Development Tools: IEDA, JDK1.8, WinHex
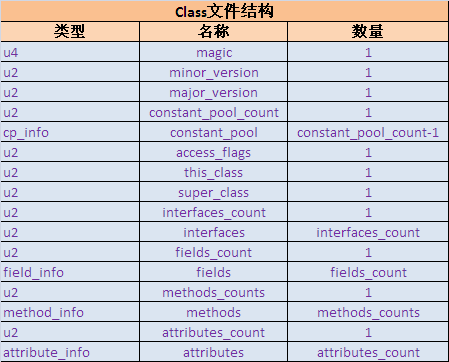
1. Byte code file structure
source code
package com.jalja.java.bytecode; /** * @Auther: XL * @Date: 2020/1/4 12:58 * @Description: */ public class BytecodeTest { private int num=1; public int getNum() { return num; } public void setNum(int num) { this.num = num; } }
Javap-verbose parses a byte code file and outputs the magic number, version number, constant pool, class information, class construction method, method information in class, class variables and member variables of the byte code file
F:\workspace\IDEA\study\jalja-base-utils\target\test-classes>javap -verbose com.jalja.java.bytecode.BytecodeTest Classfile /F:/workspace/IDEA/study/jalja-base-utils/target/test-classes/com/jalja/java/bytecode/BytecodeTest.class Last modified 2020-1-4; size 514 bytes MD5 checksum b661c2792027e7c9169a0266523412c1 Compiled from "BytecodeTest.java" public class com.jalja.java.bytecode.BytecodeTest minor version: 0 major version: 52 flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER Constant pool: #1 = Methodref #4.#20 // java/lang/Object."<init>":()V #2 = Fieldref #3.#21 // com/jalja/java/bytecode/BytecodeTest.num:I #3 = Class #22 // com/jalja/java/bytecode/BytecodeTest #4 = Class #23 // java/lang/Object #5 = Utf8 num #6 = Utf8 I #7 = Utf8 <init> #8 = Utf8 ()V #9 = Utf8 Code #10 = Utf8 LineNumberTable #11 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable #12 = Utf8 this #13 = Utf8 Lcom/jalja/java/bytecode/BytecodeTest; #14 = Utf8 getNum #15 = Utf8 ()I #16 = Utf8 setNum #17 = Utf8 (I)V #18 = Utf8 SourceFile #19 = Utf8 BytecodeTest.java #20 = NameAndType #7:#8 // "<init>":()V #21 = NameAndType #5:#6 // num:I #22 = Utf8 com/jalja/java/bytecode/BytecodeTest #23 = Utf8 java/lang/Object { public com.jalja.java.bytecode.BytecodeTest(); descriptor: ()V flags: ACC_PUBLIC Code: stack=2, locals=1, args_size=1 0: aload_0 1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V 4: aload_0 5: iconst_1 6: putfield #2 // Field num:I 9: return LineNumberTable: line 8: 0 line 9: 4 LocalVariableTable: Start Length Slot Name Signature 0 10 0 this Lcom/jalja/java/bytecode/BytecodeTest; public int getNum(); descriptor: ()I flags: ACC_PUBLIC Code: stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1 0: aload_0 1: getfield #2 // Field num:I 4: ireturn LineNumberTable: line 12: 0 LocalVariableTable: Start Length Slot Name Signature 0 5 0 this Lcom/jalja/java/bytecode/BytecodeTest; public void setNum(int); descriptor: (I)V flags: ACC_PUBLIC Code: stack=2, locals=2, args_size=2 0: aload_0 1: iload_1 2: putfield #2 // Field num:I 5: return LineNumberTable: line 16: 0 line 17: 5 LocalVariableTable: Start Length Slot Name Signature 0 6 0 this Lcom/jalja/java/bytecode/BytecodeTest; 0 6 1 num I } SourceFile: "BytecodeTest.java"
WinHex: Open the class file
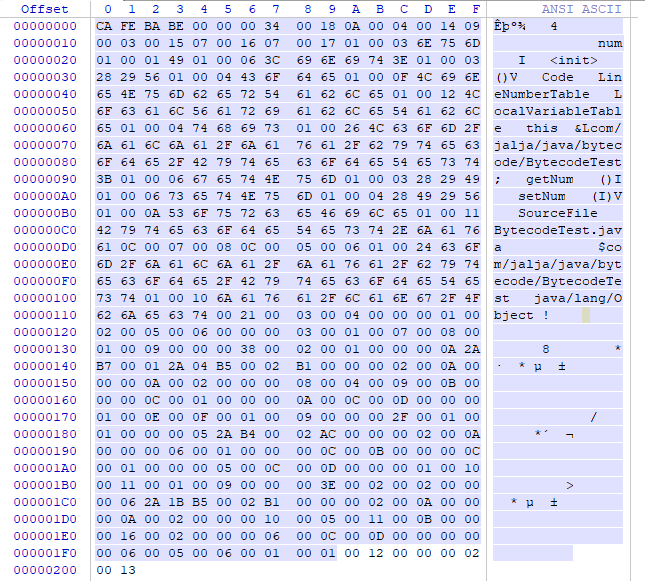
2. Magic Number
1. Magic number: The first four bytes of all class byte code files are magic numbers. Magic number is a fixed value of 0XCAFEBABE. When JVM loads classes, it verifies that the data conforms to the specifications.
2. Version number
2. Version number:
The four bytes after magic number are version information, the first two bytes (00 00 00) are minor version: 0, the last two bytes (00 34) are major version: 52, the last two bytes are hexadecimal conversion 52, and the corresponding JDK1.8; so the class file version number = 1.8.0; can be verified with java-version.Since JVM is downward compatible, how your byte code file version number is less than or equal to the current version of JVM can run in the current JVM.
Next section: Constant Pool for JAVA Byte Code Files