I. reflection
Reflection mechanism is the most commonly used in java development. For example, reflection mechanism is used in all three frameworks. JAVA reflection mechanism is in the running state. For any class, you can know all the properties and methods of this class. For any object, you can call any of its methods and properties.
The reflection mechanism seems to split a statement commonly used in java into many statements, but it greatly improves its flexibility. See the following code for specific examples:
First, define a javaBean to encapsulate the data: rewrite the toString method to output the class later.
public class Bean implements Serializable{
private String id;
private String className;
public String description;
public Bean(String id) {
super();
this.id = id;
System.out.println("A parameter construction");
}
private Bean(String id, String className) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.className = className;
System.out.println("Two parameter construction");
}
private int show(int age){
return age;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(args));
}
public Bean() {
System.out.println("Non parametric structure");
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Bean [id=" + id + ", className=" + className + ",des=" + description + "]";
}
}
Here are three ways to get the class object of this javaBean:
public class ClassDemo {
@Test
public void Demo1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1. It is convenient to obtain the fully qualified class name from the configuration file in development
Class clazz = Class.forName("cn.ahut.gbl.Bean");
System.out.println(clazz);
}
@Test
public void Demo2() throws ClassNotFoundException {
//2. Determine the construction method. When different method parameter lists are available, you need to obtain them by type
Class clazz = Bean.class;
System.out.println(clazz);
}
@Test
public void Demo3() throws ClassNotFoundException {
//3. Method internal use acquisition
Bean bean = new Bean();
Class clazz = bean.getClass();
System.out.println(clazz);
}
}2, Obtain the public and private construction methods in JavaBeans through the reflection mechanism. The specific code is as follows:
public class ClassDemo2 {
@Test
public void Demo1() throws Exception {
//Get nonparametric construction method
Class clazz = Class.forName("cn.ahut.gbl.Bean");
Constructor con = clazz.getConstructor();
Object object = con.newInstance(); //Object to instantiate
}
@Test
public void Demo2() throws Exception {
//Get the construction method with parameters
//Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("cn.ahut.gbl.Bean");
//Construction with one parameter
Constructor con = clazz.getConstructor(String.class);
Object object = con.newInstance("abc123");
System.out.println(object);
}
@Test
//Shorthand for nonparametric construction
public void Demo3() throws Exception {
Class clazz = Class.forName("cn.ahut.gbl.Bean");
//Created directly through clazz
Object object = clazz.newInstance();
}
@Test
public void Demo4() throws Exception {
//Gets the private constructor in the specified class
//Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("cn.ahut.gbl.Bean");
//Acquisition structure
/*clazz.getConstructor(....);Specifies the common constructor in a class
* clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(....);Specify any construction method in the class
*/
Constructor cons = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,String.class);
//Notify JVM to run private construct parameters (not allowed by default)
cons.setAccessible(true);
Object object = cons.newInstance("adf123","Full name");
System.out.println(object);
}
}3, Obtain public, private, and static methods, as well as public and private fields in the specified class through reflection. The specific code is as follows:
public class ClassDemo3 {
@Test
//Get common and common methods through reflection
public void Demo1() throws Exception {
//Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("cn.ahut.gbl.Bean");
//instantiation
Object object = clazz.newInstance();
//Get data through setId
Method method = clazz.getMethod("setId", String.class);
//Set data and execute method
method.invoke(object, "ab001");
//print data
Method method1 = clazz.getMethod("getId");
String string = (String) method1.invoke(object);
System.out.println(string);
}
@Test
//Get private common methods through reflection
public void Demo2() throws Exception {
//Get class object
Class clazz = Class.forName("cn.ahut.gbl.Bean");
//instantiation
Object object = clazz.newInstance();
//Get data through setId
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show", int.class);
method.setAccessible(true);
//Setting data
Object object2 = method.invoke(object, 18);
//print data
System.out.println(object2);
}
@Test
//Static master method by reflection
public void Demo3() throws Exception {
//Get the class object. The main method is static and does not need to be instantiated
Class clazz = Class.forName("cn.ahut.gbl.Bean");
//Acquisition method
Method method = clazz.getMethod("main", String[].class);
//Execute main method
/*The first parameter is the instance object (variable name). The main method is static and does not need to be
* The second parameter is a string array, which is the actual parameter
* When the variable parameters are executed again, the JVM scrambles the amount parameters into multiple parameters, so an error will be reported
* So here you can cast the array to the Object type
*/
String[] args= {"Zhang San","male","abc121"};
method.invoke(null, (Object)args);
}
@Test
//Get public field through reflection
public void Demo4() throws Exception {
//Get class object,
Class clazz = Class.forName("cn.ahut.gbl.Bean");
Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
//Acquisition method
Field field = clazz.getField("description");
//Assign a value to a field
field.set(obj, "describe");
//Fetch the value of the field
String string = (String) field.get(obj);
System.out.println(string);
}
@Test
//Get private field by reflection
public void Demo5() throws Exception {
//Get class object,
Class clazz = Class.forName("cn.ahut.gbl.Bean");
Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
//Acquisition method
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("className");
field.setAccessible(true);
//Assign a value to a field
field.set(obj, "javaBean");
//Fetch the value of the field
String string = (String) field.get(obj);
System.out.println(string);
}
}4, Properties are stored in java as key value pairs, ending with. Properties, and used as configuration files in development. In the development of the framework, we need to read the configuration file and code dynamically. The following shows how to write and read the properties file.
public class PropsDemo {
@Test
public void Demo1() throws IOException {
//Operation of properties: write file
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("name", "Lao Zhang");
properties.setProperty("sex", "male");
properties.setProperty("age", "65");
//Write properties to hard disk
Writer writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("1.properties"), "UTF-8");
properties.store(writer, "describe");
writer.close();
}
@Test
public void Demo2() throws IOException {
////Operation of properties: reading files
//Get the properties object
Properties properties = new Properties();
//Get stream resources
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("1.properties"), "UTF-8");
//Download resources through the properties object
properties.load(reader);
//Traversal content
for (String name : properties.stringPropertyNames()) {
String value = properties.getProperty(name);
System.out.println(name+":"+value);
}
}
}5, Now write a Demo to see how to dynamically get the contents of the configuration file to call javaBean.
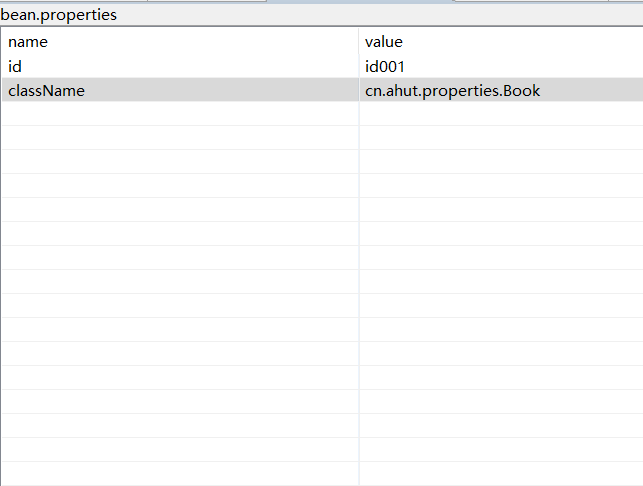
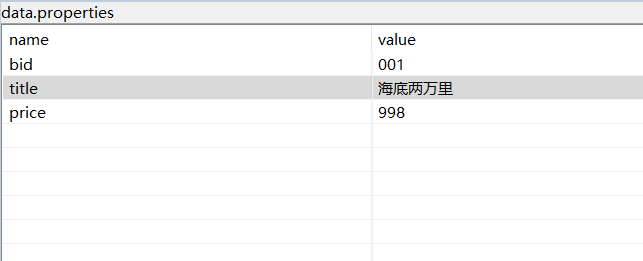
Here we write three javaBean files, bean config, bean and book, as well as bean.properties and data.properties. Bean.properties stores the id of data.properties file and the class object of jabaBean. Data.properties file stores the specific data corresponding to javaBean.
As follows:
public class BeanConfig {
private String id;
private String className;
Properties properties = new Properties();
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BeanConfig [id=" + id + ", className=" + className
+ ", properties=" + properties + "]";
}
}public class Book {
private String bid;
private String title;
private String price;
public String getBid() {
return bid;
}
public void setBid(String bid) {
this.bid = bid;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(String price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book [bid=" + bid + ", title=" + title + ", price=" + price
+ "]";
}
}public class UserBean {
private String uid;
private String userName;
private String passWord;
public String getUid() {
return uid;
}
public void setUid(String uid) {
this.uid = uid;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserBean [uid=" + uid + ", userName=" + userName
+ ", passWord=" + passWord + "]";
}
}
Next, add the field information for bianconfig by reading the properties:
public class DemoTest {
public BeanConfig getConfig() throws Exception {
//Read profile
BeanConfig beanConfig = new BeanConfig();
//Read the bean.properties file to get the ID and className
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("bean.properties"),"UTF-8"));
beanConfig.setId(properties.getProperty("id"));
beanConfig.setClassName(properties.getProperty("className"));
//System.out.println(beanConfig);
//Read the contents of the data.properties file
Properties dataProperties = new Properties();
dataProperties.load(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("data.properties"),"UTF-8"));
for(String name : dataProperties.stringPropertyNames()){
System.out.println(name);
String value = dataProperties.getProperty(name);
beanConfig.getProperties().setProperty(name, value);
}
return beanConfig;
}
@Test
public void method1() throws Exception {
//Real data
BeanConfig beanConfig = getConfig();
//Use data to create javaBean instances and encapsulate specific data for JavaBeans
Class clazz = Class.forName(beanConfig.getClassName());
Object object = clazz.newInstance();
//Call the set method in javaBean for encapsulation
for(String name : beanConfig.getProperties().stringPropertyNames()){
String value = beanConfig.getProperties().getProperty(name);
//Get method name
String methodName = "set" + name.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() + name.substring(1);
//Call set method
Method method = clazz.getMethod(methodName, String.class);
method.invoke(object, value);
}
System.out.println(object);
}

