I have combed the workflow and key source code of MyBatis when it is used alone. Now let's see how MyBatis works when it is integrated with Spring
Start with use
Spring integrates MyBatis
1. Introduce dependency. In addition to the dependency of MyBatis, you need to introduce the dependency of MyBatis spring
2. Configure SqlSessionFactoryBean in the spring configuration file applicationContext.xml. From the name, we can see that we create SqlSessionFactory through this Bean
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"></property>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapper/*.xml"></property>
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>3. Configure the path to scan Mapper in applicationContext.xml
There are three ways
1.To configure MapperScannerConfigurer
<bean id="mapperScanner" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.XXX.XXX"/>
</bean>
2.To configure<scan>Label
<context:component-scan base-package="com.XXX.XXX">
3.Use@MapperScan annotationPrinciple analysis
Create session factory
First, look at the SqlSessionFactoryBean configured earlier. Its class diagram is as follows
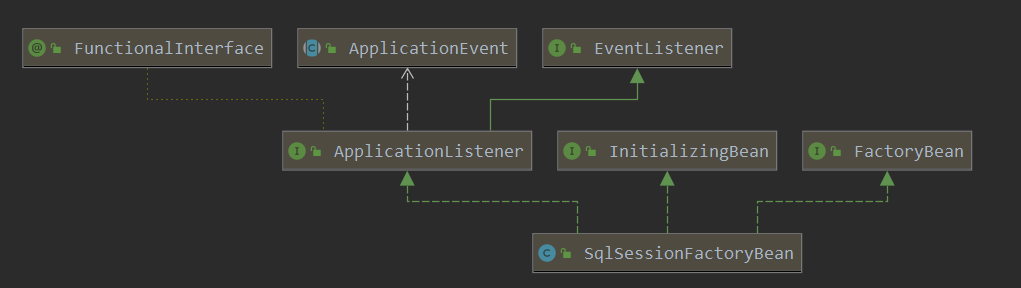
The InitializingBean has a afterPropertiesSet to be implemented, which will be called after initializing Bean. Here is the SqlSessionFactory object created in the afterPropertiesSet implementation method.
//After Bean is initialized, it is called.
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(this.dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
Assert.notNull(this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
Assert.state(this.configuration == null && this.configLocation == null || this.configuration == null || this.configLocation == null, "Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
//Create SqlSessionFactory
this.sqlSessionFactory = this.buildSqlSessionFactory();
} protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
Configuration targetConfiguration;
//If the configuration already exists, add the Properties property of the current Bean to the configuration
if (this.configuration != null) {
targetConfiguration = this.configuration;
if (targetConfiguration.getVariables() == null) {
targetConfiguration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
} else if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
targetConfiguration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties);
}
//If the configuration does not exist, but the configLocation exists, use XmlConfigBuilder to resolve the corresponding configuration file
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), (String)null, this.configurationProperties);
targetConfiguration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
//If the configuration object does not exist and the configurationlocation path does not exist, the default configurationProperties are used to assign a value to the configuration
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration";
});
targetConfiguration = new Configuration();
Optional.ofNullable(this.configurationProperties).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVariables);
}
//Based on the existing attributes in the current factoryBean, assign values to the attributes in the targetConfiguration object
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectWrapperFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectWrapperFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.vfs).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVfsImpl);
String[] typeHandlersPackageArray;
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
typeHandlersPackageArray = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeAliasesPackage, ",; \t\n");
Stream.of(typeHandlersPackageArray).forEach((packageToScan) -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(packageToScan, this.typeAliasesSuperType == null ? Object.class : this.typeAliasesSuperType);
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for aliases";
});
});
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
Stream.of(this.typeAliases).forEach((typeAlias) -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'";
});
});
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.plugins)) {
Stream.of(this.plugins).forEach((plugin) -> {
targetConfiguration.addInterceptor(plugin);
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Registered plugin: '" + plugin + "'";
});
});
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.typeHandlersPackage)) {
typeHandlersPackageArray = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeHandlersPackage, ",; \t\n");
Stream.of(typeHandlersPackageArray).forEach((packageToScan) -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(packageToScan);
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for type handlers";
});
});
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
Stream.of(this.typeHandlers).forEach((typeHandler) -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(typeHandler);
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Registered type handler: '" + typeHandler + "'";
});
});
}
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {
try {
targetConfiguration.setDatabaseId(this.databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(this.dataSource));
} catch (SQLException var23) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed getting a databaseId", var23);
}
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.cache).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::addCache);
//If XMLConfigBuilder is not empty, call the parse method, which is the same as called in MyBatis
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'";
});
} catch (Exception var21) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, var21);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
//Create environment, transaction factory (spring managedtransactionfactory is used by default)
targetConfiguration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment, (TransactionFactory)(this.transactionFactory == null ? new SpringManagedTransactionFactory() : this.transactionFactory), this.dataSource));
//According to the configured MapperLocation, use XMLMapperBuilder to parse mapper.xml, and register the interface and corresponding MapperProxyFactory into MapperRegistry.
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
Resource[] var24 = this.mapperLocations;
int var4 = var24.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
Resource mapperLocation = var24[var5];
if (mapperLocation != null) {
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(), targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception var19) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", var19);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'";
});
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified or no matching resources found";
});
}
//Using the build method of SqlSessionFactoryBuilder to build SqlSessionFactory
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);
}Create SqlSession
When creating a SqlSession, Spring does not directly use the DefaultSqlSession of MyBatis, but encapsulates a SqlSessionTemplate. This is because DefaultSqlSession is not thread safe, so Spring features encapsulate a thread safe SqlSessionTemplate (line program safety is inevitable in web scenarios)
The SqlSession created in SqlSessionTemplate is the jdk dynamic proxy used. All method calls are actually made through this proxy
private final SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
private final ExecutorType executorType;
private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy;
private final PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator;
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
this(sqlSessionFactory, sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getDefaultExecutorType());
}
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType) {
this(sqlSessionFactory, executorType, new MyBatisExceptionTranslator(sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getEnvironment().getDataSource(), true));
}
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType, PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
Assert.notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
Assert.notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
//Creating proxy objects through JDK dynamic proxy
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession)Proxy.newProxyInstance(SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{SqlSession.class}, new SqlSessionTemplate.SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
//Create InvocationHandler for proxy object
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
private SqlSessionInterceptor() {
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//Get SqlSession object. commit and close are the methods of the object. Guess that SqlSessionTemplate thread is safe because of this code
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory, SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
Object unwrapped;
try {
//Calling the target object method, actually calling the DefaultSqlSession method
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!SqlSessionUtils.isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
unwrapped = result;
} catch (Throwable var11) {
unwrapped = ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var11);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
SqlSessionUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException)unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw (Throwable)unwrapped;
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
SqlSessionUtils.closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
return unwrapped;
}
}This section analyzes the reasons for thread safety
Knowing that SqlSessionTemplate is used in spring to ensure thread safety, how can we get this Template and use it? In the early version of spring, to use SqlSessionTemplate, we need to let our dao class inherit SqlSessionDaoSupport, which holds a SqlSessionTemplate object and provides the method of getSqlSession
public abstract class SqlSessionDaoSupport extends DaoSupport {
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate;
public SqlSessionDaoSupport() { }
//When inheriting SqlSessionDaoSupport, you need to call setSqlSessionFactory to inject SqlSessionFactory (or xml)
public void setSqlSessionFactory(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
if (this.sqlSessionTemplate == null || sqlSessionFactory != this.sqlSessionTemplate.getSqlSessionFactory()) {
this.sqlSessionTemplate = this.createSqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
protected SqlSessionTemplate createSqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
public final SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() {
return this.sqlSessionTemplate != null ? this.sqlSessionTemplate.getSqlSessionFactory() : null;
}
//Method to obtain SqlSessionTemplate provided externally (SqlSessionTemplate also implements SqlSession interface)
public SqlSession getSqlSession() {
return this.sqlSessionTemplate;
}
...
}But in this way, if we want to operate the database, we need to implement SqlSessionDaoSupport to get a SqlSessionTemplate
The current spring has already optimized the way to use SqlSessionTemplate. You can directly use the Mapper interface that @ Autowired automatically injects in the Service layer
Scan registration for interface
These mappers are registered when MapperScannerConfigurer is configured in applicationContext.xml
<bean id="mapperScanner" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <property name="basePackage" value="com.XXX.XXX"/> </bean>
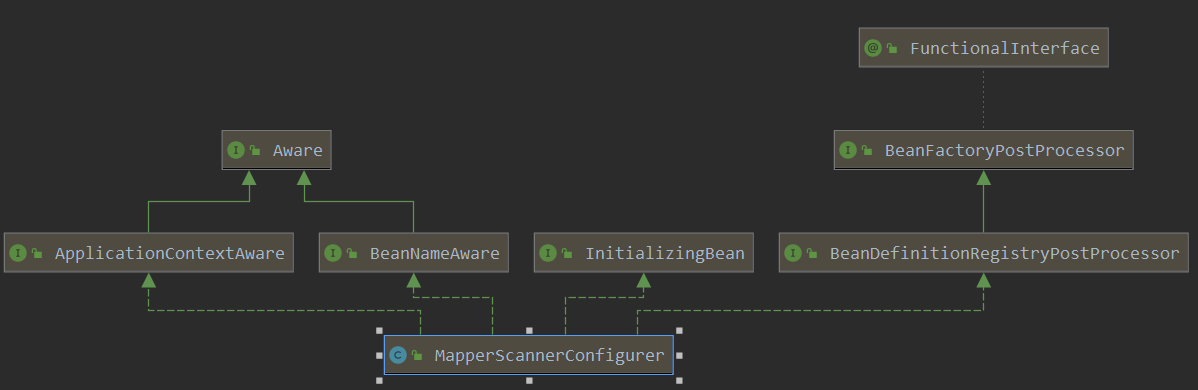
MapperScannerConfigurer implements the postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry method of the beandefinitionregistrypostprocessor (this interface is used to do some post-processing after BeanDefinition registration, such as modifying BeanDefinition)
//MapperScannerConfigurer
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
this.processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.registerFilters();
//Scan package path, register Mapper
scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ",; \t\n"));
}
-----scanner.scan It will call ClassPathMapperScanner Of doScan Method
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> {
return "No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration.";
});
} else {
//How to process bean definitions
this.processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) {
Iterator var3 = beanDefinitions.iterator();
while(var3.hasNext()) {
BeanDefinitionHolder holder = (BeanDefinitionHolder)var3.next();
GenericBeanDefinition definition = (GenericBeanDefinition)holder.getBeanDefinition();
String beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName();
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "' and '" + beanClassName + "' mapperInterface";
});
//the mapper interface is the original class of the bean
//but the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(beanClassName);
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBean.getClass());
definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig);
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
//Add SqlSessionFactory and sqlSessionTemplate to BeanDefinition's properties
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> {
return "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.";
});
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> {
return "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.";
});
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (!explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.debug(() -> {
return "Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'.";
});
definition.setAutowireMode(2);
}
}
}
As you can see from the above, Mapper will set its BeanClass of BeanDefinition to MapperFactoryBean, So the MapperFactoryBean object is actually generated when instantiating, and our MapperFactoryBean inherits SqlSessionDaoSupport, and we added SqlSessionTemplate and SqlSessionFactory attributes to BeanDefinition, so the MapperFactoryBean generated actually inherits SqlSessionDaoSupport and injects SqlSessionTemplate And SqlSessionFactory
Use of interface injection
As mentioned earlier, when spring uses Mapper, it is better to directly inject @ Autowired into Mapper interface in the class annotated with Service
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
//Press id to query
public Employee getEmp(Integer id) {
Employee employee = employeeMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
return employee;
}
}
When spring starts, it instantiates the EmployeeService, and the EmployeeMapper object needs to be injected into the EmployeeService,
Spring will get its beandefinition from BeanFactory and BeanClass from beandefinition according to Mapper's name. At this time, its BeanClass has been replaced with MapperFactoryBean
Next, you just need to create MapperFactoryBean instance object. Because MapperFactoryBean implements the FactoryBean interface, it will get the corresponding instance object through getObject()
//The actual call is the getMapper method of sqlsession (the returned object here is SqlSessionTemplate)
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return this.getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
----SqlSessionTemplate Called here Configuration Of getMapper
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return this.getConfiguration().getMapper(type, this);
}
----Configuration Finally, through configuration Of mapperRegistry Get the corresponding Mapper,What we actually got was
//MapperProxy enhanced proxy object obtained through the factory class MapperProxyFactory
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return this.mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
To summarize:
| Key class | function |
| SqlSessionTemplate | The thread safe SqlSession implementation class in Spring calls the DefaultSqlSession method by proxy |
| SqlSessionInterceptor (inner class) | Defined in SqlSessionTemplate to enhance the agent DefaultSqlSession |
| SqlSessionDaoSupport | To get SqlSessionTemplate, you need to inherit it and inject SqlSessionFactory |
| MapperFactoryBean | The Mapper interface replacement class registered in IOC container inherits SqlSessionDaoSupport, which can be used to obtain SqlSessionTemplate. When the interface is injected, its getObject() method will be called to finally call the getMapper method of Configuration |
| SqlSessionHolder | Control SqlSession and transactions |

