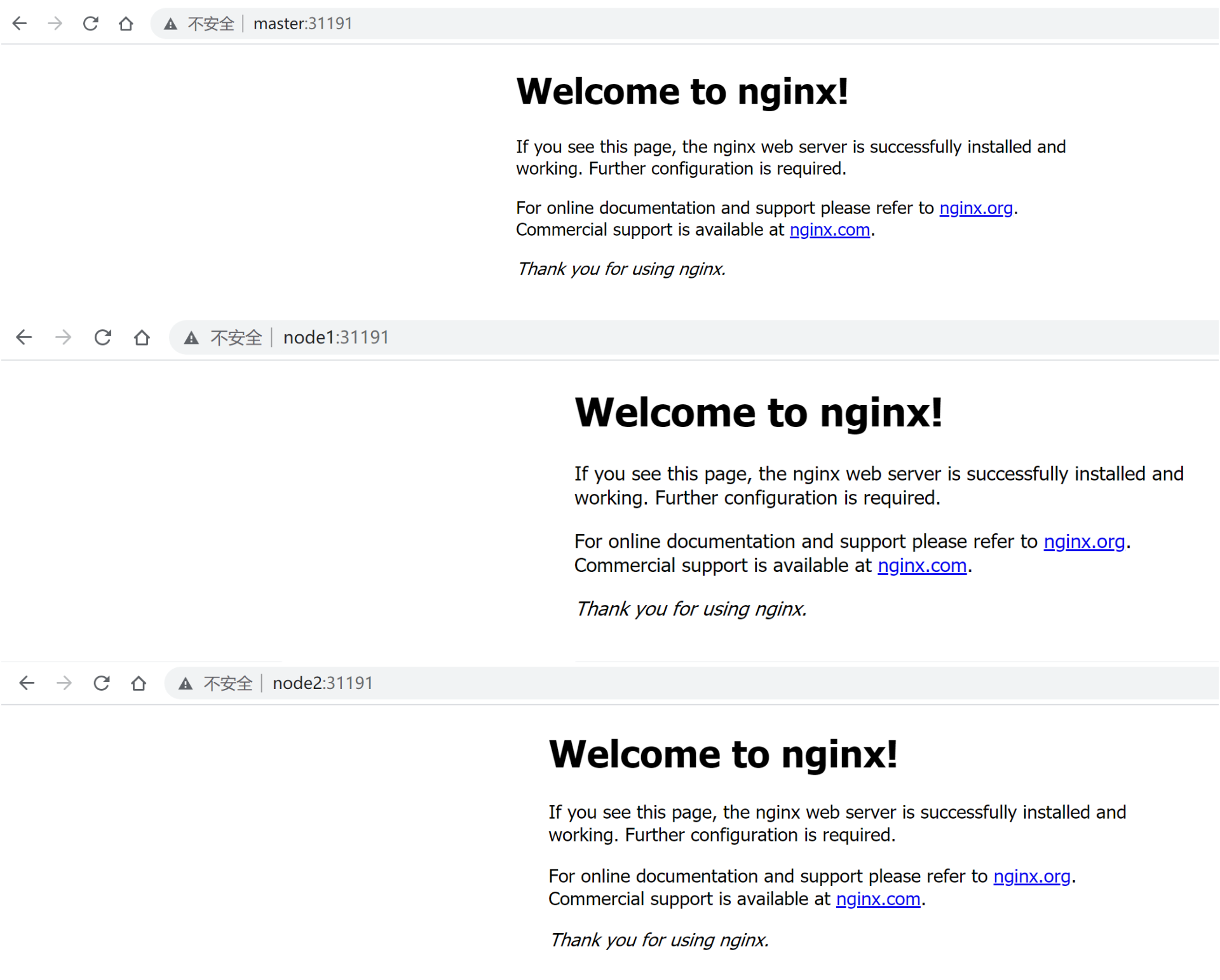
kubeadm is a tool launched by the official community for rapid deployment of kubernetes clusters. This tool can complete the deployment of a kubernetes cluster through two instructions:
- Create a Master node kubedm init
- Join the Node to the current cluster $kubedm join < IP and port of the master Node >
Installation requirements
Before you start, you need to meet the following conditions to deploy Kubernetes cluster machines:
- One or more machines, operating system CentOS7.x-86_x64
- Hardware configuration: 2GB or more RAM, 2 CPUs or more CPUs, hard disk 30GB or more
- Network interworking between all machines in the cluster
- You can access the Internet. You need to pull the image
- Disable swap partition
ultimate objective
- Install Docker and kubedm on all nodes
- Deploy Kubernetes Master
- Deploy container network plug-in
- Deploy the Kubernetes Node and add the node to the Kubernetes cluster
- Deploy the Dashboard Web page to visually view Kubernetes resources
Prepare environment
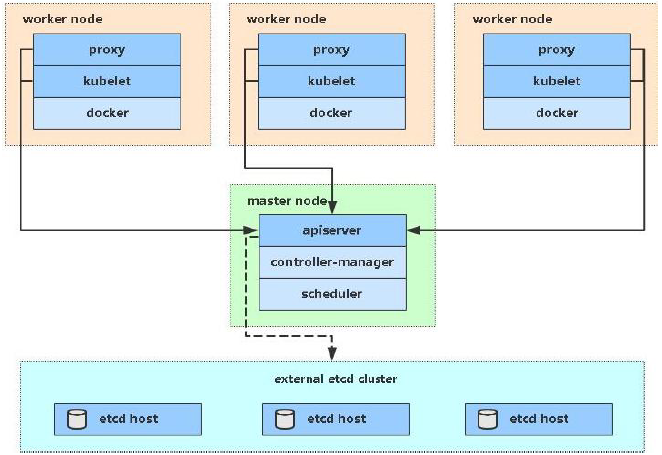
| role | IP address | assembly |
|---|---|---|
| master01 | 192.168.5.3 | docker,kubectl,kubeadm,kubelet |
| node01 | 192.168.5.4 | docker,kubectl,kubeadm,kubelet |
| node02 | 192.168.5.5 | docker,kubectl,kubeadm,kubelet |
Environment initialization
Check the version of the operating system
# Installing kubernetes clusters in this mode requires Centos version 7.5 or above [root@master ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release Centos Linux 7.5.1804 (Core)
#####Host name resolution
In order to facilitate direct calls between cluster nodes, host name resolution is configured in this configuration. Internal DNS servers are recommended in enterprises
# Edit the / etc/hosts file of the three servers by parsing the host name, and add the following content 192.168.90.100 master 192.168.90.106 node1 192.168.90.107 node2
time synchronization
kubernetes requires that the node time in the cluster must be accurate all the time. Here, the chronyd service is used to synchronize the time from the network
It is recommended to configure an internal synchronization server in an enterprise
# Start the chronyd service [root@master ~]# systemctl start chronyd [root@master ~]# systemctl enable chronyd [root@master ~]# date
Disable iptable and firewalld services
kubernetes and docker will generate a large number of iptables rules during operation. In order not to confuse the system rules with them, close the system rules directly
# 1 turn off firewalld service [root@master ~]# systemctl stop firewalld [root@master ~]# systemctl disable firewalld # 2 close iptables service [root@master ~]# systemctl stop iptables [root@master ~]# systemctl disable iptables
Disable selinux
selinux is a security service under linux system. If it is not shut down, all kinds of wonderful problems will occur in the installation cluster
# Edit the / etc/selinux/config file and change the value of SELINUX to disable # Note that the linux service needs to be restarted after modification SELINUX=disabled
Disable swap partition
The swap partition value refers to the virtual memory partition. Its function is to use the virtual disk space as memory after the physical memory is used up. Enabling the sqap device will have a very negative impact on the system performance. Therefore, kubernetes requires that each node disable the swap device, but if the swap partition cannot be closed for some reasons, You need to specify the configuration through explicit parameters during cluster installation
# Edit the partition configuration file / etc/fstab and comment out the swap partition line # Note that the linux service needs to be restarted after modification vim /etc/fstab Comment out /dev/mapper/centos-swap swap # /dev/mapper/centos-swap swap
Modify linux kernel parameters
# Modify the number of linux kernel adoption, and add bridge filtering and address forwarding functions # Edit the / etc/sysctl.d/kubernetes.conf file and add the following configuration: net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 # Reload configuration [root@master ~]# sysctl -p # Load bridge filter module [root@master ~]# modprobe br_netfilter # Check whether the bridge filter module is loaded successfully [root@master ~]# lsmod | grep br_netfilter
Configure ipvs function
In Kubernetes, there are two Service delivery models, one based on iptables and the other based on ipvs. Compared with the two models, the performance of ipvs is obviously higher, but if you want to use it, you need to manually load the ipvs module
# 1. Install ipset and ipvsadm [root@master ~]# yum install ipset ipvsadmin -y # 2. Add the module to be loaded and write the script file [root@master ~]# cat <<EOF> /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules #!/bin/bash modprobe -- ip_vs modprobe -- ip_vs_rr modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr modprobe -- ip_vs_sh modprobe -- nf_conntrack_ipv4 EOF # 3. Add execution permission for script [root@master ~]# chmod +x /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules # 4. Execute script file [root@master ~]# /bin/bash /etc/sysconfig/modeules/ipvs.modules # 5. Check whether the corresponding module is loaded successfully [root@master ~]# lsmod | grep -e -ip_vs -e nf_conntrack_ipv4
Install docker
# 1. Switch mirror source
[root@master ~]# wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d.docker-ce.repo
# 2. View the supported docker versions in the current image source
[root@master ~]# yum list docker-ce --showduplicates
# 3. Install a specific version of docker CE
# You must specify -- setopt=obsoletes=0, otherwise yum will automatically install a later version
[root@master ~]# yum install --setopt=obsoletes=0 docker-ce-18.06.3.ce-3.e17 -y
# 4. Add a profile
#Docker uses Vgroup Driver as cgroups by default, while Kubernetes recommends using systemd instead of cgroups
[root@master ~]# mkdir /etc/docker
[root@master ~]# cat <<EOF> /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
"registry-mirrors": ["https://kn0t2bca.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
# 5. Start dokcer
[root@master ~]# systemctl restart docker
[root@master ~]# systemctl enable docker
Installing Kubernetes components
# 1. Since the image of kubernetes is abroad and the speed is relatively slow, switch to the domestic image source here # 2. Edit / etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo to add the following configuration [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=http://mirror.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64 enabled=1 gpgchech=0 repo_gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg # 3. Install kubedm, kubelet, and kubectl [root@master ~]# yum install --setopt=obsoletes=0 kubeadm-1.17.4-0 kubelet-1.17.4-0 kubectl-1.17.4-0 -y # 4. Configure cgroup of kubelet #Edit / etc/sysconfig/kubelet to add the following configuration KUBELET_CGROUP_ARGS="--cgroup-driver=systemd" KUBE_PROXY_MODE="ipvs" # 5. Set kubelet to start automatically [root@master ~]# systemctl enable kubelet
Prepare cluster image
# Before installing kubernetes cluster, you must prepare the image required by the cluster in advance. The required image can be viewed through the following command
[root@master ~]# kubeadm config images list
# Download Image
# This image cannot be connected in the warehouse of kubernetes due to network reasons. An alternative scheme is provided below
images=(
kube-apiserver:v1.17.4
kube-controller-manager:v1.17.4
kube-scheduler:v1.17.4
kube-proxy:v1.17.4
pause:3.1
etcd:3.4.3-0
coredns:1.6.5
)
for imageName in ${images[@]};do
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/$imageName
docker tag registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/$imageName k8s.gcr.io/$imageName
docker rmi registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/$imageName
done
Cluster initialization
The following operations only need to be performed on the master node
# Create cluster [root@master ~]# kubeadm init --apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.90.100 --image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers --kubernetes-version v1.17.4 --service-cidr=10.96.0.0/12 --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 # Create necessary files [root@master ~]# mkdir -p $HOME/.kube [root@master ~]# sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config [root@master ~]# sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
The following operations only need to be performed on the node node
kubeadm join 192.168.0.100:6443 --token awk15p.t6bamck54w69u4s8 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:a94fa09562466d32d29523ab6cff122186f1127599fa4dcd5fa0152694f17117
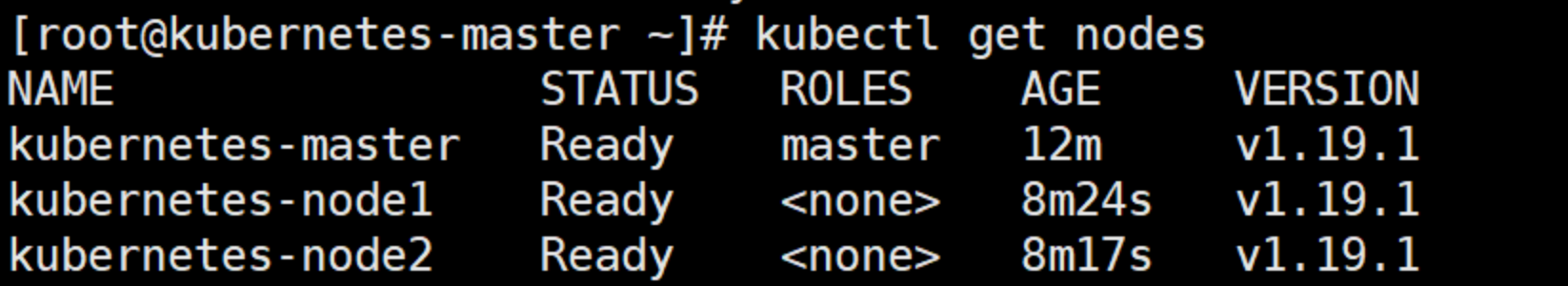
View node information on the master
[root@master ~]# kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION master NotReady master 6m v1.17.4 node1 NotReady <none> 22s v1.17.4 node2 NotReady <none> 19s v1.17.4
Install the network plug-in. Only operate on the master node
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
Because it is difficult to access the Internet, if you cannot access it, you can directly use the following file name: kube-flannel.yml, location: / root/kube-flannel.yml, content:
https://github.com/flannel-io/flannel/tree/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
Resetting the cluster using kubedm reset
#Operate on nodes other than the master node kubeadm reset systemctl stop kubelet systemctl stop docker rm -rf /var/lib/cni/ rm -rf /var/lib/kubelet/* rm -rf /etc/cni/ ifconfig cni0 down ifconfig flannel.1 down ifconfig docker0 down ip link delete cni0 ip link delete flannel.1 ##Restart kubelet systemctl restart kubelet ##Restart docker systemctl restart docker
Restart kubelet and docker
# Restart kubelet systemctl restart kubelet # Restart docker systemctl restart docker
Start the fan using the configuration file
kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
Wait until it is installed. It is found that the status of the cluster is Ready
Commands in kubedm
# Generate a new token [root@master ~]# kubeadm token create --print-join-command
Cluster test
Create an nginx service
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx:1.14-alpine
Exposed port
kubectl expose deploy nginx --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=NodePort
View services
kubectl get pod,svc
View pod
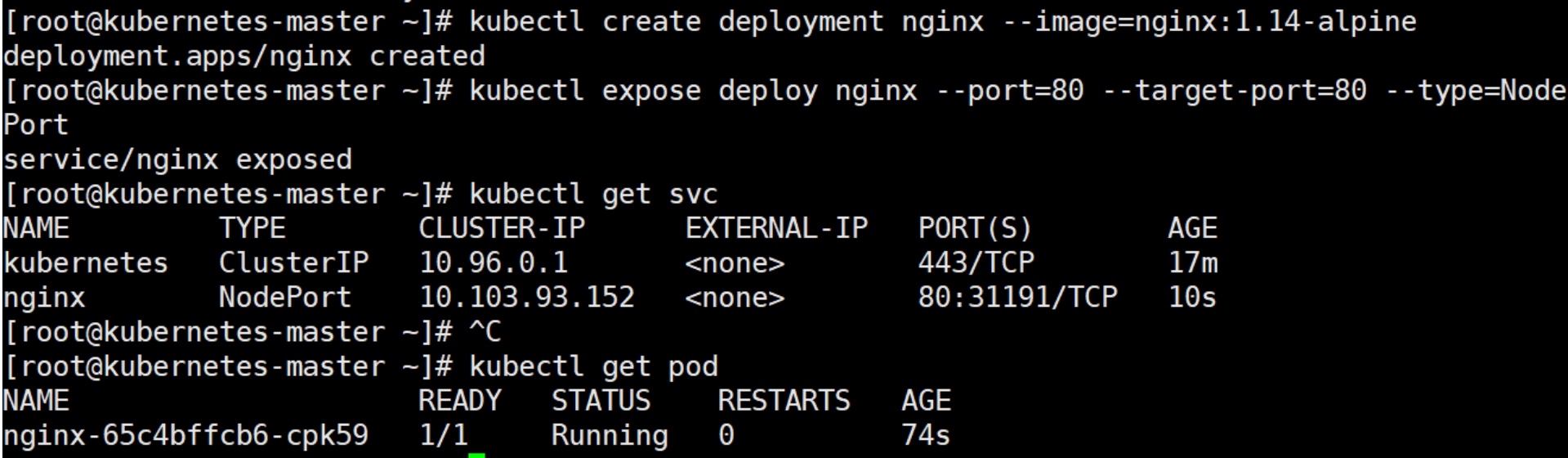
Browser test results: