ingress Nginx daemons will only be deployed on these nodes. At the same time, when deploying daemonset, you can see that the startup parameters of Ingress Nginx are as follows:
- args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
- --tcp-services-configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/tcp-services
- --udp-services-configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/udp-services
- --publish-service=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/ingress-nginx
- --annotations-prefix=nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io
It includes configmap for ingress nginx, configmap for exposing tcp/udp services, etc.
2.2 NodePort service deployment
After deploying the daemonset, you need to deploy the NodePort Service to access the external traffic:
piVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
nodePort: 80
- name: https
port: 443
targetPort: 443
protocol: TCP
nodePort: 443
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
The above Ingress Nginx will access 80 and 443 traffic. The figure below shows that the requests of different back-end services enter Ingress through NodePort, and finally enter into each business POD:
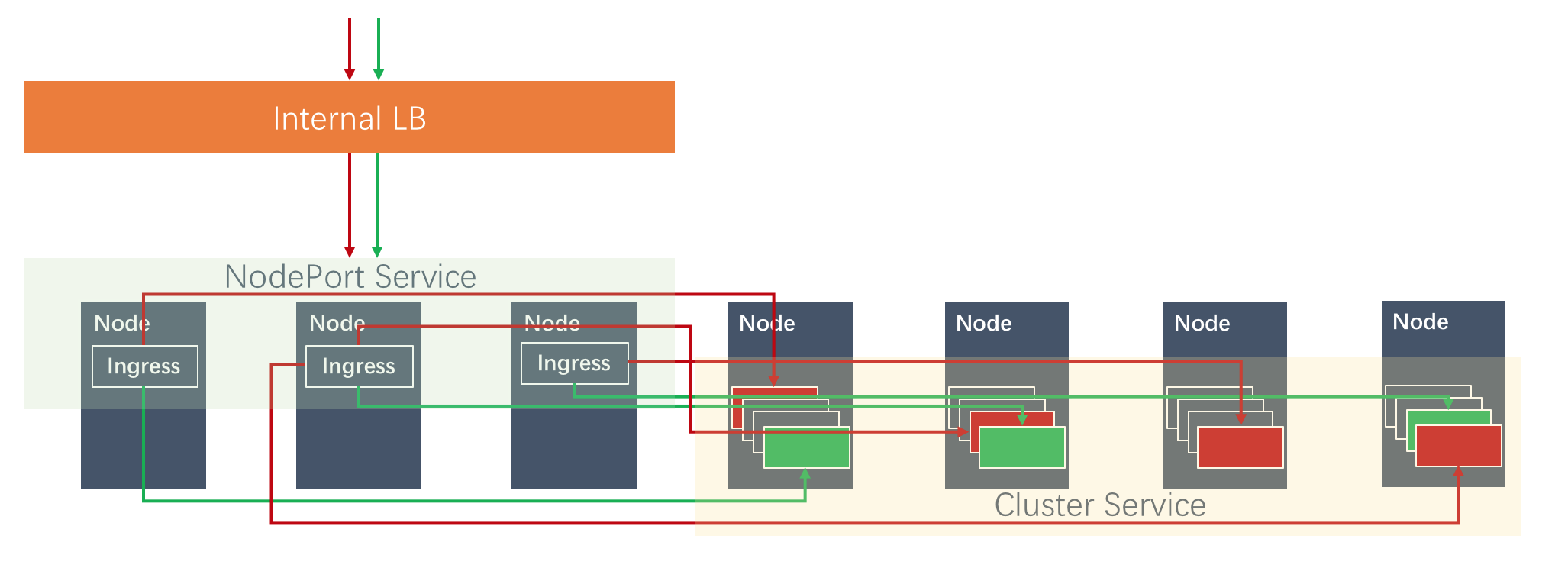 Access external traffic through the node port of Ingress
Access external traffic through the node port of Ingress
Reprinted from https://blog.csdn.net/cloudvtech
3, Log scheme
3.1 log drop path
The log of Ingress is written to the log path inside the POD, which is the local path of the host as the hostPath and mounted inside the POD, so the log of Nginx is actually landed on the host disk. For this reason, we mount a log disk on each host for log storage. When deploying Daemonset, the configuration of the path mount is as follows:
...
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/log/nginx/
name: log-volume
...
volumes:
- hostPath:
path: /var/log/pod-logs/ingress-nginx
type: Directory
name: log-volume
3.2 log format
You can define the log format of Ingress Nginx in the configmap of nginx configuration:
log-format-upstream: $remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] $server_name:$server_port
$scheme "$request" $status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent"
"$http_x_forwarded_for" $connection $upstream_addr $upstream_response_time $request_time
$request_length
3.3 log rotate
Because all requests of the business system will go through Ingress, the log volume of Ingress is very large, so it needs to be compressed and rotated in time. The biggest difficulty of log rotate in Ingress Nginx POD is to achieve two things through the host cronjob:
- Use kill to send reload signal to nginx process in the container to switch logs without affecting business
- Can run logrotate externally to rotate logs
The following figure shows the process:
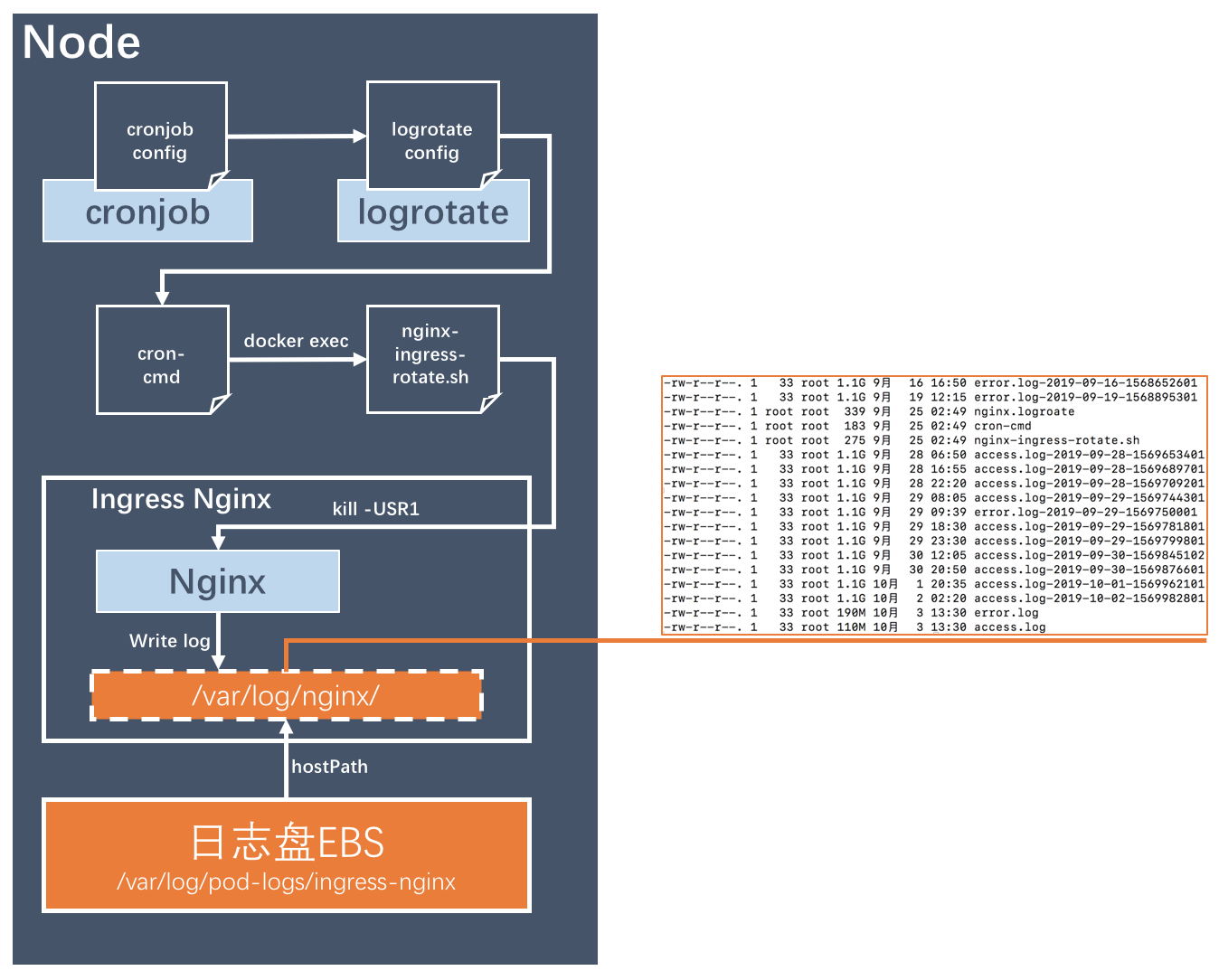 Progress nginx log rotate process
Progress nginx log rotate process
Our system will rotate every hour, and the corresponding cron job s are as follows:
*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/logrotate /var/log/pod-logs/ingress-nginx/nginx.logroate >/dev/null 2>&1
nginx.logroate The contents are as follows:
/var/log/pod-logs/ingress-nginx/*.log {
size 1024M
rotate 10
missingok
notifempty
sharedscripts
dateext
dateformat -%Y-%m-%d-%s
postrotate
if [ `/usr/bin/docker ps | grep ingress-controller_nginx-ingress | grep -v pause | awk '{print $1}'` ]; then
/bin/bash /var/log/pod-logs/ingress-nginx/cron-cmd || true
fi
endscript
}
The content of cron CMD is as follows:
#!/bin/bash
CID=`/usr/bin/docker ps | grep ingress-controller_nginx-ingress | grep -v pause | awk '{print $1}'`
/usr/bin/docker exec $CID bash /var/log/nginx/nginx-ingress-rotate.sh
nginx-ingress-rotate.sh The contents are as follows:
#!/bin/bash
getdatestring()
{
TZ='Asia/Chongqing' date "+%Y%m%d%H%M"
}
datestring=$(getdatestring)
#mv /var/log/nginx/access.log /var/log/nginx/access.${datestring}.log
#mv /var/log/nginx/error.log /var/log/nginx/error.${datestring}.log
kill -USR1 `cat /tmp/nginx.pid`
The final rotate effect is as follows:
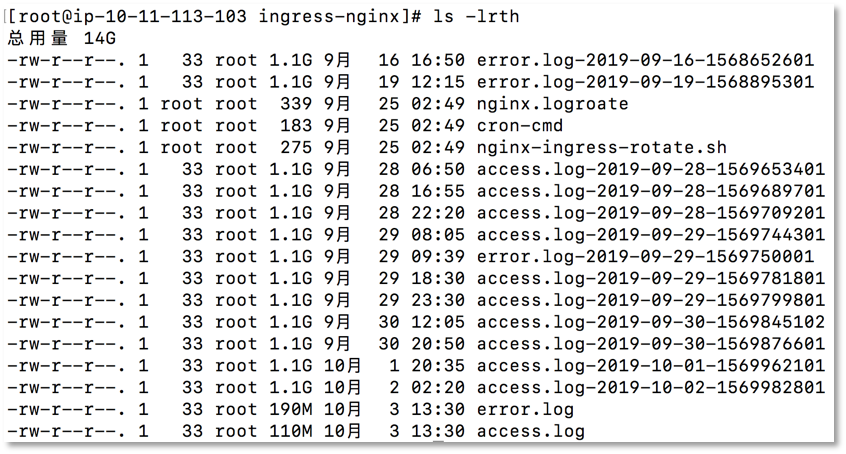
Reprinted from https://blog.csdn.net/cloudvtech
4, Monitoring plan
By default, Ingress Nginx opens the monitoring data interface compatible with Prometheus, so we can define the following cluster service to expose these interfaces:
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
namespace: ingress-nginx
name: nginx-ingress-prometheus
labels:
k8s-app: ingress
spec:
type: ClusterIP
clusterIP: None
ports:
- name: metrics
port: 10254
protocol: TCP
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
Then define the following servicemonitor to register with prometheus:
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: kube-nginx-ingress
namespace: monitoring
labels:
k8s-app: ingress
spec:
jobLabel: k8s-app
endpoints:
- port: metrics
interval: 30s
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: ingress
namespaceSelector:
matchNames:
- ingress-nginx
Finally, it is shown in grafana:
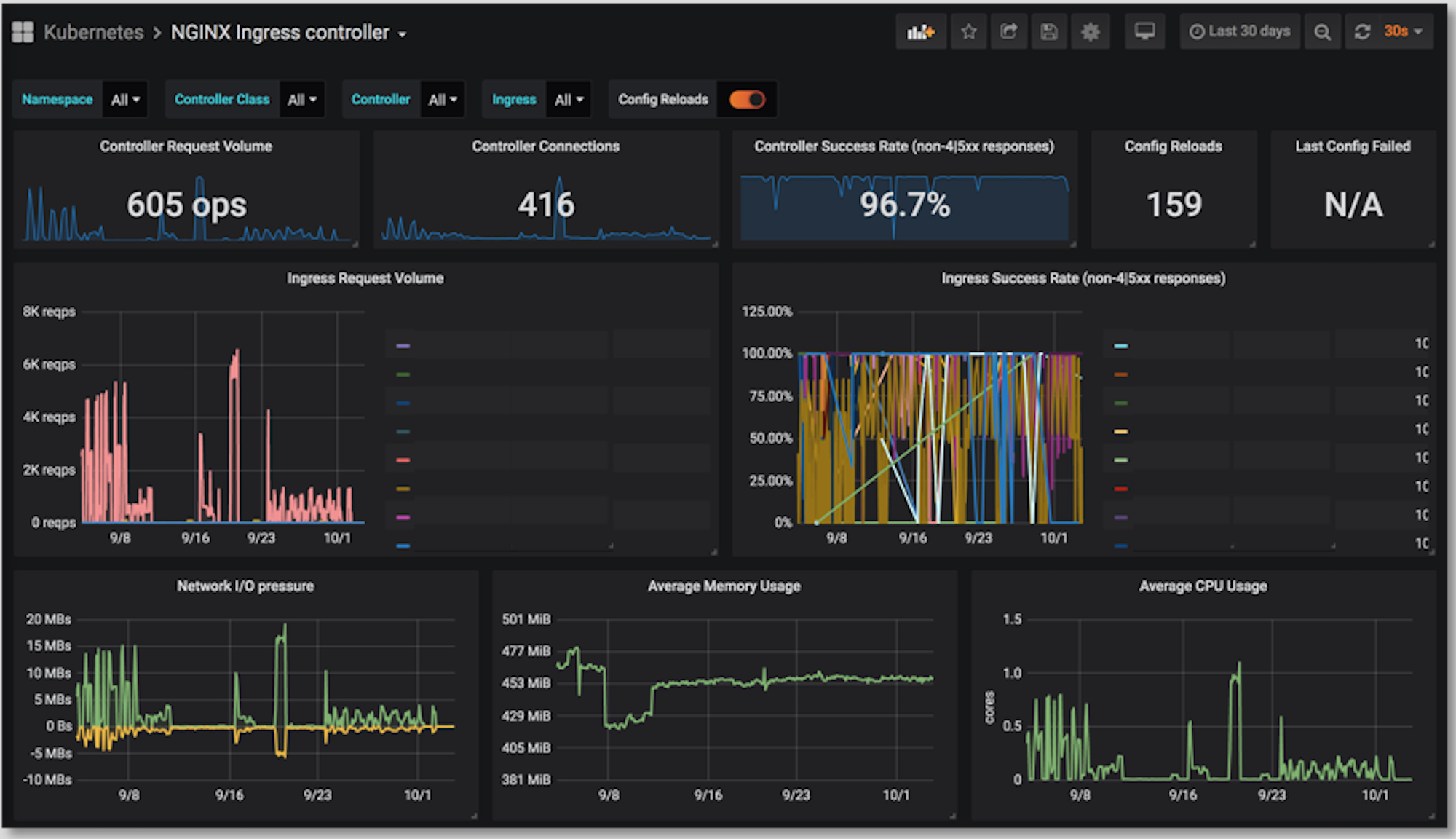
Reprinted from https://blog.csdn.net/cloudvtech
5, Configure Ingress exposure service
5.1 exposing HTTP services
This path gives some configuration types of ingress for reference:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/ingress/#types-of-ingress
Classic case:
piVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 50m
labels:
app: myapi-service-ingress
name: myapi-service-ingress
namespace: myapi
spec:
rules:
- host: myapi.test.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: myapi-service-service
servicePort: 8080
path: /
Case of Path replacement:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 50m
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$2
labels:
app: my-api-kong-ingress
name: my-api-kong-ingress
namespace: myapp
spec:
rules:
- host: platform.test.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: my-api-service
servicePort: 8080
path: /brand(/|$)(.*)
fanout's case:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 50m
labels:
app: my-service-ingress
name: my-service-ingress
namespace: myapp
spec:
rules:
- host: my.test.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: my-service
servicePort: 8000
path: /
- backend:
serviceName: my-service
servicePort: 9102
path: /metrics
5.2 exposing TCP/UDP services
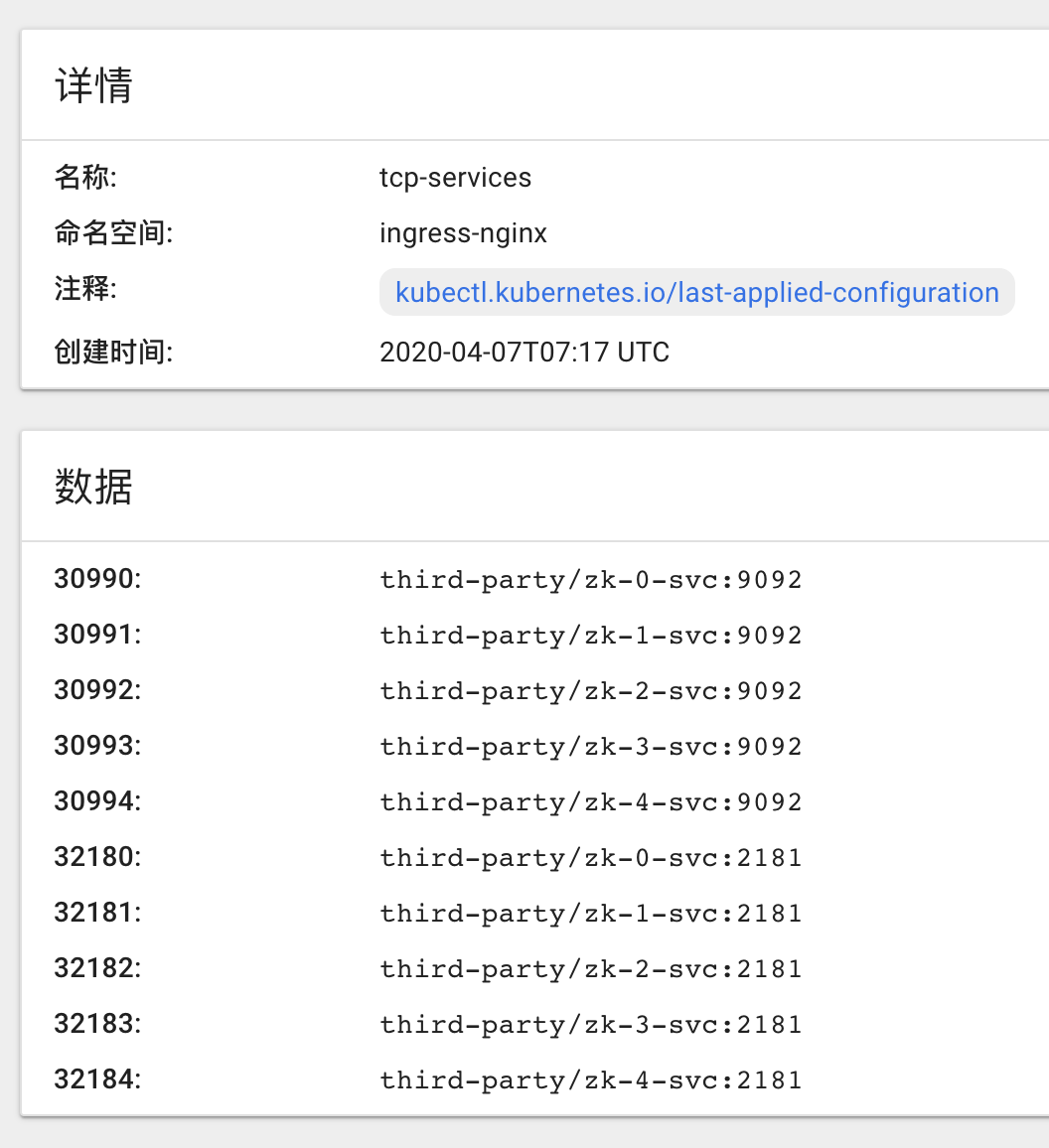
In our business scenario, we need to expose TCP services to provide TCP services deployed inside the cluster to applications outside the cluster, such as MySQL/Etcd/Zookeeper, which is used for service discovery of virtual machines and pods, while Zookeeper is used for HA guarantee of Kafka based on virtual machine installation.
Ingress Nginx can specify the following two configmaps when starting. All TCP/UDP services to be exposed can be specified in these two configmaps:
Exposed zookeeper's TCP services are as follows:
Reprinted from https://blog.csdn.net/cloudvtech