preface
Basic principles and common commands of docker
virtual machine
- Host OS and Guest OS
- Software such as VMWare operates the hardware directly or through the Host OS, as shown in the following figure
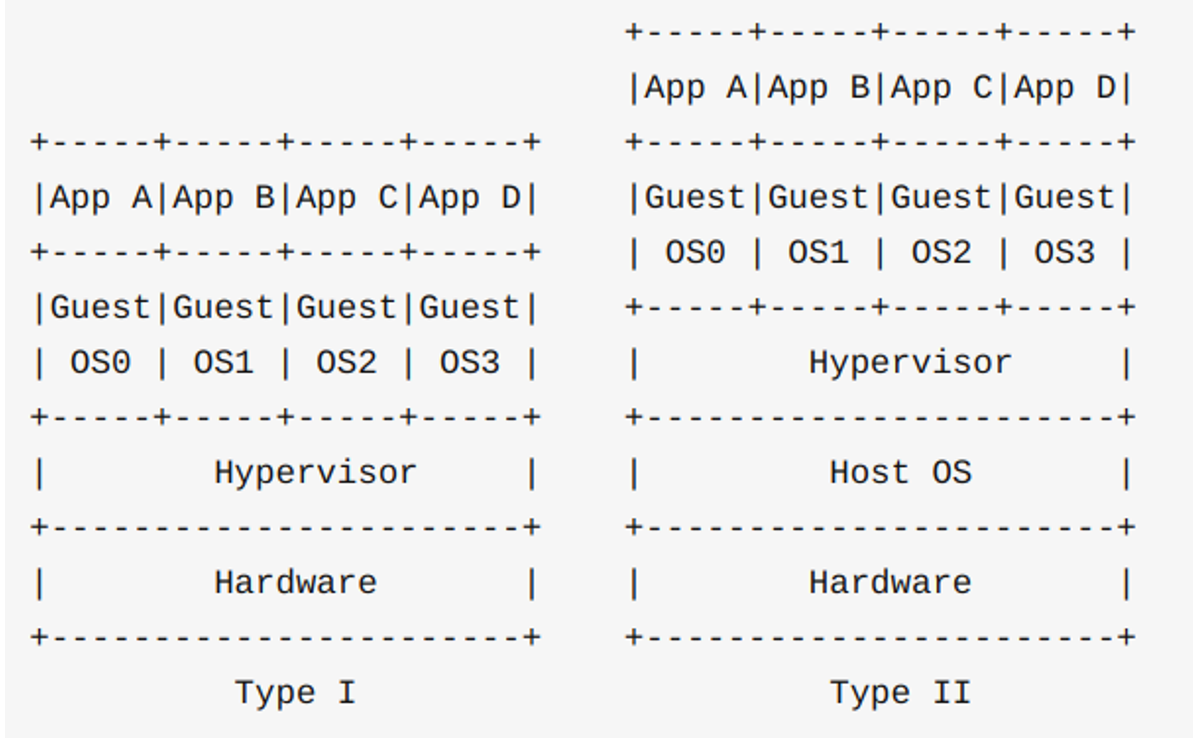
- Running multiple virtual machines will cause a lot of waste of hardware resources, and docker technology came into being
container
-
Difference between container and virtual machine
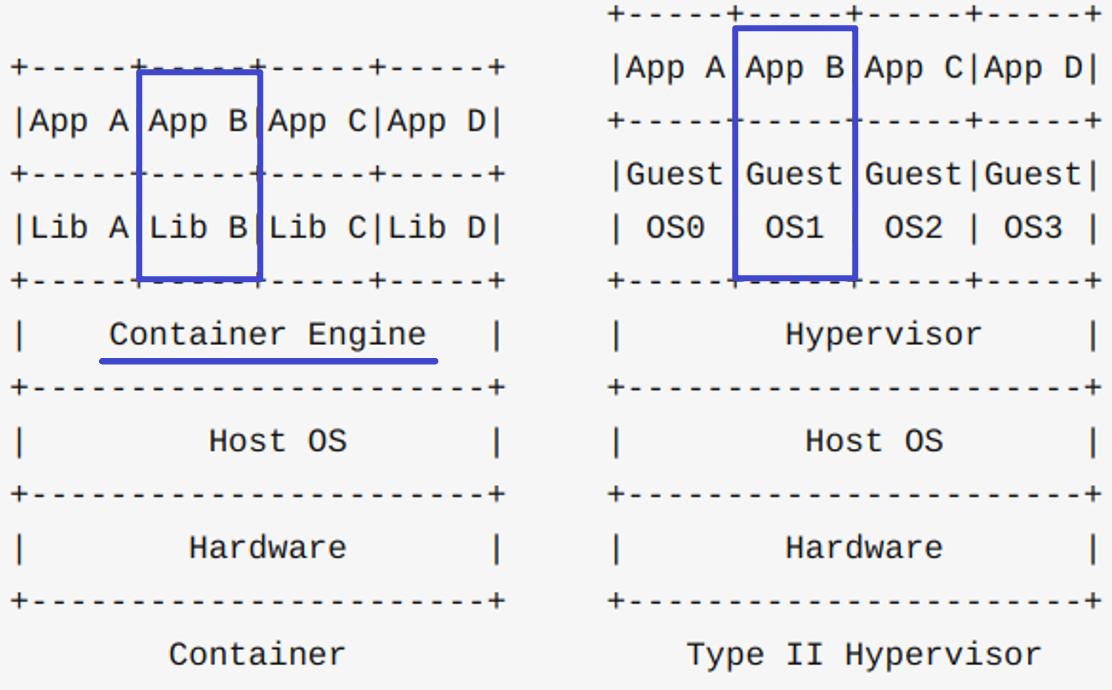
-
Operating system layer virtualization. The container packages the application and runtime
-
The combination of App + Lib is a container, that is, the container of docker
-
Compared with virtual machines, container features
@Start quickly. The container has no initialization of virtual machine hardware and no guest os startup process, saving startup time and "out of the box"
@Occupy less resources. There is no memory overhead required to run Guest OS, there is no need to reserve running memory for virtual machine, there is no need to install and run Runtime / operating system services that App does not need, and the memory and storage space are much smaller
@Kernel crash has a great impact. Containers share the kernel and are isolated through the control group cgroup, which is not as complete as the virtual machine. When the kernel crashes, all containers crash, and the impact between different virtual machines is not so great
docker
-
docker's two slogans
build, ship and run.
build once, run anywhere. -
And three concepts
Image: image, docker image
Container: container, docker container
Warehouse: repository, docker warehouse -
Other concepts of docker
docker registry: public warehouse. docker image management. There are many images
Image: a special file system that contains programs, libraries, resources, configurations, etc. required for runtime.
Container: refers to the image runtime, including file resources and system resources. File resources: expand image; System resources: become process and exist in the system
Docker Swarm: container scheduling platform launched by docker company
Kubernetes: k8s, a container scheduling platform dominated by Google
Container scheduling platform: a cluster composed of m master nodes and n worker nodes. Integrate host resources, complete the management of network, storage, CPU, memory and other resources, and run the container on different hosts
docker common commands
- Go to sudo to execute
sudo groupadd docker // Add docker task group sudo gpasswd -a $USER docker // Add the login user to the docker user group newgrp docker // Update user groups docker ps -a // Test whether the docker command works normally
- Version information
docker // View all docker commands docker version // View docker version docker info // View docker container information
- Mirror operation
docker images // View all downloaded images docker images -q // Display mirror id docker search ubuntu // Mirror search. Show all ubuntu images docker search mysql // Display all mysql images docker pull ubuntu // Download the ubuntu basic image locally docker pull redis // Download the latest image docker pull -a redis // Download all redis images in the warehouse docker pull image_Name // Select the desired mirror docker rmi redis // Single mirror deletion docker rmi -f redis // Force delete docker rmi -f redis tomcat // Delete multiple mirrors, separated by spaces Mirror build:
- Container view
docker ps -a // Check which docker containers are running + running history docker ps // View running containers docker ps -n 3 // Displays the 3 recently created containers
- Stopping and deleting containers
docker start containerId // Restart container docker stop containerId // Stop container docker kill containerId // Kill a running container docker rm containerId // Delete a stopped container docker rm -f containerId // Delete a running container, otherwise it will occupy memory -f docker rm -f $(docker ps -a -q) // Delete all containers
- Container creation and exit
docker exec -it containerId /bin/bash // Commonly used. Entering the container and exiting the container terminal will not cause the container to stop docker run -it ubuntu:18.04 /bin/bash // Start the container based on the 18.04 image docker run -it --name myubuntu /bin/bash // Specify container name docker create ubuntu:18.04 docker run -itd -p 6800:6800 image_name // Start container -i interactive operation -t terminal -d The container is started in the background, and the terminal is closed and still running -p Specify the port number /bin/bash After the image name is the command, indicating shell interactive exit // Close the container and exit
- Data copy and log
docker logs containerId // Display container log docker logs -f -t --tail=20 containerId // Track and display the latest 20 logs with time stamp docker cp containerId:file_path/file local_path // docker to host docker cp local_path containerId:file_path // host to docker // File and folder copies are cp, not home plus - r, which is different from scp
Reference article:
Popular explanation of docker principle
docker common commands (recommended)
docker usage
created by shuaixio, 2021.11.11