Learning objectives
Grammatical format Define a variable in the interpreter val and var variables Use type inference to define variables Lazy assignment
Grammatical format
Java variable definition
int a = 0;
In scala, you can use val or var to define variables. The syntax format is as follows:
val/var variable ID: variable type = initial value
among
val defines variables that cannot be reassigned var defines a variable that can be reassigned
Note:
The variable type defined in scala is written after the variable name scala statements don't need semicolons at the end
Define a variable in the interpreter
Example: define a variable to hold a person's name "tom"
Steps:
1. Open the scala interpreter 2. Define a variable of string type to save the name
Reference code
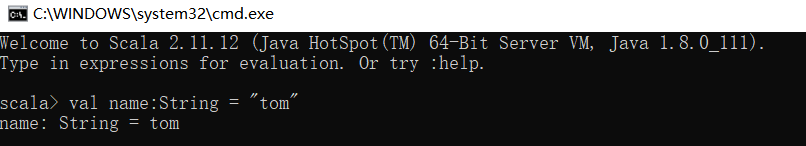
scala> val name:String = "tom" name: String = tom
val and var variables
Example
Reassign the name variable to Jim and observe its operation results
Reference code
scala> name = "Jim"
<console>:12: error: reassignment to val
name = "Jim"
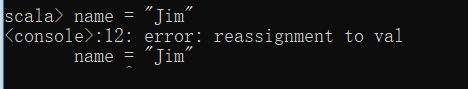
It can be seen from the result that name cannot be reassigned to "Jim" because val variable cannot be reassigned
Example
Use var to redefine the variable to save the name "tom", and try to reassign it to Jim, and observe the results
Reference code
scala> var name:String = "tom" name: String = tom scala> name = "Jim" name: String = Jim

Note:
Use 'val' first to define variables. If the variables need to be reassigned, use 'var`
Use type inference to define variables
scala's syntax is simpler than Java's. We can define variables in a more concise way
Example
Define a variable in a more concise way to save a person's name "tom"
Reference code
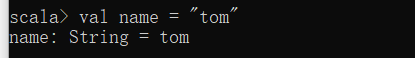
scala> val name = "tom" name: String = tom
Note:
scala can automatically infer the type of variable according to the value of variable, which makes the code more concise
Lazy assignment
In big data development of enterprises, sometimes very complex SQL statements are written, These SQL statements can be hundreds or even thousands of lines. If these SQL statements are directly loaded into the JVM, there will be a lot of memory overhead. How to solve this problem?
When some variables hold large data, but do not need to be loaded into the JVM memory immediately, lazy assignment can be used to improve efficiency
Grammatical format
lazy val/var variable name = expression
Example
We need to execute the following complex SQL statement in the program. We hope to load it only when we use this SQL statement.
"""insert overwrite table adm.itcast_adm_personas
select
a.user_id,
a.user_name,
a.user_sex,
a.user_birthday,
a.user_age,
a.constellation,
a.province,
a.city,
a.city_level,
a.hex_mail,
a.op_mail,
a.hex_phone,
a.fore_phone,
a.figure_model,
a.stature_model,
b.first_order_time,
b.last_order_time,
...
d.month1_hour025_cnt,
d.month1_hour627_cnt,
d.month1_hour829_cnt,
d.month1_hour10212_cnt,
d.month1_hour13214_cnt,
d.month1_hour15217_cnt,
d.month1_hour18219_cnt,
d.month1_hour20221_cnt,
d.month1_hour22223_cnt
from gdm.itcast_gdm_user_basic a
left join gdm.itcast_gdm_user_consume_order b on a.user_id=b.user_id
left join gdm.itcast_gdm_user_buy_category c on a.user_id=c.user_id
left join gdm.itcast_gdm_user_visit d on a.user_id=d.user_id;"""
Reference code
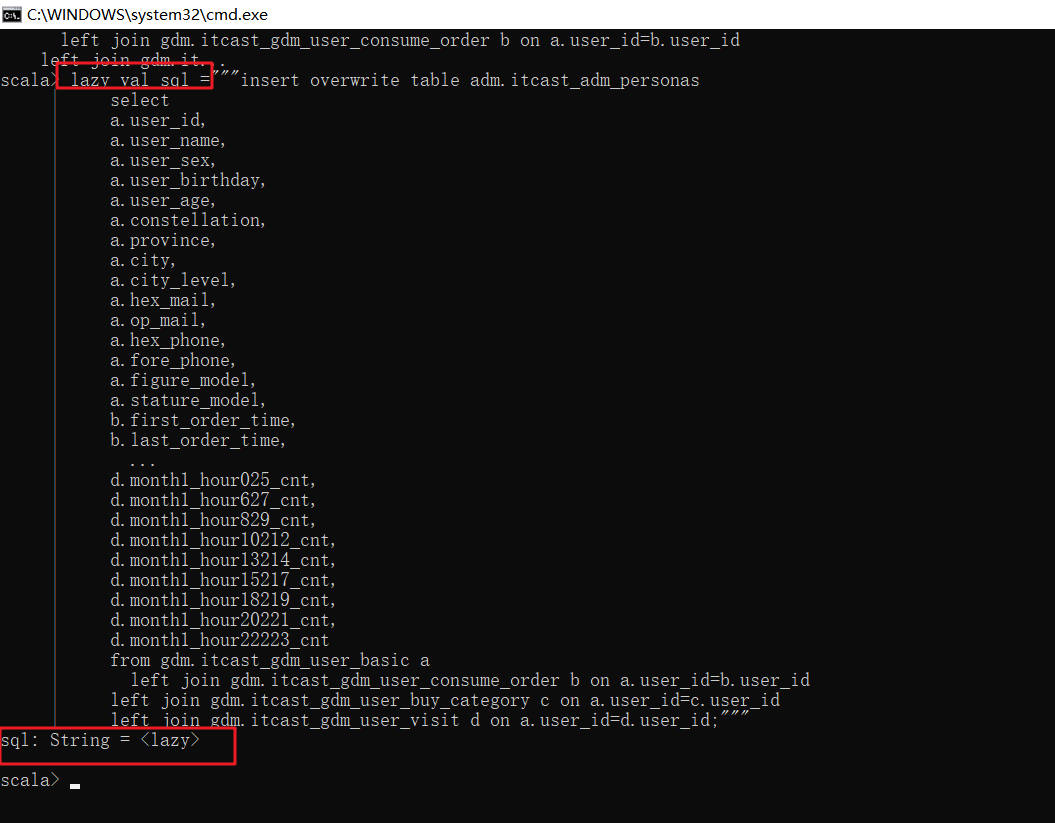
scala> lazy val sql = """insert overwrite table adm.itcast_adm_personas
| select
| a.user_id,
....
| left join gdm.itcast_gdm_user_buy_category c on a.user_id=c.user_id
| left join gdm.itcast_gdm_user_visit d on a.user_id=d.user_id;"""
sql: String = <lazy>