Collect all the information on the Internet, organize some steps, personal records, memorandums!
Install Docker
centos7 installs docker
Refer to https://www.runoob.com/docker/centos-docker-install.html and follow these steps for installation
- Remove the old version
yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-selinux \
docker-engine-selinux \
docker-engine
- Install some necessary system tools
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
- Adding Software Source Information
yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
- Update yum cache
yum makecache fast
- Install Docker-ce
yum -y install docker-ce
- Start Docker Background Service
systemctl start docker
- Test run hello-world
docker run hello-world
Use the docker images command to view the installed images
Building Mirrors with Dockerfile
Install jdk
First install jdk using centos base image
FROM centos
RUN mkdir /usr/local/java
ADD jdk-8u181-linux-x64.tar.gz /usr/local/java/
RUN ln -s /usr/local/java/jdk1.8.0_181 /usr/local/java/jdk
ENV JAVA_HOME /usr/local/java/jdk
ENV JRE_HOME ${JAVA_HOME}/jre
ENV CLASSPATH .:${JAVA_HOME}/lib:${JRE_HOME}/lib
ENV PATH ${JAVA_HOME}/bin:$PATH
ENV JAVA ${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java
Execute the command: docker build -t centos-jdk:1.8.0-181. Build the mirror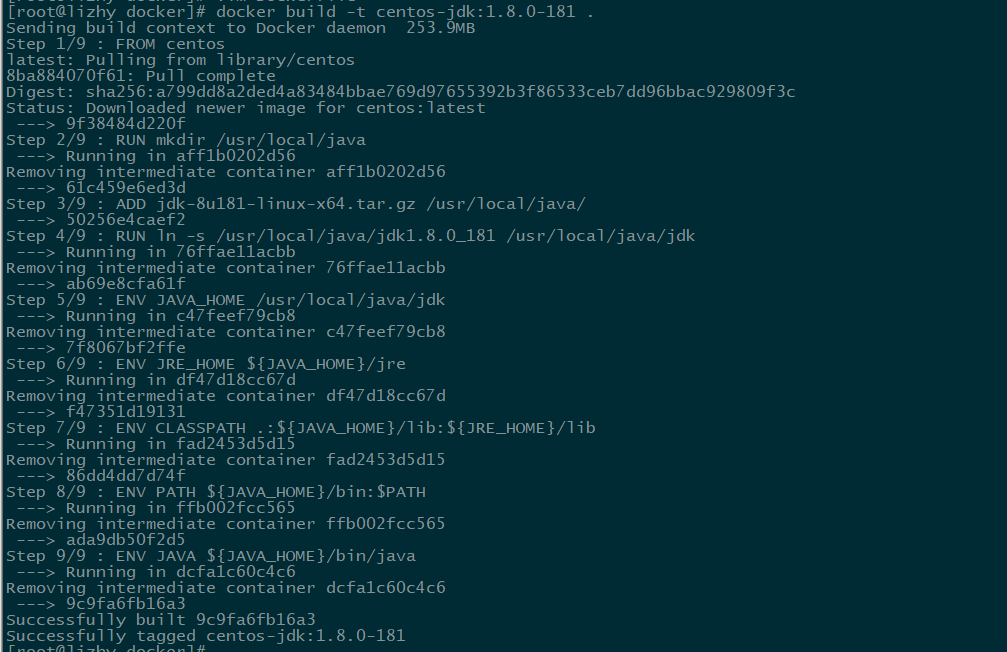
Use the command docker images to view the built images. Because we use centos, we build a CentOS image first, and then a jdk image.
Execute the command: docker run-it centos-jdk: 1.8.0-181/bin/bash, start a container, and enter the container to check whether the JDK has been installed successfully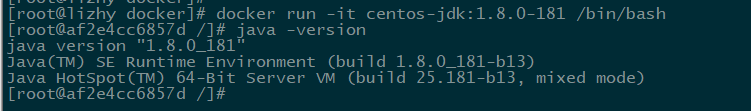
Execution command: The docker PS-A command looks at the list of all containers that have been started and started, and you can view the status through STATUS
docker rm container id----------------------------------- Delete container
docker stop container id--------------------------------- stop container
Doker RMI Mirror id - --------------------------------------------------- Delete Mirror
Install the application
FROM centos-jdk:1.8.0-181
ADD canal.deployer.tar.gz /data/application/canal-deploy
RUN \
chmod +x /data/application/canal-deploy/bin/*.sh
EXPOSE 11111 11112
When the container starts, it is mounted into a process, and if the process stops, the container stops. After the container is built, start it with the command docker run-itd canal: 1.1.3/bin/bash-c "/ data/application/canal-deploy/bin/startup.sh"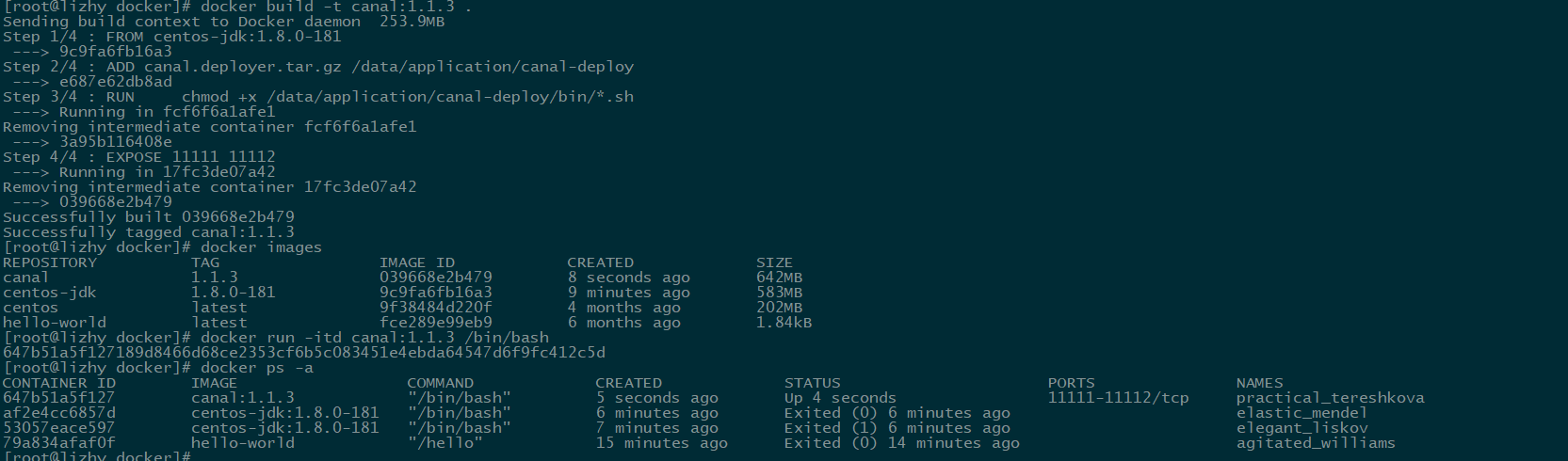
You need to specify the startup script by the - c parameter, and the container is attached to the script process. You can also specify the execution command by CMD or ENTRYPOINT in the Dockerfile.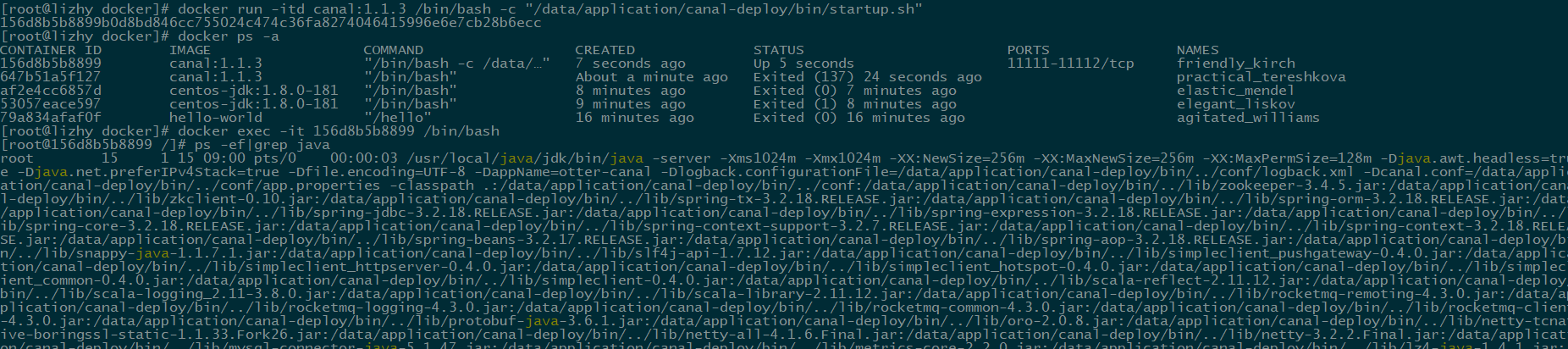
In the process of using the container, when the process hangs up, the container will be finished running. We need a daemon process. If the application process hangs down, it can be restarted and implemented with s6.
When building a Dockerfile, add the following commands, override the installation to the / usr directory, and add run and finish scripts to start and stop.
Note the directory structure: s6 listener directory: / data/application/service, run and finish script directory: / data/application/service/canal, can monitor the operation of multiple processes
ADD s6-overlay-amd64.tar.gz /usr/
RUN mkdir -p /data/application/service/canal
COPY run /data/application/service/canal
COPY finish /data/application/service/canal
RUN chmod +x /data/application/service/canal/run && \
chmod +x /data/application/service/canal/finish
ENTRYPOINT ["/usr/bin/s6-svscan", "/data/application/service"]
run script content is the execution of commands
#!/bin/bash sh /data/application/canal-deploy/bin/startup.sh