Chapter 1 installing Docker
Introduction: 1. What is Dokcer?
An open source application container engine allows developers to package their applications and dependency packages into a portable container, and then publish them to any popular Linux machine. Virtualization can also be realized.
The container is completely encapsulated on the basis of LCX (linux container) by using the sandbox mechanism, without any interface between them, and written in go language.
2. Why use docker?
Provide a one-time environment. If Mysql, RocketMQ and RabbitMQ need to be installed, many dependent libraries and versions need to be installed. If Docker is used, it can be started and run directly through image
For rapid dynamic capacity expansion, an application is deployed with docker, which can be made into an image, and then quickly started through Dokcer
Build a microservice architecture, which can simulate multiple microservices and start multiple applications on one machine
Better resource isolation and sharing
1. Run the following commands to add an update source
yum update yum install epel-release -y yum clean all yum list
yum update: execute and select yes, and wait for the update to succeed
Yum install EPEL release - y wait for success
Execute yum clean all and wait for success. If you don't execute it, it won't affect you, but it's best to avoid reporting errors
yum list is executed successfully. It will not be affected if it is not executed, but it is best to avoid error reporting
2. CentOS 7.9 install and run Docker
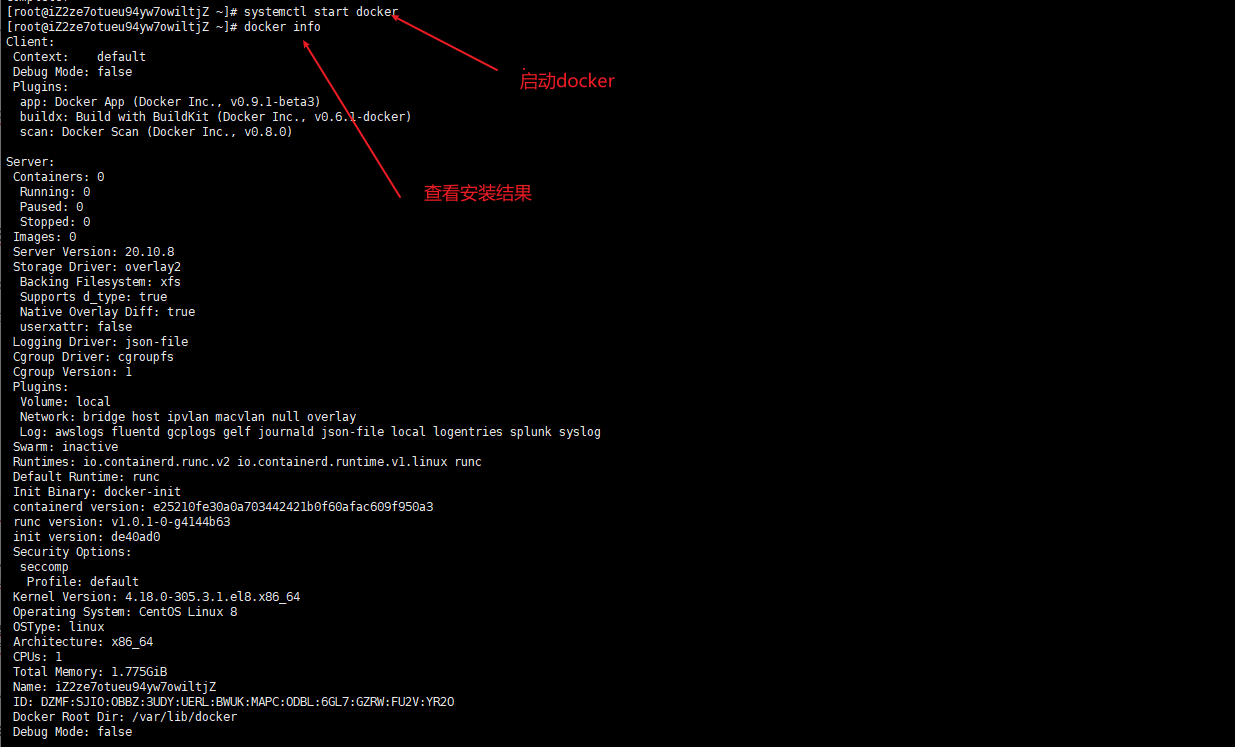
yum install docker-io -y install docker command systemctl start docker start-up docker command docker info View installation results
3. CentOS 8.4 install and run Docker
Note: CentOS 8 uses podman instead of docker by default, so containerd.io needs to be installed
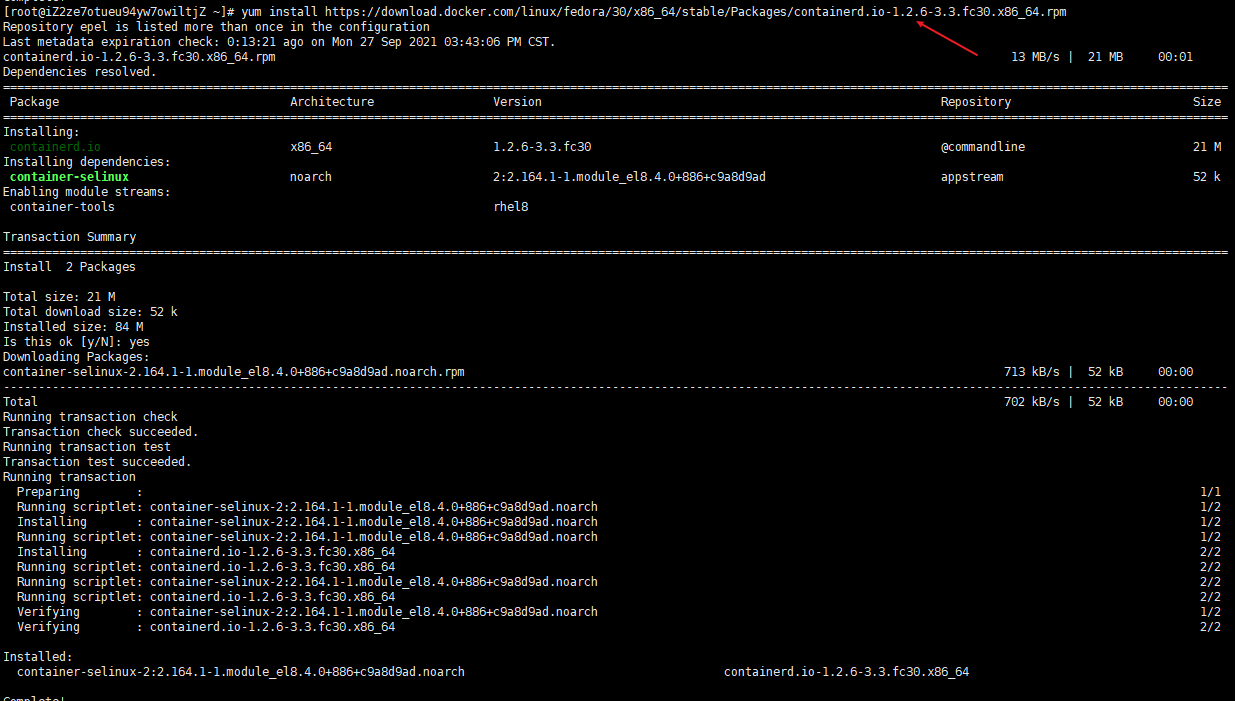
Use the following command to install and its dependent packages
yum install https://download.docker.com/linux/fedora/30/x86_64/stable/Packages/containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.fc30.x86_64.rpm
Install other dependent packages
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
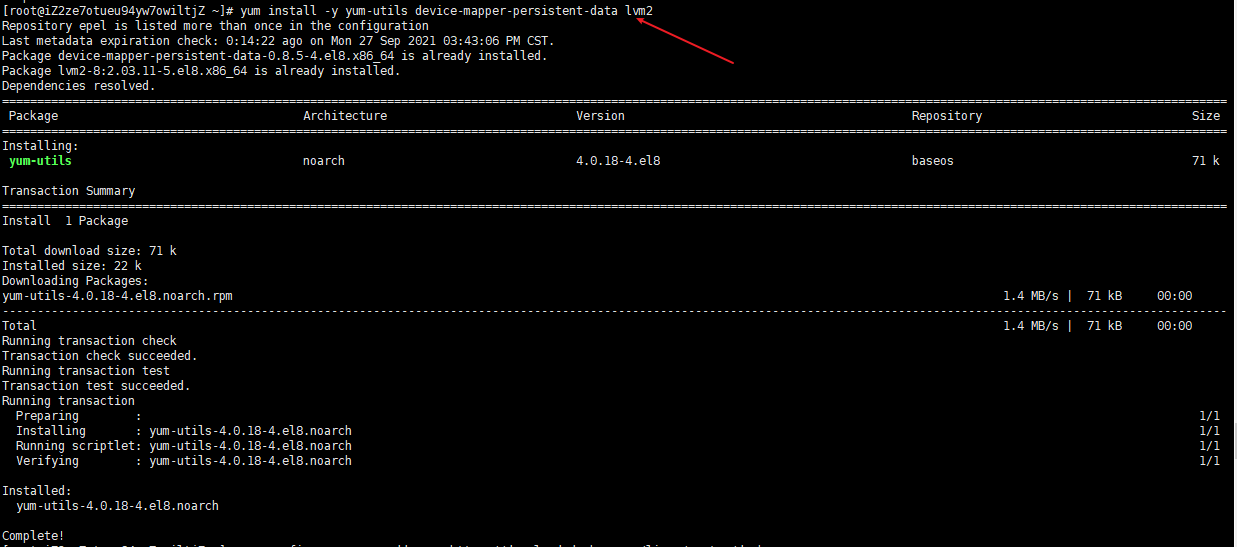

Install docker
yum install -y docker-ce
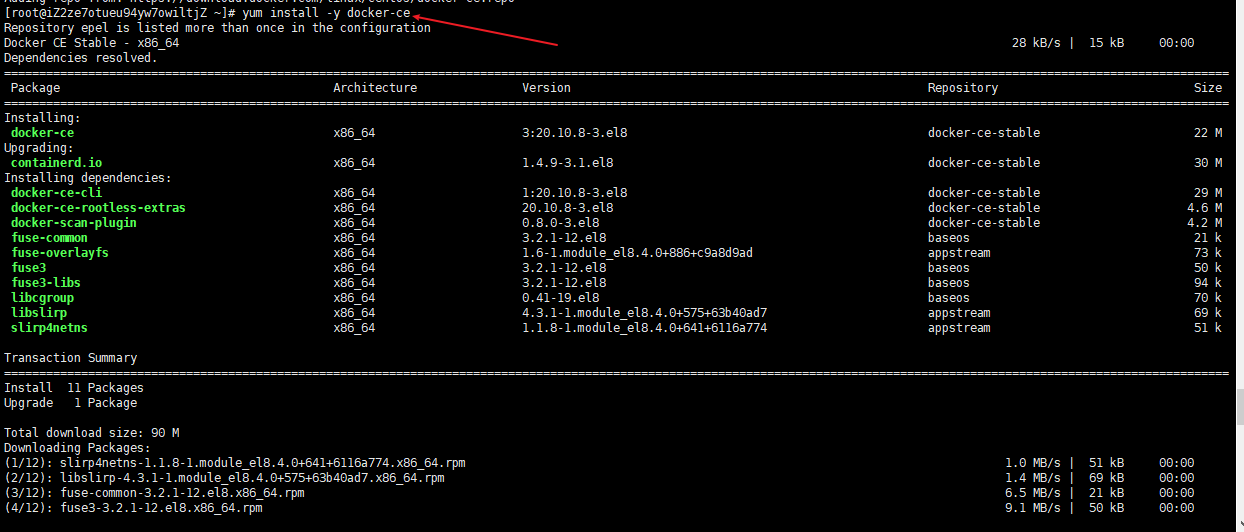
Start docker and view the installation results
systemctl start docker start-up docker docker info View installation results
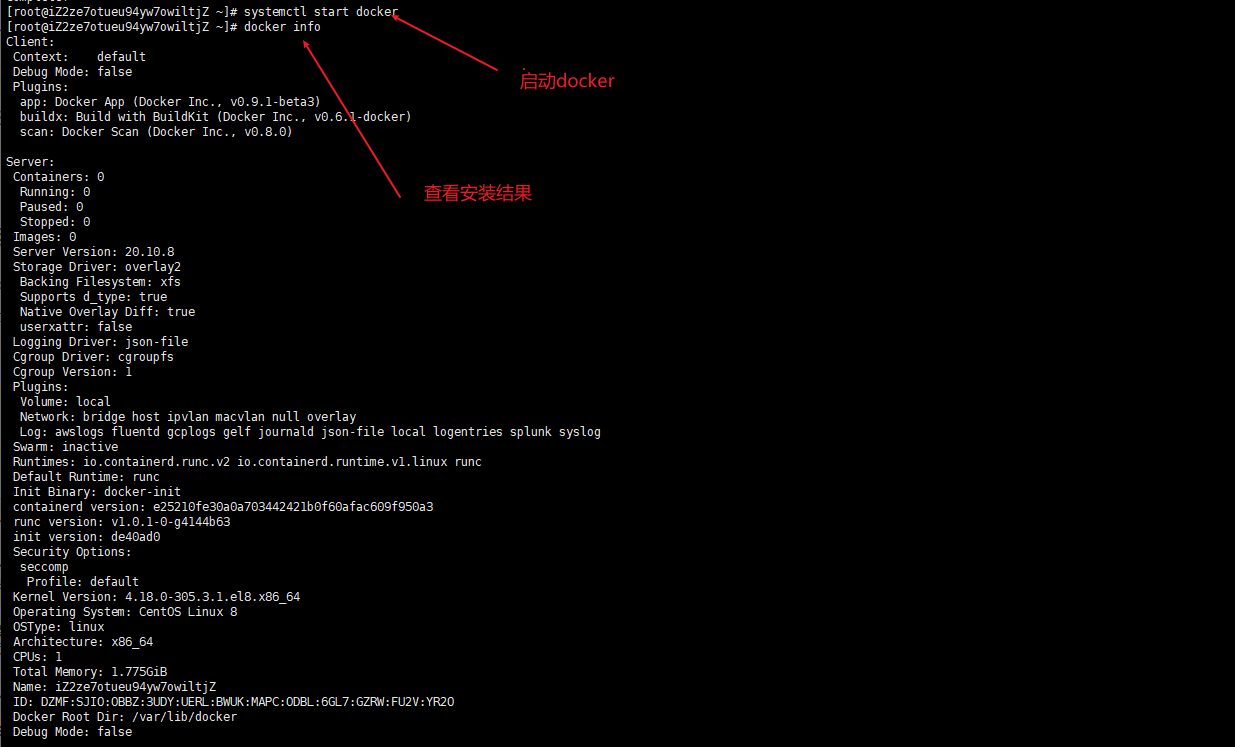
5. Start using Docker
systemctl start docker function docker Daemon systemctl stop docker stop it docker Daemon systemctl restart docker restart docker Daemon
6. Modify mirror warehouse
Enter modify profile
vim /etc/docker/daemon.json

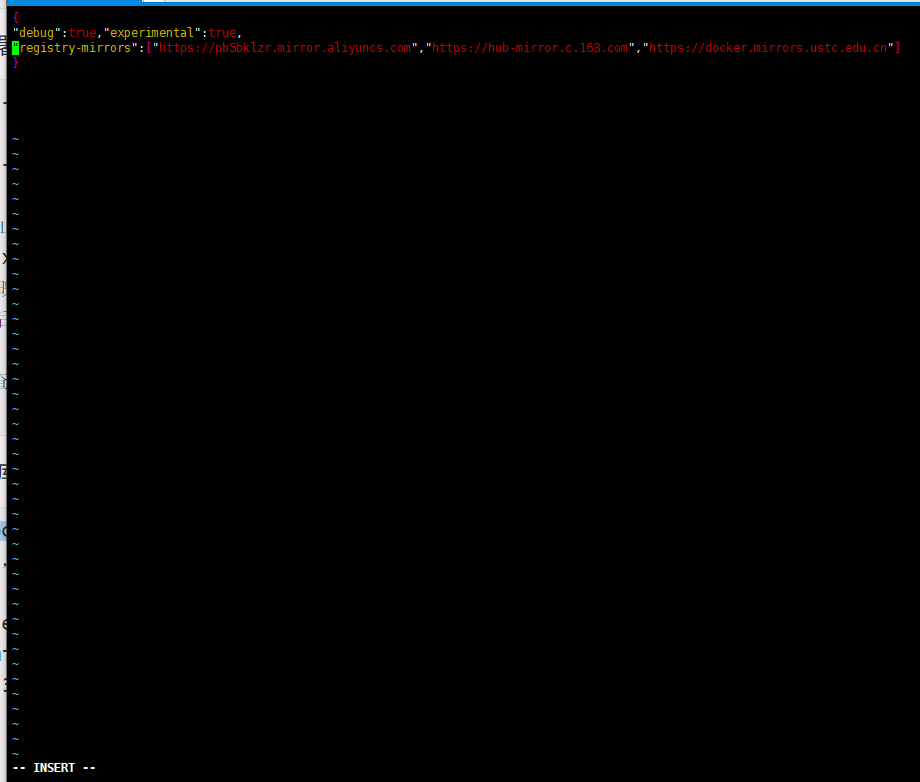
Add the following and enter: wq saveexit
{
"debug":true,"experimental":true,
"registry-mirrors":["https://pb5bklzr.mirror.aliyuncs.com","https://hub-mirror.c.163.com","https://docker.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn"]
}
Restart docker
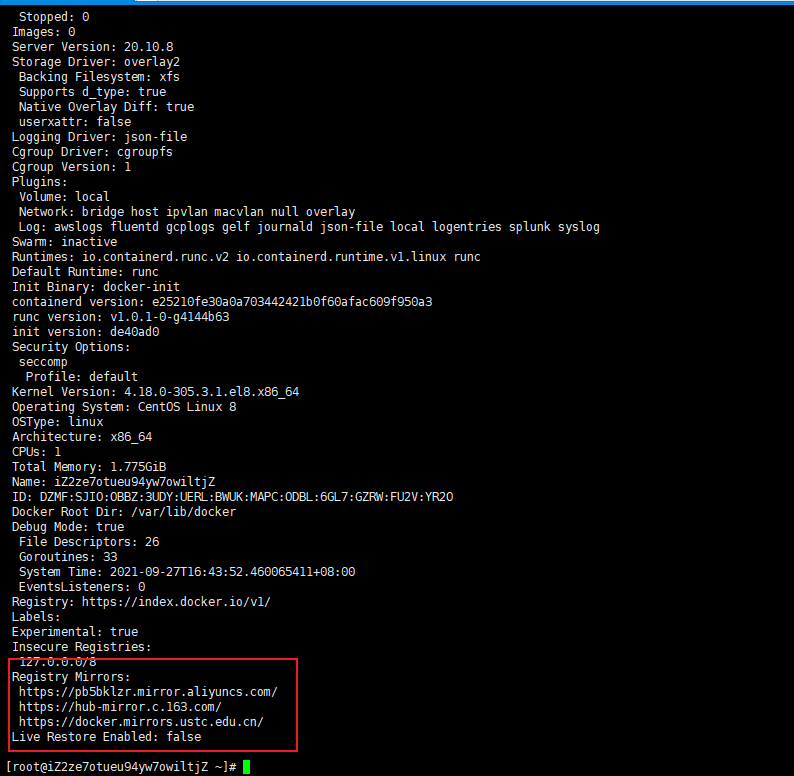
Use the docker info command to check whether it is successful
docker info
Chapter 2 deployment of Nginx
1. Deploy Nginx
Start Nginx deployment using the following command
docker run --name nginx-test -p 8080:80 -d nginx Parameter explanation --rm: After the container terminates, the container file is automatically deleted( docker run --rm --name nginx-test -p 8080:80 -d nginx) --name nginx-test: The name of the container is nginx-test,The name is defined by yourself. The name must be unique -p: Port mapping, mapping the local 8080 port to the 80 port inside the container -d: After the container starts, it runs in the background

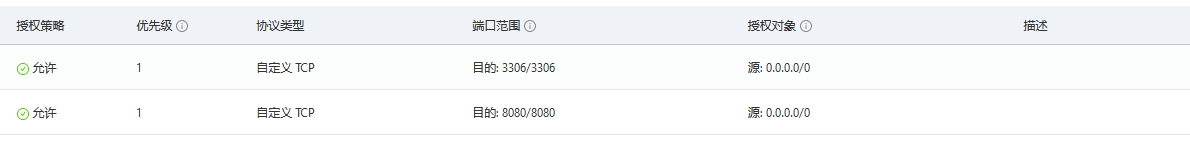
Alicloud security group opens the corresponding 8080 port
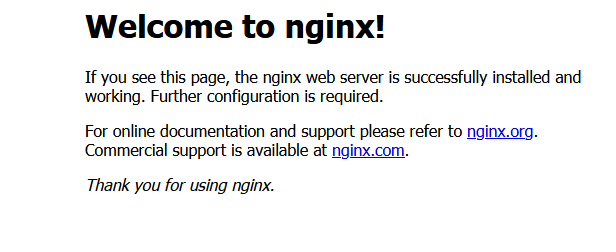
Check whether Nginx is successful: enter "ecs server public ip +: + 8080" in the browser address, and a message appears
Welcome to nginx
2. View container log
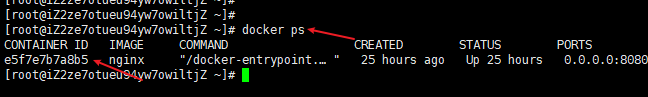
Query running container ID
docker ps
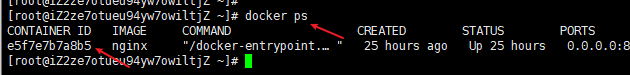
Query stopped container ID

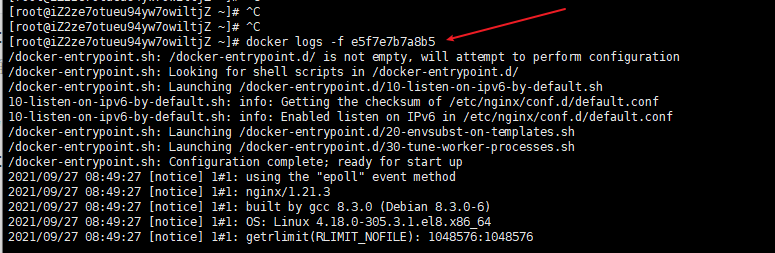
Query Docker log
docker logs -f container ID
3. Stop, start container
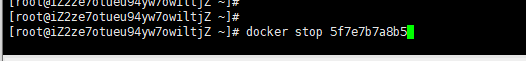
Stop container
docker stop container ID
Start container
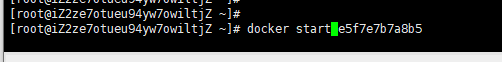
docker start container ID
Chapter 3 installing MySQL database
1. Install MySQL database
Find any path on the server and install the mysql database using the following command:
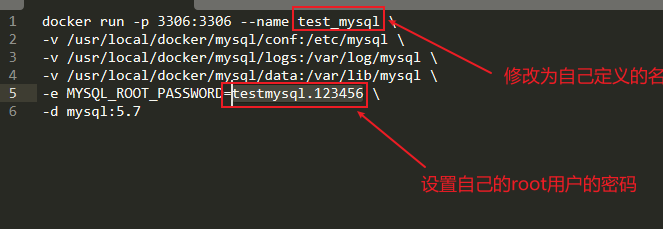
docker run -p 3306:3306 --name test_mysql \ -v /usr/local/docker/mysql/conf:/etc/mysql \ -v /usr/local/docker/mysql/logs:/var/log/mysql \ -v /usr/local/docker/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql \ -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=testmysql.123456 \ -d mysql:5.7
2. Check whether the installation is successful
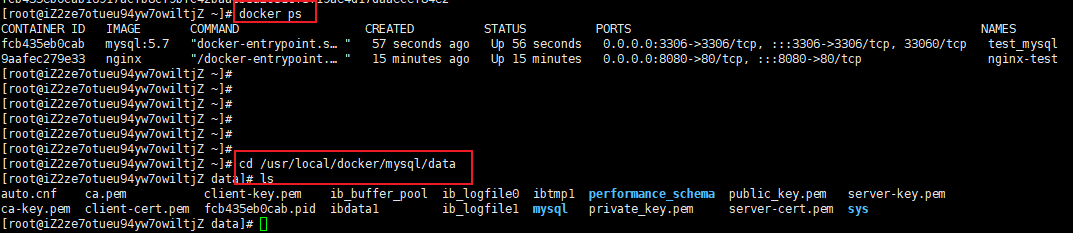
docker ps View running containers cd /usr/local/docker/mysql/data get into datamul ls View content
2. MySQL database connection
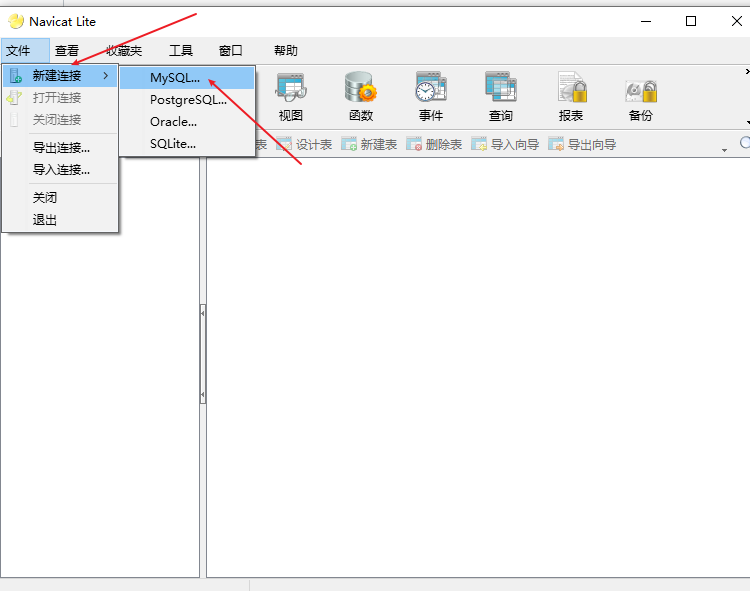
window Connection tool: Navicat,HeidiSQL mac Connection tool: Sequel Pro
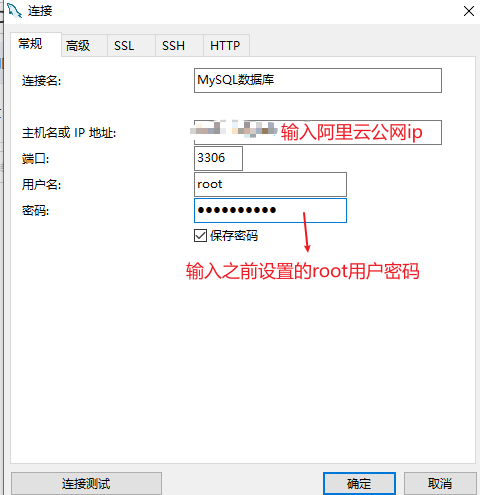
New connection - MySQL
Enter the host IP and password: after configuration, click [connection test] to test. If successful, the configuration is OK (Alibaba cloud security group must open port 3306)