Nginx is a lightweight web server, reverse proxy server. Compared with Apache and lighttpd, it has the advantages of less memory and higher stability. Its most common use is to provide reverse proxy services.
1. Installation package compilation and installation 2.yum source installation 3. Use docker to install
You need to confirm whether port 80 is open. If it's alicloud, you need to set port group open on the console
#Make sure the firewall is open to port 80 if not firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp #Reload firewall-cmd --reload #view list firewall-cmd --list-all
1. Installation package compilation and installation (relatively troublesome)
Installing the PCRCT Library
#Make sure that the operating system is equipped with a GCC compiler collection, a powerful compiler. The compiled languages include: C, C + +, Objective-C, Fortran, Java, etc. Autoconf and Automake tools must also be installed. They are used to automatically create functional makefiles. Currently, most software packages use this tool to generate makefiles, and Nginx is no exception. Under CentOS system, use yum command to install GCC compiler and related tools. #If not installed using yum yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ autoconf automake #Installing the PCRE Library #Download cd /usr/local/tools/ngnix in the directory of ngnix wget http://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-1.0.1j.tar.gz #decompression tar -zxvf openssl-1.0.1j.tar.gz #Enter and initialize the source code installation (the source code installation generally consists of three steps: configure, make, and make install) cd openssl-1.0.1j ./config make && make install
Install nginx
#Check to see if it is installed which nginx #Entry directory cd /usr/local/tools/ngnix #Download and unzip nginx 1.8 wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz tar -zxvf nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz #Enter directory compilation and installation cd nginx-1.8.0 ./configure make && make install
After downloading, the installation package can be deleted and nginx can be started
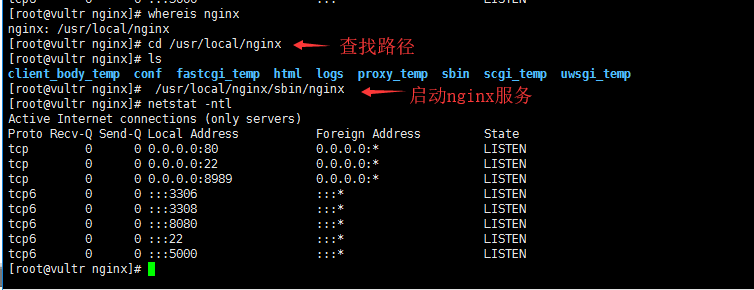
#Find nginx path whereis nginx #After starting nginx (just. / configure will prompt for the start path), you can only enter ip to test the default port 80 of nginx in the browser /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #Reload nginx here. If it is in stop state, an error will be reported /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload #Stop it /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop #Compulsory stop pkill nginx #Test whether the configuration file is normal /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t #View the default configuration file (according to where is nginx. CONF) cat nginx.conf
2. Install nginx (fast) from yum
#yum install nginx sudo yum install -y nginx #start nginx sudo systemctl start nginx.service #Set power on self start sudo systemctl enable nginx.service #The nginx configuration files installed from yum are stored in / etc/nginx/nginx.conf by default vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf #uninstall yum remove nginx
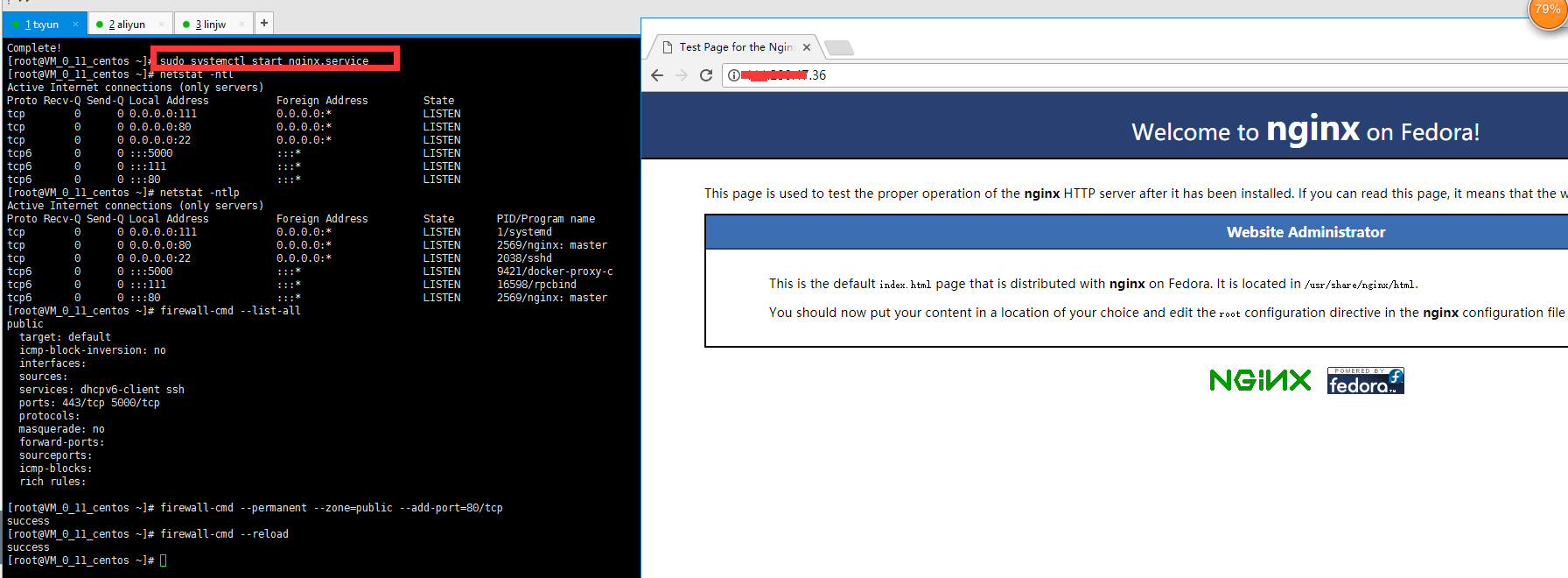
This is not the official default interface, maybe because
When you have an epel source and use yum install nginx to install it, you will see Welcome to nginx on Fedora! Because the epel source is maintained by fedora
3. Use Docker to install nginx
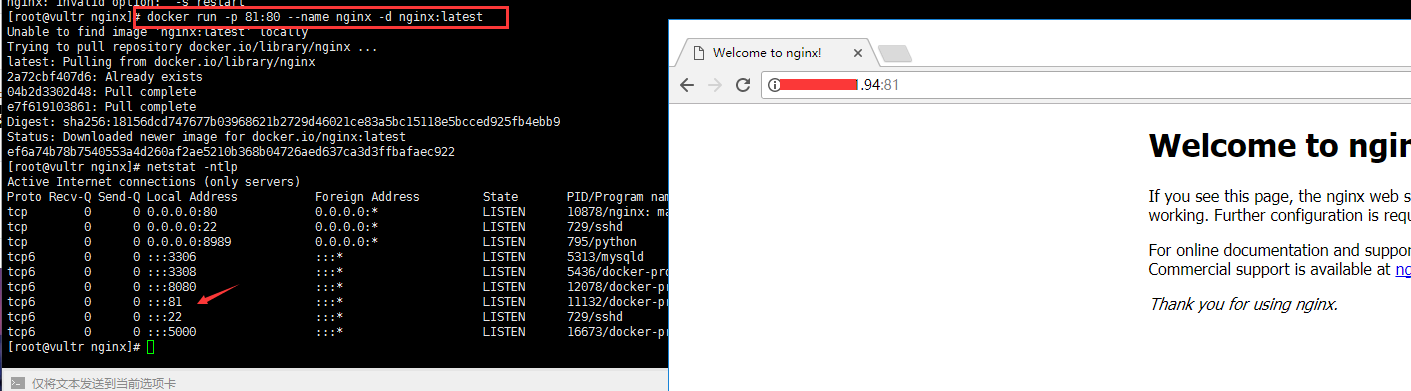
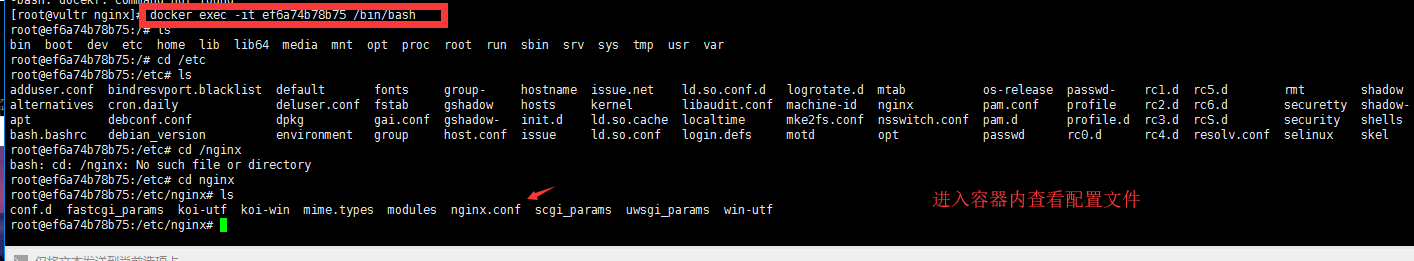
#If the server is equipped with docker service, port 80 is already occupied and port 81 is used docker run -p 81:80 --name nginx -d nginx:latest #Enter the container to start nginx image docker exec -it ef6a74b78b75 /bin/bash #Note whether port 81 is enabled in the test. If it is alicloud, Tencent cloud, etc., pay attention to the security group settings. To ensure the persistence of the configuration file (not disappear due to the restart of the container), you can mount the configuration file or log file in the container on the host computer according to your needs