Write before
In the last article kubernetes Series Tutorials (5) Deep understanding of core concepts pod yaml's first introduction to kubernetes is an important concept of pod, followed by introduction kubernetes series tutorials resource management of pod and Quality of service of pod.
1. Pod Resource Management
1.1 resource definition
Containers need to allocate resources during operation. How can they work with cggroup?The answer is to allocate resources by defining a resource, which is mainly cpu and memory. There are two definitions of resources: requests and limits. requests represent requests for resources, which are mainly used as the basis for initial kubernetes dispatch of pods to indicate the allocation of resources that must be met. limits indicate the limits of resources, that is, pods cannot exceed the limits defined by limits and exceed themWith the cggroup restriction, resources defined in a pod can be defined in the following four fields:
- spec.container[].resources.requests.cpu Request the size of CPU resources, such as 0.1 CPU and 100m means 1/10 CPU is allocated;
- spec.container[].resources.requests.memory Request memory size in M, Mi, G, Gi;
- spec.container[].resources.limits.cpu limits the size of the CPU and cannot exceed the threshold, which is the limit in cggroup;
- spec.container[].resources.limits.memory limits the size of memory beyond the threshold, beyond which OOM will occur;
1. Start learning how to define resource resources for a pod. For example, using nginx-demo as an example, containers request 250 m cpu resources, limit 500 m, request 128 Mi memory resources, and limit 256 Mi memory resources. Of course, you can also define resources for multiple containers, which together are the total resources for a pod, as follows:
[root@node-1 demo]#cat nginx-resource.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-demo
labels:
name: nginx-demo
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-demo
image: nginx:1.7.9
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: nginx-port-80
protocol: TCP
containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 0.25
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 256Mi2. Apply the configuration definition of the pod (if the previous pod still exists, first delete the kubectl delete pod <pod-name>), or name the pod another name
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl apply -f nginx-resource.yaml pod/nginx-demo created
3. View the allocation details of pod resources
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
demo-7b86696648-8bq7h 1/1 Running 0 12d
demo-7b86696648-8qp46 1/1 Running 0 12d
demo-7b86696648-d6hfw 1/1 Running 0 12d
nginx-demo 1/1 Running 0 94s
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl describe pods nginx-demo
Name: nginx-demo
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: node-3/10.254.100.103
Start Time: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 12:10:49 +0800
Labels: name=nginx-demo
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Pod","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"name":"nginx-demo"},"name":"nginx-demo","namespace":"default"},"sp...
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.2.13
Containers:
nginx-demo:
Container ID: docker://55d28fdc992331c5c58a51154cd072cd6ae37e03e05ae829a97129f85eb5ed79
Image: nginx:1.7.9
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:e3456c851a152494c3e4ff5fcc26f240206abac0c9d794affb40e0714846c451
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 12:10:51 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Limits: #Limit resources
cpu: 500m
memory: 256Mi
Requests: #Request Resources
cpu: 250m
memory: 128Mi
Environment: <none>
...ellipsis...4. How are Pod's resources allocated?There is no doubt that it is allocated from nodes. When we create a pod with requests set, kube-scheduler of kubernetes performs two scheduling processes: filter filtering and weight weighting, and kube-scheduler filters the eligible nodes based on the requested resources, then sorts them, filters the nodes that best satisfy the running pod, and thenRun pod on a specific node.Scheduling algorithms and details can be referred to below Introduction of kubernetes scheduling algorithm .The following are the allocation details of node-3 node resources:
[root@node-1 ~]# kubectl describe node node-3 ...ellipsis... Capacity: #Total resource condition of resources on nodes, 1 cpu, 2 g memory, 110 pod s cpu: 1 ephemeral-storage: 51473888Ki hugepages-2Mi: 0 memory: 1882352Ki pods: 110 Allocatable: #Allowable allocation of resources by nodes, partially reserved resources are drained in the Allocatable category cpu: 1 ephemeral-storage: 47438335103 hugepages-2Mi: 0 memory: 1779952Ki pods: 110 System Info: Machine ID: 0ea734564f9a4e2881b866b82d679dfc System UUID: FFCD2939-1BF2-4200-B4FD-8822EBFFF904 Boot ID: 293f49fd-8a7c-49e2-8945-7a4addbd88ca Kernel Version: 3.10.0-957.21.3.el7.x86_64 OS Image: CentOS Linux 7 (Core) Operating System: linux Architecture: amd64 Container Runtime Version: docker://18.6.3 Kubelet Version: v1.15.3 Kube-Proxy Version: v1.15.3 PodCIDR: 10.244.2.0/24 Non-terminated Pods: (3 in total) #When running pod resources on a node, there are more than one pod in addition to nginx-demo Namespace Name CPU Requests CPU Limits Memory Requests Memory Limits AGE --------- ---- ------------ ---------- --------------- ------------- --- default nginx-demo 250m (25%) 500m (50%) 128Mi (7%) 256Mi (14%) 63m kube-system kube-flannel-ds-amd64-jp594 100m (10%) 100m (10%) 50Mi (2%) 50Mi (2%) 14d kube-system kube-proxy-mh2gq 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 12d Allocated resources: #Allocated cpu and memory resources (Total limits may be over 100 percent, i.e., overcommitted.) Resource Requests Limits -------- -------- ------ cpu 350m (35%) 600m (60%) memory 178Mi (10%) 306Mi (17%) ephemeral-storage 0 (0%) 0 (0%) Events: <none>
1.2 Resource Allocation Principles
The resource requests and limits defined by Pod work on kube-sheduler, the dispatcher of kubernetes. In fact, the cpu and memory-defined resources are applied on containers and the cggroup on containers is used to isolate resources. Next, we describe the principles of resource allocation.
- spec.containers[].resources.requests.cpu acts on CpuShares, indicating the weight of the allocated CPU and the proportion of the allocation during a race
- spec.containers[].resources.requests.memory is mainly used for the kube-scheduler scheduler and does not make sense for containers
- spec.containers[].resources.limits.cpu acts on CpuQuota and CpuPeriod in microseconds, calculated as CpuQuota/CpuPeriod, which represents the percentage of maximum usable cpu, such as 500m, which allows 50% of a cpu's resources to be used
- spec.containers[].resources.limits.memory acts on the emory, indicating the maximum available Memory size of the container, beyond which OOM will occur
Taking nginx-demo as an example, this paper studies the parameters that requests and limits defined in pod apply to docker in effect:
1. View the node where the pod is located and nginx-demo is dispatched to the node-3 node
[root@node-1 ~]# kubectl get pods -o wide nginx-demo NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES nginx-demo 1/1 Running 0 96m 10.244.2.13 node-3 <none> <none>
2. To get the id number of the container, you can get the id of the container by using the containerID of kubectl describe pods nginx-demo, or you can get the id number of the container by logging on to the node-3 node through name filtering. By default, there are two pods: one created by pause mirror and the other by applying mirror.
[root@node-3 ~]# docker container list |grep nginx 55d28fdc9923 84581e99d807 "nginx -g 'daemon of..." 2 hours ago Up 2 hours k8s_nginx-demonginx-demo_default_66958ef7-507a-41cd-a688-7a4976c6a71e_0 2fe0498ea9b5 k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.1 "/pause" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours k8s_POD_nginx-demo_default_66958ef7-507a-41cd-a688-7a4976c6a71e_0
3. View docker container details
[root@node-3 ~]# docker container inspect 55d28fdc9923
[
...Partial Output Omitting...
{
"Image": "sha256:84581e99d807a703c9c03bd1a31cd9621815155ac72a7365fd02311264512656",
"ResolvConfPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/2fe0498ea9b5dfe1eb63eba09b1598a8dfd60ef046562525da4dcf7903a25250/resolv.conf",
"HostConfig": {
"Binds": [
"/var/lib/kubelet/pods/66958ef7-507a-41cd-a688-7a4976c6a71e/volumes/kubernetes.io~secret/default-token-5qwmc:/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount:ro",
"/var/lib/kubelet/pods/66958ef7-507a-41cd-a688-7a4976c6a71e/etc-hosts:/etc/hosts",
"/var/lib/kubelet/pods/66958ef7-507a-41cd-a688-7a4976c6a71e/containers/nginx-demo/1cc072ca:/dev/termination-log"
],
"ContainerIDFile": "",
"LogConfig": {
"Type": "json-file",
"Config": {
"max-size": "100m"
}
},
"UTSMode": "",
"UsernsMode": "",
"ShmSize": 67108864,
"Runtime": "runc",
"ConsoleSize": [
0,
0
],
"Isolation": "",
"CpuShares": 256, CPU Weight assigned to requests.cpu upper
"Memory": 268435456, The size of the memory allocation used for limits.memory upper
"NanoCpus": 0,
"CgroupParent": "kubepods-burstable-pod66958ef7_507a_41cd_a688_7a4976c6a71e.slice",
"BlkioWeight": 0,
"BlkioWeightDevice": null,
"BlkioDeviceReadBps": null,
"BlkioDeviceWriteBps": null,
"BlkioDeviceReadIOps": null,
"BlkioDeviceWriteIOps": null,
"CpuPeriod": 100000, CPU The allocated usage ratio, and CpuQuota Working together in limits.cpu upper
"CpuQuota": 50000,
"CpuRealtimePeriod": 0,
"CpuRealtimeRuntime": 0,
"CpusetCpus": "",
"CpusetMems": "",
"Devices": [],
"DeviceCgroupRules": null,
"DiskQuota": 0,
"KernelMemory": 0,
"MemoryReservation": 0,
"MemorySwap": 268435456,
"MemorySwappiness": null,
"OomKillDisable": false,
"PidsLimit": 0,
"Ulimits": null,
"CpuCount": 0,
"CpuPercent": 0,
"IOMaximumIOps": 0,
"IOMaximumBandwidth": 0,
},
}
]1.3. cpu resource testing
The limits of CPU in pod are mainly defined by requests.cpu and limits.cpu. Limits are CPU sizes that cannot be exceeded. We verify through stress mirroring that stress is a compression side tool for CPU and memory, and the size of the compression side CPU is defined by specifying the args parameter.The CPU and memory for monitoring pods can be viewed by kubectl top, depending on monitoring components such as metric-server or promethus, which are not currently installed, and we view them by docker stats.
1. Define a pod with stress mirror, assign 0.25 cores and limit 0.5 cores usage ratio
[root@node-1 demo]# cat cpu-demo.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: cpu-demo
namespace: default
annotations:
kubernetes.io/description: "demo for cpu requests and"
spec:
containers:
- name: stress-cpu
image: vish/stress
resources:
requests:
cpu: 250m
limits:
cpu: 500m
args:
- -cpus
- "1"2. Applying yaml file to generate pod
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl apply -f cpu-demo.yaml pod/cpu-demo created
3. View pod resource allocation details
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl describe pods cpu-demo
Name: cpu-demo
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: node-2/10.254.100.102
Start Time: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 14:33:12 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Pod","metadata":{"annotations":{"kubernetes.io/description":"demo for cpu requests and"},"name":"cpu-demo","nam...
kubernetes.io/description: demo for cpu requests and
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.1.14
Containers:
stress-cpu:
Container ID: docker://14f93767ad37b92beb91e3792678f60c9987bbad3290ae8c29c35a2a80101836
Image: progrium/stress
Image ID: docker-pullable://progrium/stress@sha256:e34d56d60f5caae79333cee395aae93b74791d50e3841986420d23c2ee4697bf
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Args:
-cpus
1
State: Waiting
Reason: CrashLoopBackOff
Last State: Terminated
Reason: Error
Exit Code: 1
Started: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 14:34:28 +0800
Finished: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 14:34:28 +0800
Ready: False
Restart Count: 3
Limits: #cpu restricted usage ratio
cpu: 500m
Requests: #cpu request size
cpu: 250m4. Log on to a specific node and view the container's resource usage details through docker container stats

Viewed over top on the node to which the pod belongs, the cpu usage limit is 50%.
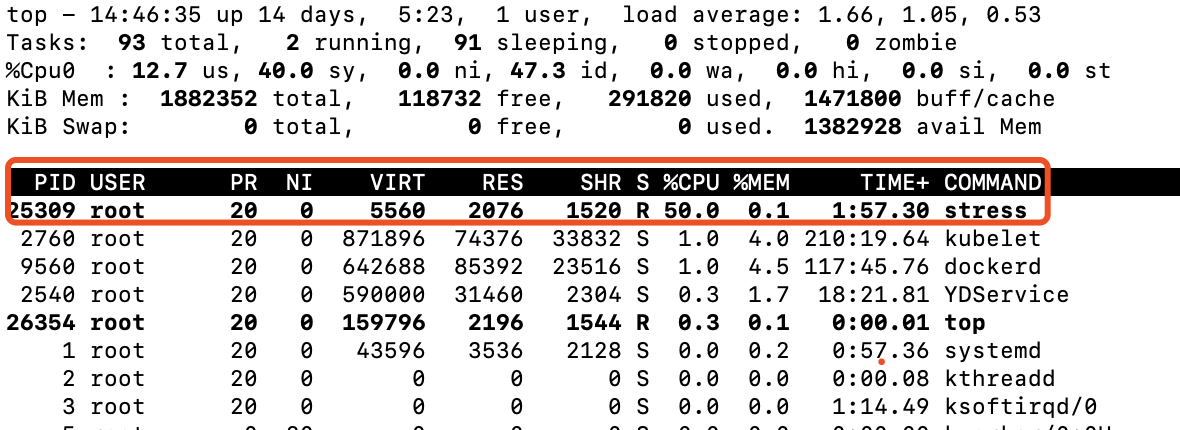
From the above validation, it can be concluded that we define a core in the stress container, limit the usable CPU size to 500m by limits.cpu, and test validation that the pod's resources are strictly limited to 50% inside the container or on the host machine (there is only one CPU on the node machine and 25% if there are two cpus).
1.4 memory Resource Test
1. Validate the validity of requests.memory and limits.memory by stress mirror test. limits.memory defines the size of memory resources available to the container. OOM occurs when the container exceeds the size set by memory. Define a test container with a maximum memory of 512M. Use stress mirror--vm-bytes to define a pressure side memory size of 256Mi
[root@node-1 demo]# cat memory-demo.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: memory-stress-demo
annotations:
kubernetes.io/description: "stress demo for memory limits"
spec:
containers:
- name: memory-stress-limits
image: polinux/stress
resources:
requests:
memory: 128Mi
limits:
memory: 512Mi
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--vm", "1", "--vm-bytes", "256M", "--vm-hang", "1"]2. Applying yaml file to generate pod
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl apply -f memory-demo.yaml pod/memory-stress-demo created [root@node-1 demo]# kubectl get pods memory-stress-demo -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES memory-stress-demo 1/1 Running 0 41s 10.244.1.19 node-2 <none> <none>
3. View the allocation of resources
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl describe pods memory-stress-demo
Name: memory-stress-demo
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: node-2/10.254.100.102
Start Time: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 15:13:06 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Pod","metadata":{"annotations":{"kubernetes.io/description":"stress demo for memory limits"},"name":"memory-str...
kubernetes.io/description: stress demo for memory limits
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.1.16
Containers:
memory-stress-limits:
Container ID: docker://c7408329cffab2f10dd860e50df87bd8671e65a0f8abb4dae96d059c0cb6bb2d
Image: polinux/stress
Image ID: docker-pullable://polinux/stress@sha256:6d1825288ddb6b3cec8d3ac8a488c8ec2449334512ecb938483fc2b25cbbdb9a
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Command:
stress
Args:
--vm
1
--vm-bytes
256Mi
--vm-hang
1
State: Waiting
Reason: CrashLoopBackOff
Last State: Terminated
Reason: Error
Exit Code: 1
Started: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 15:14:08 +0800
Finished: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 15:14:08 +0800
Ready: False
Restart Count: 3
Limits: #Memory Limit Size
memory: 512Mi
Requests: #Memory Request Size
memory: 128Mi
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-5qwmc (ro)4. Check the usage of container memory resources, allocate 256M memory, the maximum usage is 512Mi, and the utilization rate is 50%. At this time, the container is running normally without exceeding the limit size.

5. What happens when the internal size of the container exceeds the memory size? We will set the--vm-byte to 513M, the container will try to run, OOM will occur when the internal memory exceeds, kube-controller-manager will keep trying to restart the container, and the number of RESTARTS will keep increasing.
[root@node-1 demo]# cat memory-demo.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: memory-stress-demo
annotations:
kubernetes.io/description: "stress demo for memory limits"
spec:
containers:
- name: memory-stress-limits
image: polinux/stress
resources:
requests:
memory: 128Mi
limits:
memory: 512Mi
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--vm", "1", "--vm-bytes", "520M", "--vm-hang", "1"] . #520M memory in container
//View the state of the container as OOMKilled, RESTARTS keeps increasing, and keeps trying to restart
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl get pods memory-stress-demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
memory-stress-demo 0/1 OOMKilled 3 60s2. Pod quality of service
Quality of Service (QOS) is mainly used as an important factor for pod dispatch and expulsion. Different QOS have different quality of service and corresponding priority, which are mainly divided into three types of QOS:
- BestEffort does its best to allocate resources, does not specify the Qos assigned by resource by default, and has the lowest priority;
- Burstable volatile resources, at least those allocated to requests, common QOS;
- Guaranteed fully guarantees resources, with requests and limits defining the same resources with the highest priority.
2.1 BestEffort best efforts
1. There is no resource defined in the Pod. The default Qos policy is BestEffort with the lowest priority. When the resource comparison is progressing and evice s need to be expelled, the Pod defined by BestEffort should be expelled first. Define a BestEffort pod as follows
[root@node-1 demo]# cat nginx-qos-besteffort.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-qos-besteffort
labels:
name: nginx-qos-besteffort
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-qos-besteffort
image: nginx:1.7.9
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: nginx-port-80
protocol: TCP
containerPort: 80
resources: {}2. Create a pod and view the Qos policy, qosClass is BestEffort
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl apply -f nginx-qos-besteffort.yaml
pod/nginx-qos-besteffort created
//View Qos Policy
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl get pods nginx-qos-besteffort -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Pod","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"name":"nginx-qos-besteffort"},"name":"nginx-qos-besteffort","namespace":"default"},"spec":{"containers":[{"image":"nginx:1.7.9","imagePullPolicy":"IfNotPresent","name":"nginx-qos-besteffort","ports":[{"containerPort":80,"name":"nginx-port-80","protocol":"TCP"}],"resources":{}}]}}
creationTimestamp: "2019-09-28T11:12:03Z"
labels:
name: nginx-qos-besteffort
name: nginx-qos-besteffort
namespace: default
resourceVersion: "1802411"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/nginx-qos-besteffort
uid: 56e4a2d5-8645-485d-9362-fe76aad76e74
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.7.9
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: nginx-qos-besteffort
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: nginx-port-80
protocol: TCP
resources: {}
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
...ellipsis...
status:
hostIP: 10.254.100.102
phase: Running
podIP: 10.244.1.21
qosClass: BestEffort #Qos Policy
startTime: "2019-09-28T11:12:03Z"3. Delete Test Pod
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl delete pods nginx-qos-besteffort pod "nginx-qos-besteffort" deleted
2.2 Burstable can fluctuate
1. Pod's quality of service is Burstable, second only to Guaranteed's. At least one container needs to define requests, and requests define less resources than limits
[root@node-1 demo]# cat nginx-qos-burstable.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-qos-burstable
labels:
name: nginx-qos-burstable
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-qos-burstable
image: nginx:1.7.9
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: nginx-port-80
protocol: TCP
containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi2. Apply yaml file to generate pod and view Qos type
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl apply -f nginx-qos-burstable.yaml
pod/nginx-qos-burstable created
//View Qos Types
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl describe pods nginx-qos-burstable
Name: nginx-qos-burstable
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: node-2/10.254.100.102
Start Time: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 19:27:37 +0800
Labels: name=nginx-qos-burstable
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Pod","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"name":"nginx-qos-burstable"},"name":"nginx-qos-burstable","namespa...
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.1.22
Containers:
nginx-qos-burstable:
Container ID: docker://d1324b3953ba6e572bfc63244d4040fee047ed70138b5a4bad033899e818562f
Image: nginx:1.7.9
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:e3456c851a152494c3e4ff5fcc26f240206abac0c9d794affb40e0714846c451
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 19:27:39 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi
Requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-5qwmc (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-5qwmc:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-5qwmc
Optional: false
QoS Class: Burstable #Quality of service is volatile Burstable
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 95s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/nginx-qos-burstable to node-2
Normal Pulled 94s kubelet, node-2 Container image "nginx:1.7.9" already present on machine
Normal Created 94s kubelet, node-2 Created container nginx-qos-burstable
Normal Started 93s kubelet, node-2 Started container nginx-qos-burstable2.3 Guaranteed Full Guaranteed
1. The CPU and memory defined in resource must contain requests and limits. The value of requests and limits must be the same, with the highest priority. This type of Qos is guaranteed first when dispatch and expulsion occur. The following defines a container for nginx-qos-guaranteed, requests.cpu and limits.cpu are the same, requests.memory and limits are the same.
[root@node-1 demo]# cat nginx-qos-guaranteed.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-qos-guaranteed
labels:
name: nginx-qos-guaranteed
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-qos-guaranteed
image: nginx:1.7.9
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: nginx-port-80
protocol: TCP
containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi
limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi2. Guaranteed can be fully guaranteed by applying yaml file to generate pod and viewing the Qos type of pod
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl apply -f nginx-qos-guaranteed.yaml
pod/nginx-qos-guaranteed created
[root@node-1 demo]# kubectl describe pods nginx-qos-guaranteed
Name: nginx-qos-guaranteed
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: node-2/10.254.100.102
Start Time: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 19:37:15 +0800
Labels: name=nginx-qos-guaranteed
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Pod","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"name":"nginx-qos-guaranteed"},"name":"nginx-qos-guaranteed","names...
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.1.23
Containers:
nginx-qos-guaranteed:
Container ID: docker://cf533e0e331f49db4e9effb0fbb9249834721f8dba369d281c8047542b9f032c
Image: nginx:1.7.9
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:e3456c851a152494c3e4ff5fcc26f240206abac0c9d794affb40e0714846c451
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Sat, 28 Sep 2019 19:37:16 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi
Requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-5qwmc (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-5qwmc:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-5qwmc
Optional: false
QoS Class: Guaranteed #Quality of service is fully guaranteed for Guaranteed
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 25s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/nginx-qos-guaranteed to node-2
Normal Pulled 24s kubelet, node-2 Container image "nginx:1.7.9" already present on machine
Normal Created 24s kubelet, node-2 Created container nginx-qos-guaranteed
Normal Started 24s kubelet, node-2 Started container nginx-qos-guaranteedWrite at the end
This chapter is kubernetes series tutorials In the sixth article, by introducing resource resource allocation and quality of service Qos, node usage suggestions for resource are given:
- requests and limits resource definitions recommend no more than 1:2 to avoid resource contention and OOM due to excessive resource allocation.
- There is no resource defined by default in pod. It is recommended to define a limitrange for namespace to ensure that pod can allocate resources.
- To prevent the occurrence of machine hang or OOM due to excessive resources on the node, it is recommended to set up retention and expulsion of resources on the node, such as reservation of resources--system-reserved=cpu=200m,memory=1G, and expulsion condition--eviction hard=memory.available<500Mi.
appendix
Container computing resource management: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-compute-resources-container/
pod memory resource management: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/assign-memory-resource/
pod cpu resource management: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/assign-cpu-resource/
Quality of Service QOS: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/quality-service-pod/
Docker's CPU limitations: https://www.cnblogs.com/sparkdev/p/8052522.html
When your talent can't sustain your ambition, you should settle down to study