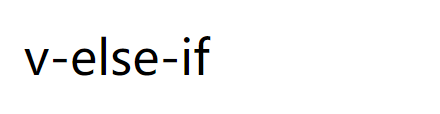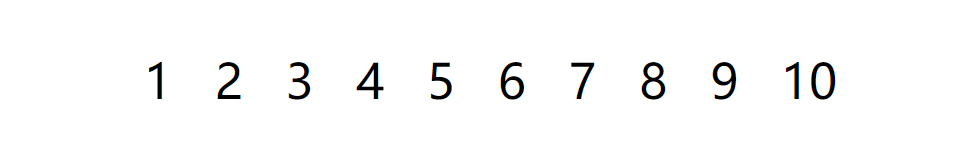| instructions | describe |
|---|
| {{}} | Interpolation expression |
| v-text | Update text content in element |
| v-html | Update innerHTML in element |
| v-if | Conditionally render elements based on the true and false values of the expression. |
| v-else-if | express v-if The else if block. Can be called chained. |
| v-else | by v-if perhaps v-else-if Add else block. |
| v-for | Render elements or template blocks multiple times based on source data. |
| v-on | Bind event listener. |
| v-bind | Dynamically bind one or more attribute s, or a component prop to an expression. |
| v-once | Render elements and components only once. |
1. Interpolation expression {}
- In the HTML page, we need to obtain the data in Vue. At this time, we can obtain it through interpolation expression.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>{{message}}</div>
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: "hello world"
};
}
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

2. v-text
- Update element textContent.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: "hello world"
};
},
template: `
<div v-text="message"></div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

3. v-html
- Update element innerHTML.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
html: "<i style='color:red;'>hello world</i>"
};
},
template: `
<div v-html="html"></div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

4. v-if
- Conditionally render elements based on the true and false values of the expression. On switching, the element and its data binding / component are destroyed and rebuilt.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
b1: true,
b2: false,
message1: "hello world true",
message2: "hello world false"
};
},
template: `
<div v-if="b1">{{message1}}</div>
<div v-if="b2">{{message2}}</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

5. v-else-if
- The previous sibling element must have v-if or v-else-if.
- express v-if The else if block. Can be called chained.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
b1: true,
b2: false,
};
},
template: `
<div v-if="b2">v-if</div>
<div v-else-if="b1">v-else-if</div>
<div v-else>v-else</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>
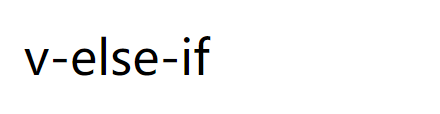
6. v-else
- The previous sibling element must have v-if or v-else-if.
- by v-if perhaps v-else-if Add else block.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
// b1: true,
b2: false,
// message1: "hello world true",
// message2: "hello world false"
};
},
template: `
<div v-if="b2">v-if</div>
<div v-else>v-else</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

7. v-for
7.1 use v-for Corresponding an array to a set of elements
- We can use v-for Instruction renders a list based on an array. v-for Instructions need to be used item in items Form, where items is the source data array, and item Is the alias of the array element being iterated.
- stay v-for Block, we can access the properties of all parent scopes. v-for It also supports an optional second parameter, the index of the current preceding item.
- v-for The default behavior of tries to modify elements in place instead of moving them. To force it to reorder elements, you need to use a special attribute key To provide a sort prompt:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="root">
</ul>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
// Use v-for to correspond an array to a set of elements
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
parentMessage: 'Parent',
items: [{ message: 'Hello' }, { message: 'world' }]
};
},
template: `
<li v-for="(item, index) in items" :key="index">
{{ parentMessage }}--{{ index }}--{{ item.message }}
</li>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

seven point two Array update detection
- one Change function using array push, pop, shift, unshift, splice, sort, reverse
vm.items.pop();
- two Direct replacement array
vm.items = [{message: "666666"}];
- three Directly update the contents of the array
vm.items[0] = {message: "111111"};
seven point three stay v-for Objects used in
- You can use it, too v-for To traverse the properties of an object.
- You can also provide the second parameter as the property name (that is, the key name).
- You can also use the third parameter as an index.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="root">
</ul>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
// Using objects in v-for
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
myObject: {
name: 'ZS',
age: 18,
sex: 'male'
}
};
},
template: `
<li v-for="(value, key, index) in myObject">
{{ index }}--{{ key }}--{{ value }}
</li>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

seven point four stay v-for Range of values used in
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="root">
</ul>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
// Range of values used in v-for
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<span v-for="item in 10" :key="item">
{{ item }}  
</span>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>
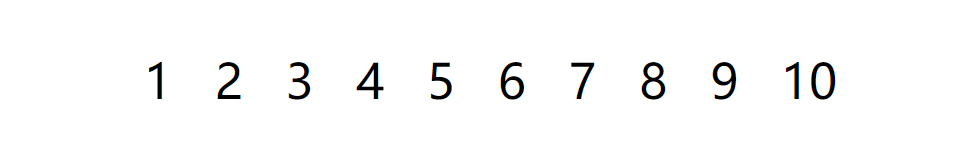
8. v-on
- Bind event listener. The event type is specified by the parameter. An expression can be the name of a method or an inline statement, or it can be omitted without modifiers.
- Using the. prevent modifier equals the call event.preventDefault().
- We can use v-on Directive (usually abbreviated as the @ symbol) to listen for DOM events and execute some JavaScript when the event is triggered. Usage is v-on:click="methodName" Or use shortcuts @ click="methodName"
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data(){
return {
message: 'hello'
};
},
methods: {
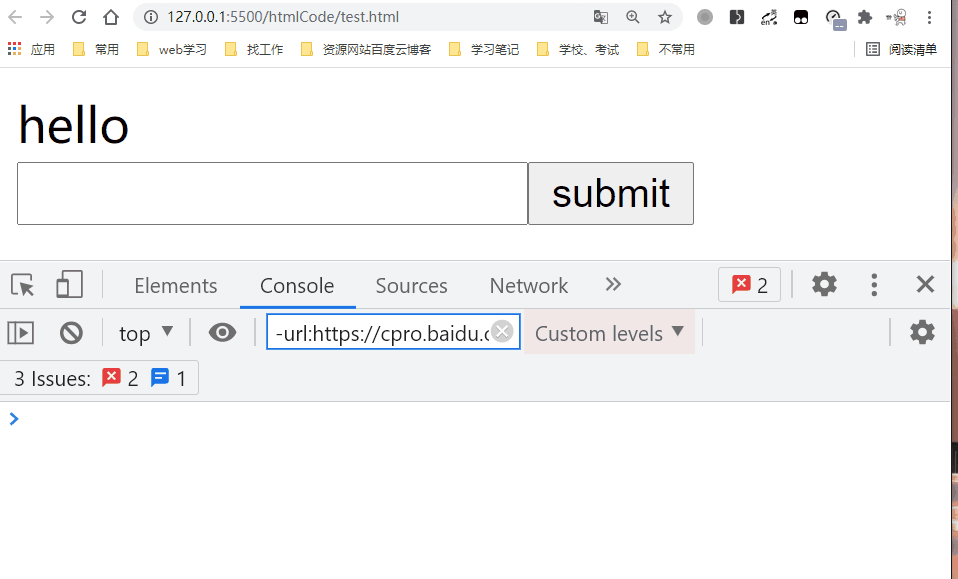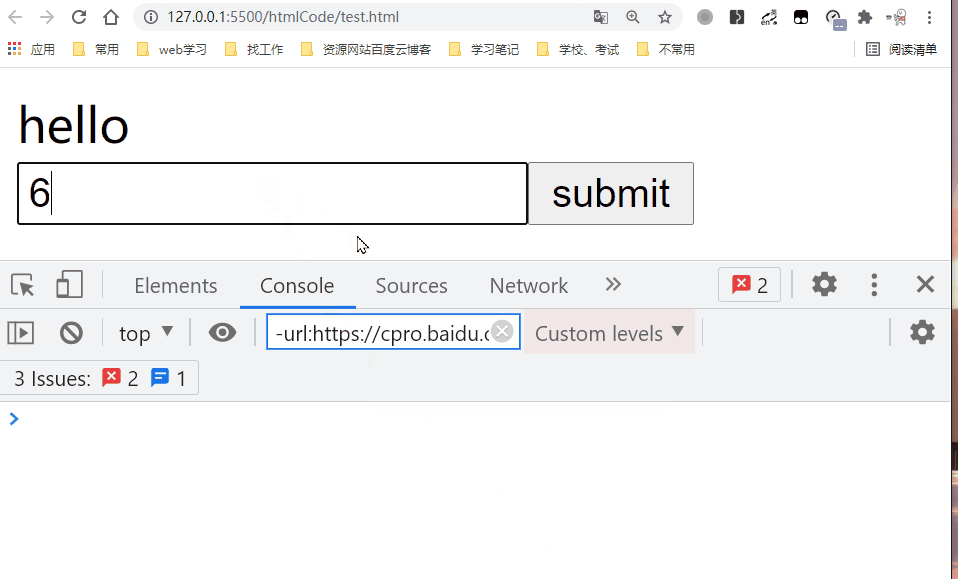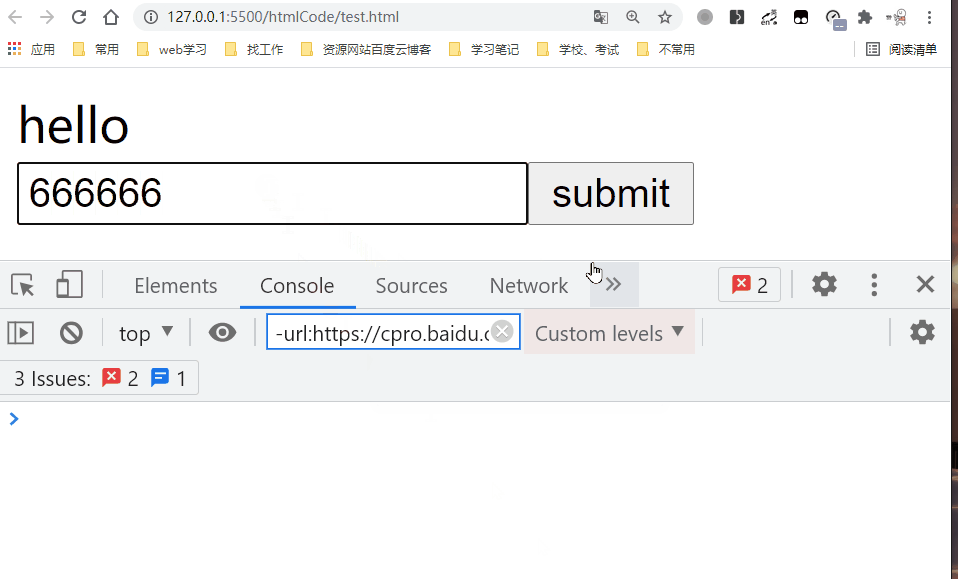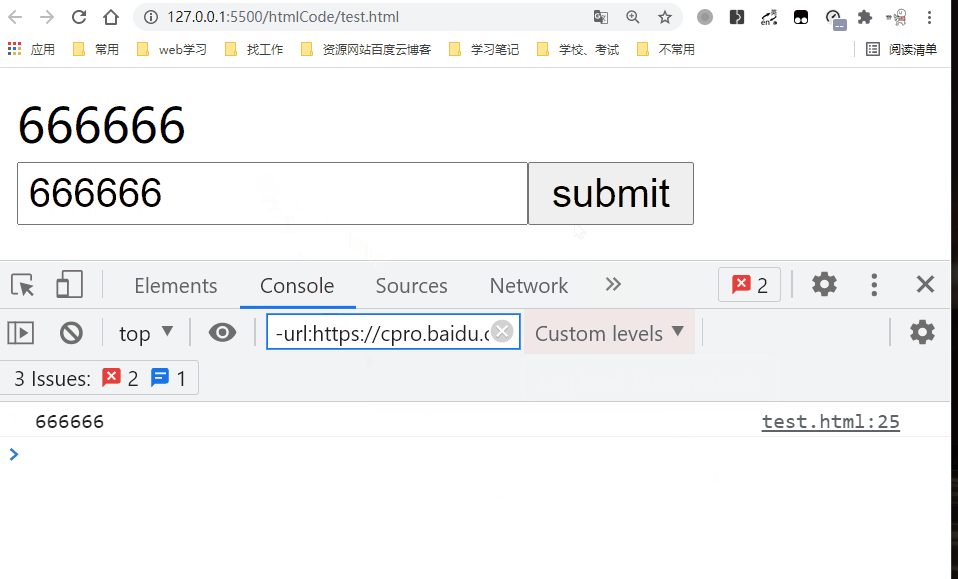
handleSubmit(){
const inputValue = document.getElementById('inputValue');
this.message = inputValue.value;
console.log(this.message);
}
},
template: `
<div>{{message}}</div>
<form action='https://www.baidu.com'>
<input type='text' id='inputValue'/>
<input type='submit' value='submit' v-on:click.prevent='handleSubmit'/>
</form>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>
9. v-bind
- Dynamically bind one or more attribute s, or a component prop to an expression.
- In binding class or style attribute, other types of values, such as arrays or objects, are supported.
9.1 String Syntax
- We can pass it on to : class (v-bind:class A string:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
<style>
.red {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
classString: 'red'
};
},
template: `
<div :class="classString">
Hello World
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

9.2 object syntax
- We can pass it on to : class (v-bind:class An object to dynamically switch classes:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
<style>
.red {
color: red;
}
.green {
color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
classObject: { red: false, green: true },
};
},
template: `
<div :class="classObject">
Hello World
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

9.3 array syntax
- We can pass an array to : class to apply a list of classes:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
<style>
.red {
color: red;
}
.green {
color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
classArray: ['red', 'green'],
};
},
template: `
<div :class="classArray">
Hello World
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

9.4 use on components
- When you use on a custom component with a single root element class attribute, these classes will be added to the element. Existing classes on this element will not be overwritten.
- If your component has multiple root elements, you need to define which parts will receive this class. have access to $ attrs Component properties do this.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
<style>
.red {
color: red;
}
.green {
color: green;
}
.italic {
font-style: italic;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
italic: 'italic',
classObject: { red: false, green: true },
};
},
template: `
<div>
<demo1 :class="classObject"
v-bind:italic='italic'></demo1>
<demo2 :class="classObject"
v-bind:italic='italic'></demo2>
</div>
`
});
app.component('demo1', {
props: ['italic'],
template: `
<div :class="$attrs.class">one</div>
<div :class="italic">two</div>
`
})
app.component('demo2', {
props: ['italic'],
template: `
<div :class="italic">three</div>
`
})
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>

10. v-once
- Render elements and components only once. For subsequent re rendering, the element / component and all its child nodes are treated as static content and skipped. This can be used to optimize update performance.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Common instructions</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: 1
};
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.message++;
}
},
template: `
<div v-once>{{message}}</div>
<div>{{message}}</div>
<button @click=handleClick>+1</button>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</body>
</html>