I. preparation
Advantages of Docker to build environment:
Simple operation, rapid construction and environmental isolation
Common Docker operation commands and parameters:
docker search # Find image from Docker Hub docker images # View local mirror list docker pull # Pull or update the specified image from the image warehouse docker run # Create a new container and run a command docker rm # Delete a container docker rmi # Delete a mirror docker inspect # Get metadata of container / image docker ps # View the started containers and add the parameter - a to view all containers docker build # Using Dockerfile to create images //Common Dockerfile instructions: FROM # The format is FROM image or FROM image:tag, and the first instruction in the Dockerfile must be a FROM instruction. When multiple images are created in the same Dockerfile, multiple FROM instructions can be used. RUN # The format is RUN command or run ["execute", "Param1", "param2"...], the former runs the command in the shell terminal, / bin/sh -c command, for example, / bin/sh -c "echo hello"; the latter uses exec to execute, and specifies that other running terminals use RUN["/bin/bash","-c","echo hello"] CMD # Specifies the command to execute when the container starts MAINTAINER # Designated maintainer information ENV # Used to specify environment variables, which can be used by RUN instructions later EXPOSE # Exposed port for container external links
II. Start to build
Order: MySQL > phpfpm > nginx
Make sure to build phpfpm first, and then build docker ﹣ nginx
- Set up docker? MySQL
First, use docker search mysql to list the mysql images existing in the warehouse
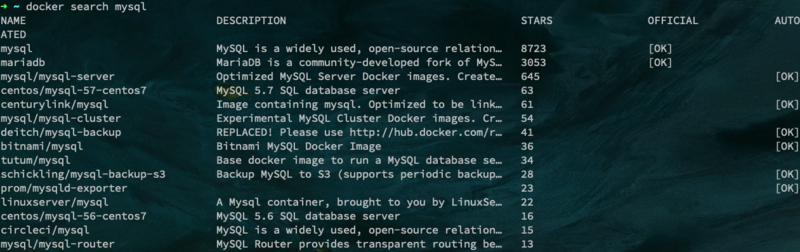
Use the docker pull command to download the images with the most STARTS locally (the download time is a little long...)
docker pull mysql
After downloading, use docker images to check whether the image has been downloaded to the local
docker images
You can see the following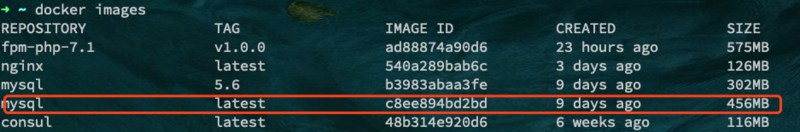
Use the docker run command to start a docker? MySQL container
docker run -di --name mydockermysql -p 3308:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 mysql
docker run command to start the container -i. interactive operation -d ා Daemons --Name specifies the container name as mydockermysql -p? Map the 3306 port of the container to the 3308 port of the host -e ා specify the environment variable, which can be used in the container to set the root password The last mysql is to specify to use a certain image
Use the docker ps command to see if the container has started
If you can see the mysql you just built, it means that the container was created successfully. If you can't see it, you can use the docker log mydockermysql command to check the errors, modify the command, and then restart it. However, you need to delete the container first, and the command is docker rm mydockermysql.

Try to use navicat tool to link database and find failed. Check it.
Enter mysql container
docker exec -it mydockermysql /bin/bash
mysql start
mysql -uroot -p123456
View mysql version
status
Authorize remote links
GRANT ALL ON *.* TO`'root'@'%'`;
Refresh authority
flush privileges;
Change encryption rules
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password' PASSWORD EXPIRE NEVER;
Change root password
ALTER USER 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '123456';
Refresh authority
flush privileges;
At this point, use Navicat to find that you can connect to mydocker mysql.
In the container, exit mysql first
Then exit the container
At this time, the construction of docker ﹣ mysql container is over. mysql version is 8.0. If you need to build version 5.x, you only need to use docker pull mysql:5.x, and use the image to start the container. In the container, you only need to authorize remote connection, and do not need to modify the encryption rules.
- Build docker phpfpm
Building docker phpfpm is a little tedious, because php has different versions, different extensions and dependencies, so you can use dockerfile to build docker phpfpm, and flexibly configure the required extensions.
Create a new Dockerfile file with the following contents
FROM php:7.1-fpm MAINTAINER your name # Define extension version number #redis extension ENV PHPREDIS_VERSION 4.0.0 #swoole extension ENV SWOOLE_VERSION 4.0.3 # Setup time RUN /bin/cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime \ && echo 'Asia/Shanghai' > /etc/timezone # Some extensions that are neither in the PHP source package nor in the PECL extension warehouse are no longer available. Use apt to install the extensions directly. RUN apt-get update \ && apt-get install -y \ curl \ wget \ git \ zip \ libz-dev \ libssl-dev \ libnghttp2-dev \ libpcre3-dev \ libmemcached-dev \ zlib1g-dev \ libfreetype6-dev \ libjpeg62-turbo-dev \ libmcrypt-dev \ libpng-dev \ && apt-get clean \ && apt-get autoremove # Install Composer RUN curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | php \ && mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composer \ && composer self-update --clean-backups # PHP source file directory comes with extension docker PHP ext install # Mysqli extension RUN docker-php-ext-install mysqli # PDO extension RUN docker-php-ext-install pdo_mysql # Bcmath RUN docker-php-ext-install bcmath # gd extension RUN docker-php-ext-install -j$(nproc) iconv mcrypt RUN docker-php-ext-configure gd --with-freetype-dir=/usr/include/ --with-jpeg-dir=/usr/include/ RUN docker-php-ext-install -j$(nproc) gd # Some extensions are not included in the PHP source file, but exist in the extension library warehouse of PHP. Use pecl install to install the extension, and then use the docker PHP ext enable command to enable the extension. RUN wget http://pecl.php.net/get/redis-${PHPREDIS_VERSION}.tgz -O /tmp/redis.tgz \ && pecl install /tmp/redis.tgz \ && rm -rf /tmp/redis.tgz \ && docker-php-ext-enable redis # msgpack extension download pecl local installation open extension (delay queue usage reduces source data space) RUN wget http://pecl.php.net/get/msgpack-${MSGPACK_VERSION}.tgz -O /tmp/msgpack.tgz \ && pecl install /tmp/msgpack.tgz \ && rm -rf /tmp/msgpack.tgz \ && docker-php-ext-enable msgpack # Hiredis depends on installation RUN wget https://github.com/redis/hiredis/archive/v${HIREDIS_VERSION}.tar.gz -O /tmp/hiredis.tar.gz \ && mkdir -p /tmp/hiredis \ && tar -xf /tmp/hiredis.tar.gz -C /tmp/hiredis --strip-components=1 \ && rm /tmp/hiredis.tar.gz \ && ( \ cd /tmp/hiredis \ && make -j$(nproc) \ && make install \ && ldconfig \ ) \ && rm -r /tmp/hiredis # Swoole extension installation open extension RUN wget https://github.com/swoole/swoole-src/archive/v${SWOOLE_VERSION}.tar.gz -O /tmp/swoole.tar.gz \ && mkdir -p /tmp/swoole \ && tar -xf /tmp/swoole.tar.gz -C /tmp/swoole --strip-components=1 \ && rm /tmp/swoole.tar.gz \ && ( \ cd /tmp/swoole \ && phpize \ && ./configure --enable-async-redis --enable-mysqlnd --enable-openssl --enable-http2 \ && make -j$(nproc) \ && make install \ ) \ && rm -r /tmp/swoole \ && docker-php-ext-enable swoole
After the Dockerfile file is created, execute the following command in the directory where the file is located to build an image
sudo docker build -t fpm-php-7.1:v1.0.0 .
Note: the last. Of the command represents the current directory
Use docker images to check whether the image is created successfully
Start a docker? Phpfpm container with the docker run command
docker run --name docker_phpfpm71 \ --restart=always \ -p 9000:9000 \ -v ~/Sites:/data/home \ -v ~/Sites/docker_phpfpm71/logs:/data/logs \ --privileged \ -d fpm-php-7.1:v1.0.0
-v ##Mount the directory in the container to the local directory --privileged ##Make the root in the container have the real root permission, otherwise the root in the container is only a common external user permission. --restart ##Set the container restart policy. When the container exits, whether the Docker daemons restart the container that just exited.
Use the docker ps command to see if the container is running
docker ps
Docker phpfpm succeeded
- Build docker
When you start docker? Nginx, you need to use the -- link parameter to associate the nginx container with the phpfpm container you just started, and you need to do some directory mounting operations.
First, create several directories locally to store nginx configuration
mkdir -p ~/Sites/docker_nginx/{conf,conf.d,html,logs}
Create nginx.conf file in ~ / sites / docker \ nginx / conf /. The content is as follows
user nginx; worker_processes auto; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; pid /run/nginx.pid; include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; keepalive_timeout 65; types_hash_max_size 2048; include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; server { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server; server_name localhost; root /usr/share/nginx/html; # Load configuration files for the default server block. include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; error_page 404 /404.html; location = /40x.html{ } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html{ } location ~ ^/assets/.*\.php$ { deny all; } location ~ \.php$ { include fastcgi_params; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_pass docker_phpfpm71:9000; #fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.sock; try_files $uri =404; } location ~* /\. { deny all; } } }
Start a nginx container with the docker run command
docker run --name docker_nginx -d -p 80:80 -v ~/Sites/docker_nginx/conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf -v ~/Sites/docker_nginx/logs:/var/log/nginx -v ~/Sites:/usr/share/nginx/html -v ~/Sites/docker_nginx/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d --link docker_phpfpm71:phpfpm --volumes-from docker_phpfpm71 nginx
--link ##Link two containers so that the source container (the linked container) and the receiving container (the actively unlinked container) can communicate with each other, and the receiving container can obtain some data of the source container, such as the environment variables of the source container --volumes-from ##Authorize one container to access the Volume of another container
Use the docker ps command to see if the container starts
Visit localhost in browser