1. Docker-related content
2. Introduction to Kubernets
3. kuadm Installation k8s
1. Docker-related content
1. Docker Toolset
Docker Three Swordsmen: Compse, swarm, machine
docker compose: for single machine, container arrangement definition
docker swarm: integration of all Docker host resources, cluster management
docker machine: Initialize the Docker environment, cross-platform supportmesos+marathon
mesos: Framework for Host Resource Integrated Allocation Scheduling Management Tool
marathon: Mesos-based private PaaS
kubernets:
2,Compse
Docker_Compse: https://docs.docker.com/compose/overview/
Yaml format resource definition defined by Compose
version: '3'
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- "5000:5000"
volumes:
- .:/code
- logvolume01:/var/log
links:
- redis
redis:
image: redis
volumes:
logvolume01: {}3,CI,CD&CD
CI: Continuous Integration Continnuous Intergration //Dev Submit Code->Test->Pass [Merge Main Line to Code Warehouse]
CD: Continuous delivery of Continnuous Delivery //Publishing applications (grayscale) to minimize friction inherent in the team during deployment or publishing
CD: Continuous deployment of Continnuous Deployment // A higher degree of automation that builds/deploys automatically whenever code changes significantly
Figure 1 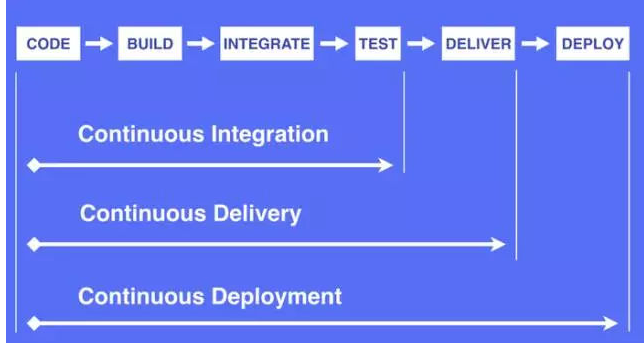
2. Introduction to Kubernets
kubernets provides a unified resource management and scheduling for the integration of multiple host resources
k8s is a copy of Google's internal Borg and CoreOS was acquired by RedHat
Official website introduction: https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/
1. k8s characteristics:
1) Automatic boxing, self-repair, horizontal expansion, service discovery and load balancing, automatic publishing and rollback
2) Key and Configuration Management
Previously, the configuration was modified based on a native file, preferably an environment variable-based modification //entrypoint script (user-passed environment variables are replaced in the configuration file)
Dynamically load configuration information at mirror startup//
If you want to modify a configuration//ansible push or if the configuration information for your application is saved on the configuration server, load it at startup (modifications only require modifying the configuration server)
3) Storage arrangement, task batch processing
2. Cluster model:
Has a central node //master+multiple slaves, k8s: three master(HA), the others are nodes
No central node//any shard can accept requests and route to other nodes
Controller: Monitor Container Status - > Controller Manager - > Controller Manager (Redundant HA)
Controller manager: Monitor the health of each controller, and the Controller manager redundancy itself
3. Components
- Master: Cluster control node, general recommendation 3HA
API Server: Gate for add-delete check in cluster
Scheduler: Schedule Pod
Controller-Manager: Automation control center for all resource objects (Chief Executive) - Node:(also known as Minion), the actual working node
kubelet: Responsible for Pod creation, startup, etc; and works closely with Master nodes to implement cluster management (register yourself with master, periodically report on yourself)
kube-proxy: Communication and Load Balancing Mechanism for Kubernets Service
docker:Docker engine - Pod: Pod is the shell of the container, encapsulation of the container, k8s minimum dispatch unit
A pod contains containers, and a pod can contain multiple containers.
pod Contentors share network namespaces//net, ups, IPC space uer, mnt, and pid are isolated
volume belongs to pod and no longer to the same container; all containers within a pod can only run on the same node
Generally, there is only one container in a pod. If you need more than one container in a pod, there is usually one main container and the other slave's
For Pod management, you can label a pod (in label,key/value format); label selector: Label selector -
Label:
Attributes added to various resource objects (can be added to Pod,Node,Service,RC, etc.)
Label Selector: Implements complex conditional selections, similar to where queries in sql
The kube-controller process monitors the number of copies of a Pod through the Label Selector defined by the Service
kube-proxy selects the corresponding Pod through the Service's label selector -
Replicatin Controller: An Expected Scene
Number of copies Pod expects
Label selector for Pod to filter targets
The ode template used to create a new Pod when the number of Pods is less than expected
Upgrade after kubernetes v1.2 Modified to Replica Sets (Next Generation RC) -
Deployment: Solve Pod Layout Problem
Internally implemented using Replication Set
Manage stateless Pod collections
Close to RC function -
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler:(HPA)
HPA: Automatically expands according to flow, load, etc. -
StatefulSet:
Pod's management objects: RC, Deploymnet, DaemonSet, Job are stateless.
Stateful service features:
1) Each node has a fixed identity ID, and members of the cluster need to discover and communicate with each other, such as MySQL, zk, etc.
2) Cluster size is fixed and cannot be changed at will
3) Each node is stateful and usually persists data to permanent storage
4) If the disk is damaged, one of the nodes of the cluster will not function properly and the cluster function will be damaged
Statefuleset is essentially the same as Deployment/RC, but has the following characteristics:
Each Pod in a StatefulSet has a stable and unique network identity to discover other members in the cluster; the StatefuleSet name for example POD 1 is (mq-0), the second is mq-1, and the third is mq-2
The starting and stopping order of containers in the StatefulSet is controlled, and the first n-1 Pod s were started at the nth operation
Each Pod in the StatefulSet uses a stable persistent storage volume, which is implemented through PV/PVC. Deleting a Pod does not delete StatefulSet-related storage volumes by default
Also used with Headless Service in the format: ${podname}.${headless service name} -
Service: A service, also known as a microservice
Front End Application->[label selector]--->{[Pod1 (label=bk1)], [Pod2 (label=bk1], [], []...}
kube-proxy, which receives requests from Service s and forwards them to back-end Pod instances for internal load balancing and session maintenance
k8s is enhanced on this basis: using Cluster IP to solve TCP network communication problems
kubectl get endpoints; get container exposed ports -
Job
Control a set of Pods to complete batch-like tasks, where each Docker runs only once, and when all copies of Pods controlled by Job are run, the corresponding Job is finished
k8s provides CronJob's ability to perform periodic, repetitive execution after 1.5 versions -
Persistent Volume:
Volume: Shared directory in Pod that can be accessed by multiple containers, supporting distributed file systems such as Ceph, ClusterFS
Persistent Volume (PV) &Persistent Volume Chain (PVC): Network storage and support read and write access isolation -
Namespace:
Implement multi-tenant resource isolation, default namespace is defaut
kubectl get namespaces -
Annotation:
Annotations are similar to Labels in that they are defined in key/value form; Labels have stricter naming rules, define objects as metadata, and Annotation is additional information that users can define at will -
configMap
Configuration information key/value, stored in the etcd database, then provides an API to facilitate k8s-related components or clients to apply CRUD to manipulate this data - Other related concepts
etcd: Stores Master data information, zookeeper class, requires HA
CNI(Conteinre Network Interface) is a container network standard developed by google and CoreoOS
Figure 4: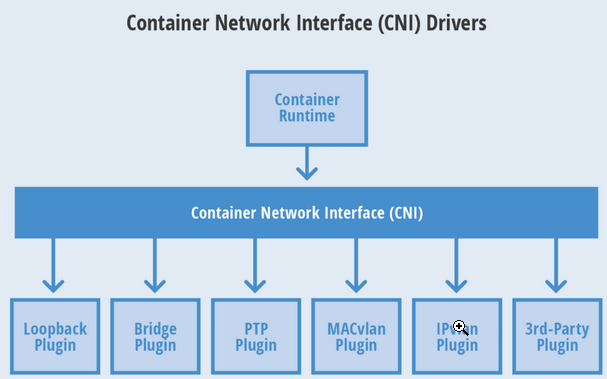
This protocol connects two components: a container management system and a network plug-in.They communicate with each other through files in JSON format to achieve the network functions of containers.Specific things are implemented by plug-ins, including creating a container network namespace, placing network interfaces in the corresponding network space, assigning IP to network interfaces, and so on.
flannel: supports network configuration, does not support network policy, simple
calico: network configuration, network strategy, more complex
canel:collection flannel and calico
Docker provides CNM standards.Currently CNM can only be used in docker, and CNI has a wider application range
Figure 6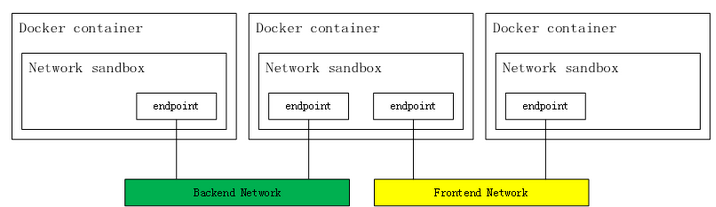
Interesting to learn about
* K8s Network 8
Pod Level
Multiple Pod internal containers see Communications:lo
Communication between Pod s: bridging, overlay network,
Service Level
Node Level
Figure 2 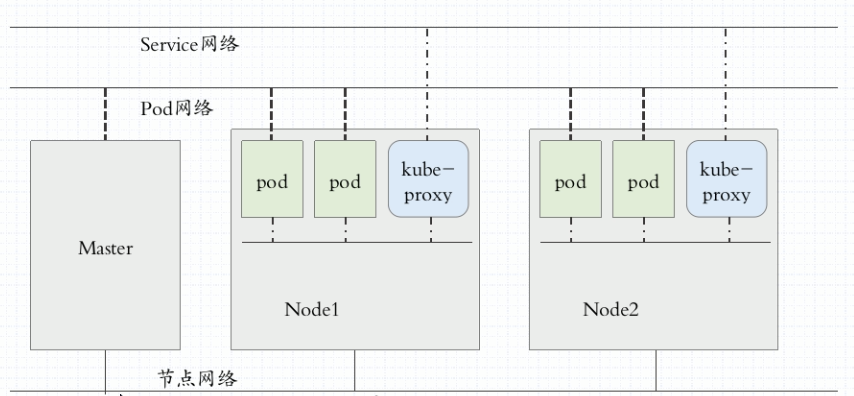
Other components: https://github.com/kubernetes/
3. kuadm Installation k8s
Figure 3: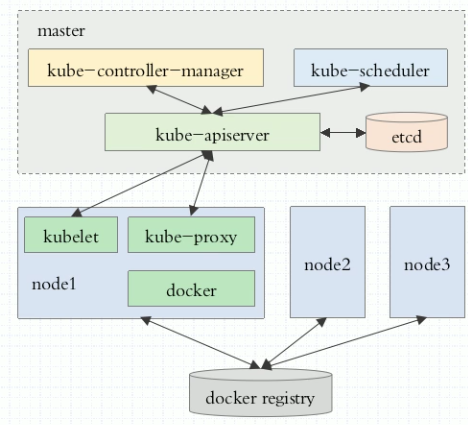
Installation Mode 1: Use process mode, accept systemctl control (more cumbersome)
Installation Mode 2: Using kubeadm mode, docker and kubelet are installed on all nodes, and the control node of k8s is also running as Pod
controller-manager,scheduler,apiserver,etcd
kube-proxy,kubelet,flannel all run as Pod
1. Experimental environment:
============================ Host ip Host Name Host Configuration 192.168.170.135 master (2c2g) 192.168.170.137 node1 (2c2g) 192.168.170.139 node2 (2c2g) ============================
2. Basic environment preparation (all nodes need to be installed)
1) hostname CTL set-hostname $hostname //Set hostname
2) Set up hosts
[root@master ~]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.170.135 matser 192.168.170.137 node1 192.168.170.139 node2
3) Turn off iptable and SELinux
systemctl stop fireward;systemctl disbale fireward setenforce 0;sed -i 's@SELINUX=.*@SELINUX=disabled@' /etc/selinux/config
4) Close swap
swapoff -a;sed -i 's/.*swap.*/#&/' /etc/fstab
5) Configure yum
kubernets source
[kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
Docker Source: wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
6) Installation Tools
yum install docker yum -y install kubelet kubeadm kubectl --disableexcludes=kubernetes systemctl enable docker //Noe1 and Noe2; Kubelet is responsible for communicating with other node clusters and managing the Pod and container life cycles of this node
3. Configure master
kubeadm config print init-defaults > /etc/kubernetes/init.default.yaml
cp init.default.yaml init-config.yaml and modify init-config.yaml
Example:
[root@master kubernetes]# cat init-config.yaml
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: ClusterConfiguration imageRepository: registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers kubernetesVersion: v1.14.0 networking: podSubnet: "192.168.3.0/24"
advertiseAddress:master machine ip
image-repository: mirror warehouse, recommended to be modified to registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
service-cidr: Service Discovery Address
pod-network-cidr:pod segment
Other parameters can be set by yourself
Download Mirror
[root@master kubernetes]# kubeadm config images pull --config=/etc/kubernetes/init-config.yaml
[config/images] Pulled registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-apiserver:v1.14.0
[config/images] Pulled registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-controller-manager:v1.14.0
[config/images] Pulled registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-scheduler:v1.14.0
[config/images] Pulled registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/kube-proxy:v1.14.0
[config/images] Pulled registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/pause:3.1
[config/images] Pulled registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/etcd:3.3.10
[config/images] Pulled registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/coredns:1.3.1
[root@master kubernetes]# kubeadm init --config=init-config.yaml
[root@master kubernetes]# kubeadm init --config=init-config.yaml
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.14.0
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING IsDockerSystemdCheck]: detected "cgroupfs" as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is "systemd". Please follow the guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/cri/
[WARNING Hostname]: hostname "i" could not be reached
[WARNING Hostname]: hostname "i": lookup i on 192.168.170.2:53: server misbehaving
error execution phase preflight: [preflight] Some fatal errors occurred:
[ERROR DirAvailable--var-lib-etcd]: /var/lib/etcd is not empty
[preflight] If you know what you are doing, you can make a check non-fatal with `--ignore-preflight-errors=...`
[root@master kubernetes]# rm -rf /var/lib/etcd/
[root@master kubernetes]# kubeadm init --config=init-config.yaml
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.14.0
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING IsDockerSystemdCheck]: detected "cgroupfs" as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is "systemd". Please follow the guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/cri/
[WARNING Hostname]: hostname "i" could not be reached
[WARNING Hostname]: hostname "i": lookup i on 192.168.170.2:53: server misbehaving
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Activating the kubelet service
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [i localhost] and IPs [192.168.170.135 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [i localhost] and IPs [192.168.170.135 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [i kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 192.168.170.135]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s
[apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 29.511659 seconds
[upload-config] storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.14" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --experimental-upload-certs
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node i as control-plane by adding the label "node-role.kubernetes.io/master=''"
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node i as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: ls1ey1.uf8m218idns3bjs8
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 192.168.170.135:6443 --token ls1ey1.uf8m218idns3bjs8 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:ef81ea9df5425aeb92ac34c08bb8a8646f82f50445cccdb6eff1e6c84aa00101 4. Configure node
[root@node1 kubernetes]# kubeadm config print init-defaults &> ./init.default.yaml
[root@node1 kubernetes]# cp init.default.yaml init-config.yaml
[root@node1 kubernetes]# cat init-config.yaml //modified configuration
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: JoinConfiguration
discovery:
bootstrapToken:
apiServerEndpoint: 192.168.170.135:6443
token: ls1ey1.uf8m218idns3bjs8
unsafeSkipCAVerification: true
tlsBootstrapToken: ls1ey1.uf8m218idns3bjs8
[root@node1 kubernetes]# kubeadm join --config=init-config.yaml
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING IsDockerSystemdCheck]: detected "cgroupfs" as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is "systemd". Please follow the guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/cri/
[preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster...
[preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -oyaml'
[kubelet-start] Downloading configuration for the kubelet from the "kubelet-config-1.14" ConfigMap in the kube-system namespace
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Activating the kubelet service
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap...
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.Do the same on node1 and node2, respectively
5. Install Network Plugins
[root@master kubernetes]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
i NotReady master 13m v1.14.3
node1 NotReady <none> 4m46s v1.14.3
node2 NotReady <none> 74s v1.14.3
[root@master kubernetes]# kubectl get cs
NAME STATUS MESSAGE ERROR
scheduler Healthy ok
controller-manager Healthy ok
etcd-0 Healthy {"health":"true"}
[root@master kubernetes]# kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version |base64 |tr -d '\n')"
serviceaccount/weave-net created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/weave-net created
daemonset.extensions/weave-net created
[root@master kubernetes]# kubectl get nodes --all-namespaces
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
i Ready master 24m v1.14.3
node1 Ready <none> 15m v1.14.3
node2 Ready <none> 11m v1.14.3
[root@master kubernetes]# kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-8686dcc4fd-cvd7k 1/1 Running 0 24m
kube-system coredns-8686dcc4fd-ntb22 1/1 Running 0 24m
kube-system etcd-i 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-system kube-apiserver-i 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-system kube-controller-manager-i 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-system kube-proxy-fvd2t 1/1 Running 0 15m
kube-system kube-proxy-jcfvp 1/1 Running 0 24m
kube-system kube-proxy-jr6lj 1/1 Running 0 12m
kube-system kube-scheduler-i 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-system weave-net-bjmt2 2/2 Running 0 104s
kube-system weave-net-kwg5l 2/2 Running 0 104s
kube-system weave-net-v54m4 2/2 Running 0 104s
[root@master kubernetes]# kubectl --namespace=kube-system describe pod etcd-i //If a pod status problem is found, check the cause of the error
kubeadmin reset Acts on the host to restore to its original state and then re-execute kubeadm init Install againContainer distribution:
master:pause 8, apiserver, controller, scheduler, kube-proxy, etcd, weave-npc, weave-kube, coredns
node1 and node2:kube-proxy, kube-proxy(pause), weave-npc, weave-kube, weave-kube(pause)
6. Install dashboard
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v1.10.1/src/deploy/recommended/kubernetes-dashboard.yaml [root@master kubernetes]# sed -i 's/k8s.gcr.io/loveone/g' kubernetes-dashboard.yaml [root@master kubernetes]# sed -i "160a \ \ \ \ \ \ nodePort: 30001" kubernetes-dashboard.yaml [root@master kubernetes]# sed -i "161a \ \ type:\ NodePort" kubernetes-dashboard.yaml [root@master kubernetes]# kubectl create -f kubernetes-dashboard.yaml [root@master kubernetes]# kubectl get deployment kubernetes-dashboard -n kube-system [root@master kubernetes]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system -o wide [root@master kubernetes]# kubectl get services -n kube-system [root@master kubernetes]# netstat -ntlp|grep 30001
Get a token: Log on using a token
[root@master kubernetes]# kubectl describe secrets -n kube-system $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | awk '/dashboard-admin/{print $1}')Figure 5
7. Create Container Tests
[root@master kubernetes]# kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx [root@master kubernetes]# kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=NodePort [root@master kubernetes]# kubectl get pod,svc [root@master kubernetes]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-65f88748fd-9tgtv 1/1 Running 0 4m19s
**Question 1:***
[root@master kubernetes]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE centos latest 49f7960eb7e4 12 months ago 200MB swarm latest ff454b4a0e84 12 months ago 12.7MB [root@master kubernetes]# docker rmi -f ff454b4a0e84 Error: No such image: ff454b4a0e84
Solution:
systemctl stop docker;rm -rf /var/lib/docker;systemctl start docker
Reference link:
Kubernets Chinese Community: https://www.kubernetes.org.cn/doc-16
Kubernets website: https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/
Kubernets Git: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes
kuadm installation k8s: https://www.kubernetes.org.cn/5462.html
kubernetes download link: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/releases