secret is used to store sensitive information, such as passwords or tokens.
Create with file
[kubeadm@server1 secret]$ echo -n "admin" > username.txt ##Create user information [kubeadm@server1 secret]$ echo -n "aekhg777" > password.txt ##Create user password file [kubeadm@server1 secret]$ kubectl create secret generic db-user-pass --from-file=./username.txt --from-file=./password.txt ##The nature of creating a secret is to create a generic name, followed by a user name password file secret/db-user-pass created [kubeadm@server1 secret]$ kubectl get secrets NAME TYPE DATA AGE db-user-pass Opaque 2 6s default-token-6qxhd kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 8d [kubeadm@server1 secret]$ kubectl describe secrets db-user-pass Name: db-user-pass Namespace: default Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Type: Opaque Data ==== password.txt: 8 bytes username.txt: 5 bytes
Or directly use the command to create, the difference is that the parameter changes from -- from file to -- from literal = username / passwd = username / password
kubectl create secret generic db-user-pass --from-literal=username=admin --from-literal=password=aekhg777
The results of the two methods are the same, and the password can be seen directly
[kubeadm@server1 secret]$ kubectl get secrets db-user-pass -o yaml apiVersion: v1 data: password.txt: YWVraGc3Nzc= username.txt: YWRtaW4= kind: Secret metadata: creationTimestamp: "2020-02-24T13:06:05Z" name: db-user-pass namespace: default resourceVersion: "611210" selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/default/secrets/db-user-pass uid: d0743c70-6697-4b16-b149-b338ea4954c7 type: Opaque
The user name and password are displayed above, but we will find that they are not the same as our original settings, because this one uses encryption, and if you want to see the password directly, you need to decode it.
[kubeadm@server1 secret]$ echo YWVraGc3Nzc= | base64 -d ##Use 64 bit decoding to get the original data aekhg777
But if there are special characters in the password, you need to use \ (backslash) for translation.
How to use yaml file to create secret.
First, we use base64 to encrypt the user name and password. The encrypted user name and password are then written to the file.
[kubeadm@server1 secret]$ echo admin | base64 YWRtaW4K [kubeadm@server1 secret]$ echo aekhg777 | base64 YWVraGc3NzcK [kubeadm@server1 secret]$ vim mysecret.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: mysecret type: Opaque data: password: YWVraGc3NzcK username: YWRtaW4K
Then use the command to create the secret.
Using secret
Using secret requires a hook,
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mysecret
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: secrets
mountPath: "/secret"
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: secrets
secret:
secretName: mysecret
First, create a pod to view the attached files in the pod.
[kubeadm@server1 secret]$ kubectl exec mysecret ls /secret password username
The internal file is your user name and password. The content in the file is the content of the previous secret file.
At the same time, we can specify the directory of the attached volume,
The content of the previous yaml file remains unchanged. Add the specified directory at the last volume
volumes:
- name: secrets
secret:
secretName: mysecret
items:
- key: username
path: my-group/my-username
The bottom path is created not directly in the current directory, but in the / secret (view the previous yaml file) directory.
[kubeadm@server1 secret]$ kubectl exec mysecret2 cat /secret/my-group/my-username admin
Setting environment variables for secret
Create another pod directly
env:
- name: SECRET_USERNAME
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysecret
key: username
- name: SECRET_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysecret
key: password
[kubeadm@server1 secret]$ kubectl exec mysecret2 env
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
HOSTNAME=mysecret2
SECRET_USERNAME=admin
##You can see it directly here
SECRET_PASSWORD=aekhg777
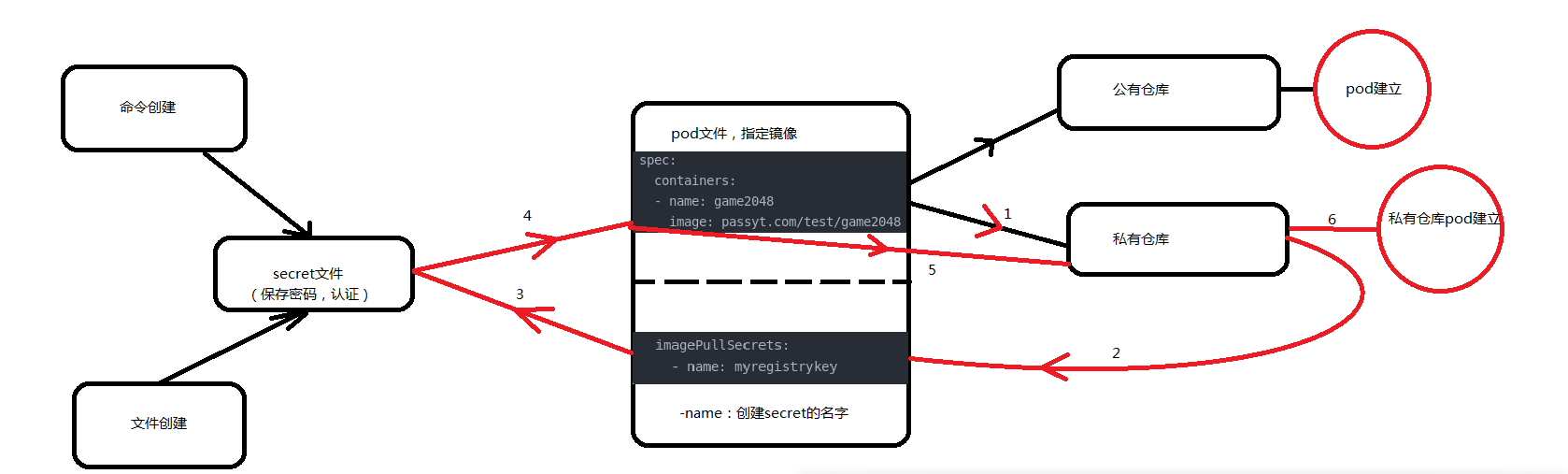
Pull the image of private warehouse
kubectl create secret docker-registry myregistrykey --docker-server=passyt.com --docker-username=admin --docker-password=aekhg777 --docker-email=passyt@passyt.com ##Create a secret named myregistrykey
Docker registry is the authentication setting of the warehouse.
After creating secret, write a yaml file and create a pod
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
containers:
- name: game2048
image: passyt.com/test/game2048
imagePullSecrets: ##This thing is required for authentication information
- name: myregistrykey ##The name of the authentication information is myregistrykey
To create a pod by using the image in the private warehouse, the first operation is to log in to the warehouse, and pull the image after the login is completed. Then our order is to create a secret to store the user's user name and password, and then call the content in the secret when creating the pod, and pull the image successfully.