Webpack is a front-end resource modular management and packaging tool. The webpack.config configuration file contains entry files, exit files, loader loader and plugin plug-ins
Package directly through the webpack command on the console
The following configurations are performed in the webpack.config.js file
1. Import file
The entry point indicates which module the webpack should use as a starting point for building its internal dependency graph. After entering the entry point, webpack will find out which modules and libraries are directly and indirectly dependent on the entry point.
module.exports = {
//Entry file
entry: './src/js/index.js',
}Index.js here represents the entry file, which introduces JS, json, css and other objects required by the project. Through the index.js file, webpack will find the corresponding modules and libraries for easy packaging
2. Export documents
The output attribute tells webpack where to output the bundles it creates and how to name these files. The default value is. / dist
//Object deconstruction is used here to deconstruct resolve
const { resolve } = require('path');
module.exports = {
//Entry file
entry: './src/js/index.js',
// Export documents
output: {
// __ The internal parameter of dirname represents the absolute directory of the current webpackVue.config.js, dist, the newly created directory, and the export file
path: resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'index-dev.js'
},
}Here__ dirname is an internal parameter, which represents the absolute directory of the current webpackVue.config.js;
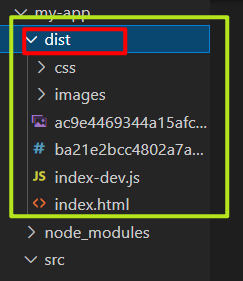
Dist newly created directories, export files, and all resource files after packaging are stored in dist
3. loader
1) css packaging - css loader, style loader
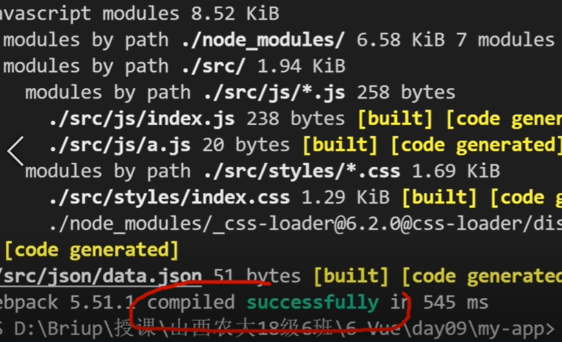
During the packaging process, css files will be stored in the js folder after successful packaging and mixed with js files, which is very inconvenient for management and maintenance
Package before adding loader: it will explode successfully, but the css style file and style exist in the js file
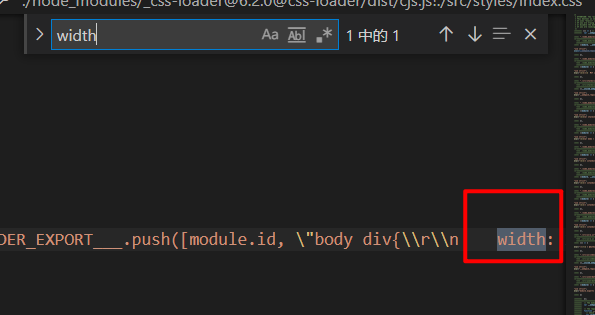
So you need something that recognizes css files
CSS loader: after parsing the CSS file, use import to load and return the CSS code
Style loader: adds the export of the module to the DOM as a style
Installation: cnpm I - D style loader CSS loader
Configure loader: configure in module
module.exports = {
//Entry file
entry: './src/js/index.js',
// Export documents
output: {
// __ The internal parameter of dirname represents the absolute directory of the current webpackVue.config.js, dist, the newly created directory, and the export file
path: resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'index-dev.js'
},
// Load loader
module: {
rules:[
{
// Using regular expressions to match css files
test: /\.css$/,
use: ['style-loader','css-loader']
},
]
}
}2) File loader - file loader
File loader: sends the file to the output folder and returns the (relative) URL. It can process the resources loaded in the css style and output the packaged css style to the specified css file
Installation: cnpm install -- save dev file loader Abbreviation = = > cnpm i -D file-loader
Configure loader:
module.exports = {
//Entry file
entry: './src/js/index.js',
// Export documents
output: {
// __ The internal parameter of dirname represents the absolute directory of the current webpackVue.config.js, dist, the newly created directory, and the export file
path: resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'index-dev.js'
},
// Load loader
module: {
rules:[
{
// Using regular expressions to match css files
test: /\.css$/,
// use: ['style-loader','css-loader']
use:[
{
loader:'file-loader',
options:{
outputPath: 'css'
}
}
]
},
{
test: /\.jpg|jpeg|png|gif$/,
// File loader handles the pictures introduced in css
use: [
{
loader:'file-loader',
options:{
// Set picture output file path
outputPath: 'images'
}
}
],
},
],
}
}3) Template loader - HTML loader
html loader: when exporting html as a string, you need to reference static resources. You can parse the static resources introduced in html
Installation: cnpm install -- save dev HTML loader Abbreviation = > cnpm I - D HTML loader
to configure:
// Load loader
module: {
rules:[
{
test: /\.html$/,
// html loader handles files imported from within html
use: ['html-loader'],
}
],
}4. Configure plugin
html webpack plugin will automatically generate an html file for the packaged file as the display page
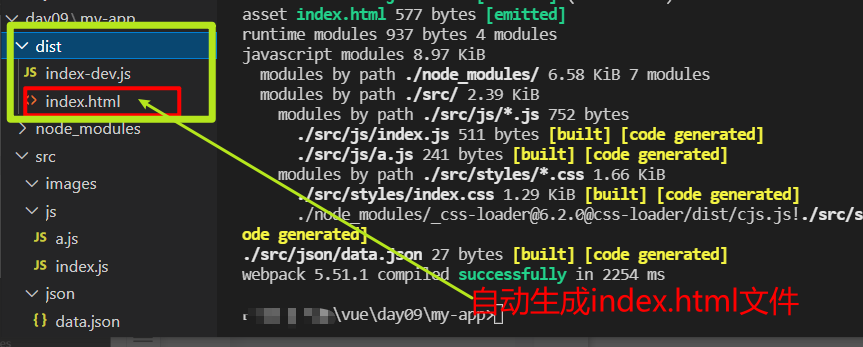
Installation: cnpm install -- D HTML webpack plugin
to configure:
// Introducing third-party plug-ins
let HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
// Configure plugin
plugins:[
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template:'./src/index.html',
})
],
}