Environmental description:
| host name | Operating system version | ip | docker version | kubelet version | To configure | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| master | Centos 7.6.1810 | 172.27.9.131 | Docker 18.09.6 | V1.14.2 | 2C2G | master host |
| node01 | Centos 7.6.1810 | 172.27.9.135 | Docker 18.09.6 | V1.14.2 | 2C2G | Node node |
| node02 | Centos 7.6.1810 | 172.27.9.136 | Docker 18.09.6 | V1.14.2 | 2C2G | Node node |
For k8s cluster deployment, please refer to: CentOS 7.6 deploy k8s(v1.14.2) cluster
k8s learning materials are detailed in: Basic concepts, kubectl commands and data sharing
I. k8s core components
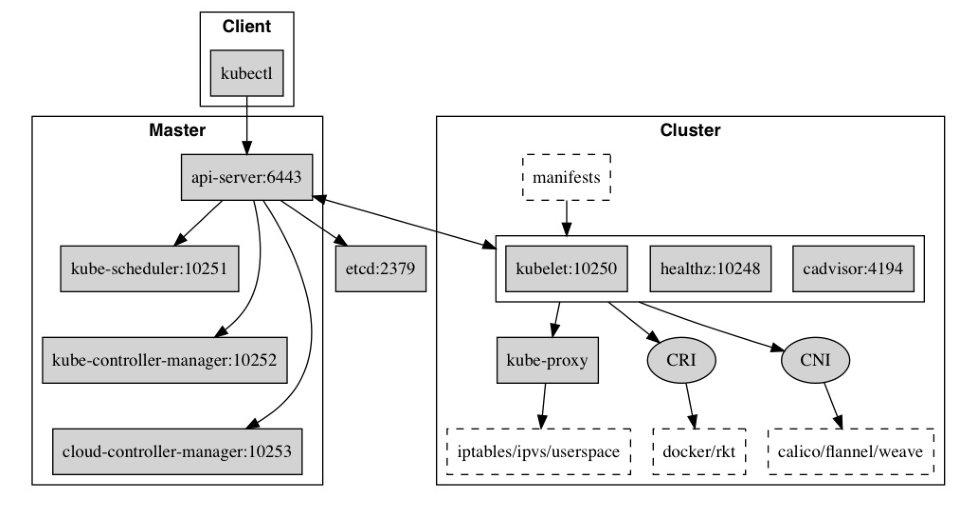
Kubernetes is mainly composed of the following core components:
- etcd keeps the state of the whole cluster;
- apiserver provides the only access to resource operation, and provides authentication, authorization, access control, API registration and discovery mechanisms;
- controller manager is responsible for maintaining the status of the cluster, such as fault detection, automatic extension, rolling update, etc;
- The scheduler is responsible for the scheduling of resources, and the Pod is scheduled to the corresponding machine according to the scheduled scheduling strategy;
- kubelet is responsible for maintaining the life cycle of the container, as well as Volume (CVI) and network (CNI) management;
- Container runtime is responsible for image management and real operation (CRI) of Pod and container;
- Kube proxy is responsible for providing Service discovery and load balancing within the cluster
II. Introduction to kubectl
kubectl is the command-line tool (CLI) of Kubernetes, which is a necessary management for users and administrators of Kubernetes
Tools. The kubectl tool controls the Kubernetes cluster manager. It allows you to check cluster resources, create, delete, and update groups
And more. kubectl provides a large number of subcommands to facilitate the management of various functions in the Kubernetes cluster.
1.kubectl usage
- kubectl -h view the list of subcommands
- kubectl options view global options
- Kubectl < command > -- help view help for subcommands
- Kubectl [command] [params] - o = < Format > set the output format (such as json, yaml, jsonpath, etc.)
- kubectl explain [RESOURCE] view resource definition
2.kubectl plug-in krew
krew is a tool for managing kubectl plug-ins, similar to apt or yum. It supports searching, installing and managing kubectl plug-ins.
III. krew installation
1.git installation
[root@master ~]# yum -y install git
2. install krew
set -x; cd "$(mktemp -d)" &&
curl -fsSLO "https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/krew/releases/download/v0.3.2/krew.{tar.gz,yaml}" &&
tar zxvf krew.tar.gz &&
./krew-"$(uname | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]')_amd64" install \
--manifest=krew.yaml --archive=krew.tar.gz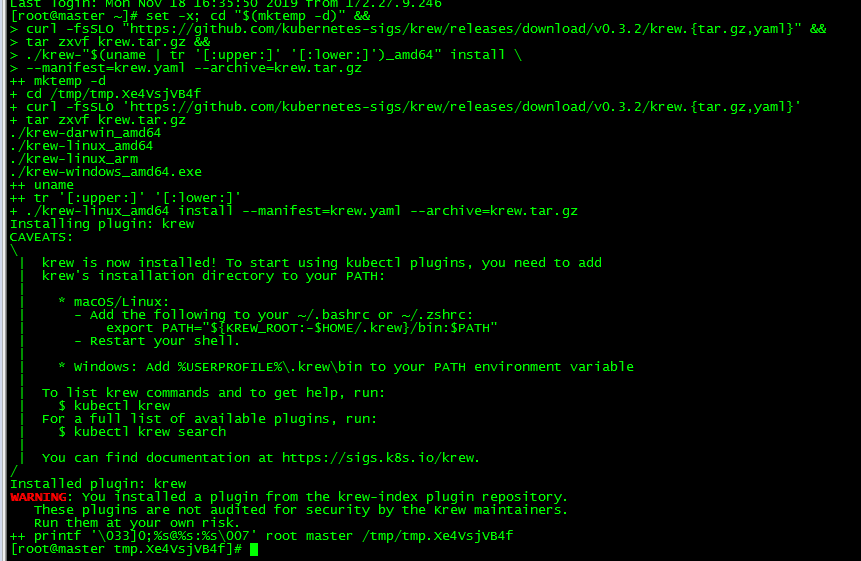
The media could not be downloaded due to network reasons. The github has been uploaded: https://github.com/loong576/krew-for-kubectl.git
3. Load environment variables
[root@master ~]# export PATH="${KREW_ROOT:-$HOME/.krew}/bin:$PATH"The environment variable files of users can be written permanently to avoid invalidation after logging out.
4. Installation confirmation
[root@master ~]# kubectl plugin list The following compatible plugins are available: /root/.krew/bin/kubectl-krew
installation is complete
IV. use of krew
1. Plug in index update
[root@master ~]# kubectl krew update Updated the local copy of plugin index.
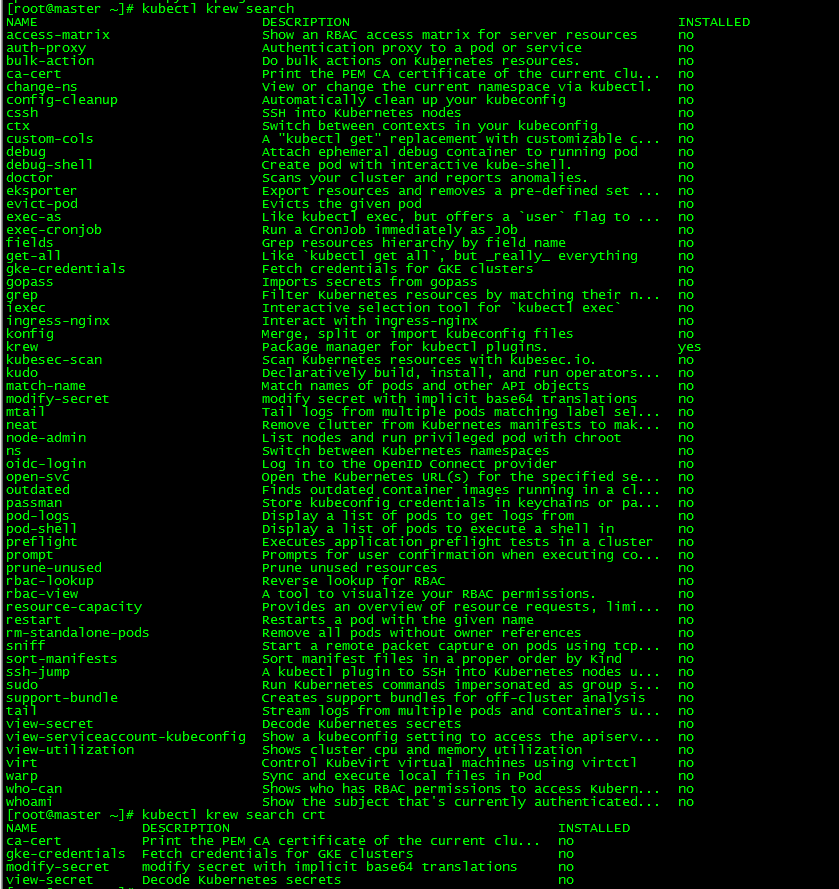
2. Plug in search
[root@master ~]# kubectl krew search [root@master ~]# kubectl krew search crt
Search all plugins and fuzzy search
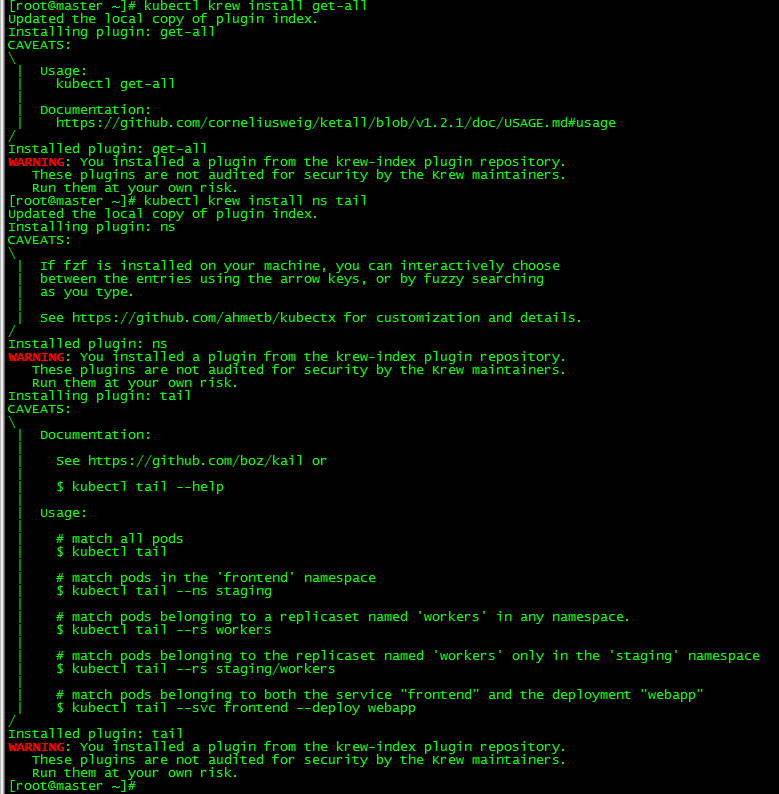
3. Install the plug-in
[root@master ~]# kubectl krew install get-all [root@master ~]# kubectl krew install ns tail
4. View the installed plug-ins
[root@master ~]# kubectl krew list PLUGIN VERSION get-all v1.2.1 krew v0.3.2 ns v0.7.1 tail v0.10.1
5. View plug-in details
[root@master ~]# kubectl krew info ns NAME: ns URI: https://github.com/ahmetb/kubectx/archive/v0.7.1.tar.gz SHA256: 6df4def2caf5a9c291310124098ad6c4c3123936ddd4080b382b9f7930a233ec VERSION: v0.7.1 HOMEPAGE: https://github.com/ahmetb/kubectx DESCRIPTION: Also known as "kubens", a utility to set your current namespace and switch between them. CAVEATS: \ | If fzf is installed on your machine, you can interactively choose | between the entries using the arrow keys, or by fuzzy searching | as you type. | | See https://github.com/ahmetb/kubectx for customization and details. /
6. Plug in update
[root@master ~]# kubectl krew upgrade ns Updated the local copy of plugin index. F1118 17:21:47.271927 81116 root.go:58] failed to upgrade plugin "ns": can't upgrade, the newest version is already installed
Update plug-ins ns. Because it is the latest version, the update fails. You can update all plug-ins with the command 'kubectl krew upgrade'
7. Use plug-ins -- ns
[root@master ~]# kubectl kubectl kubectl-get_all kubectl-krew kubectl-ns kubectl-tail [root@master ~]# kubectl ns weave [root@master ~]# kubectl-ns default
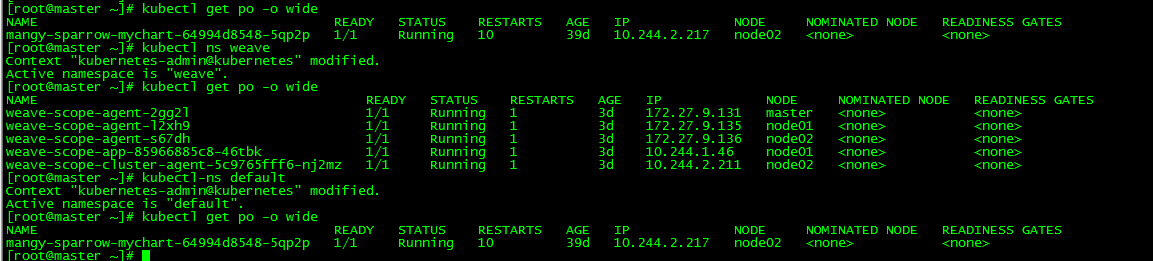
After the plug-in is installed, you can use the plug-in through the command kubectl < plugin name > or kubectl - < plugin name >, for example, 'kubectl ns weave' and 'kubectl ns default' can switch the default tablespace
8. Use plug-in get all
[root@master ~]# kubectl-get_all
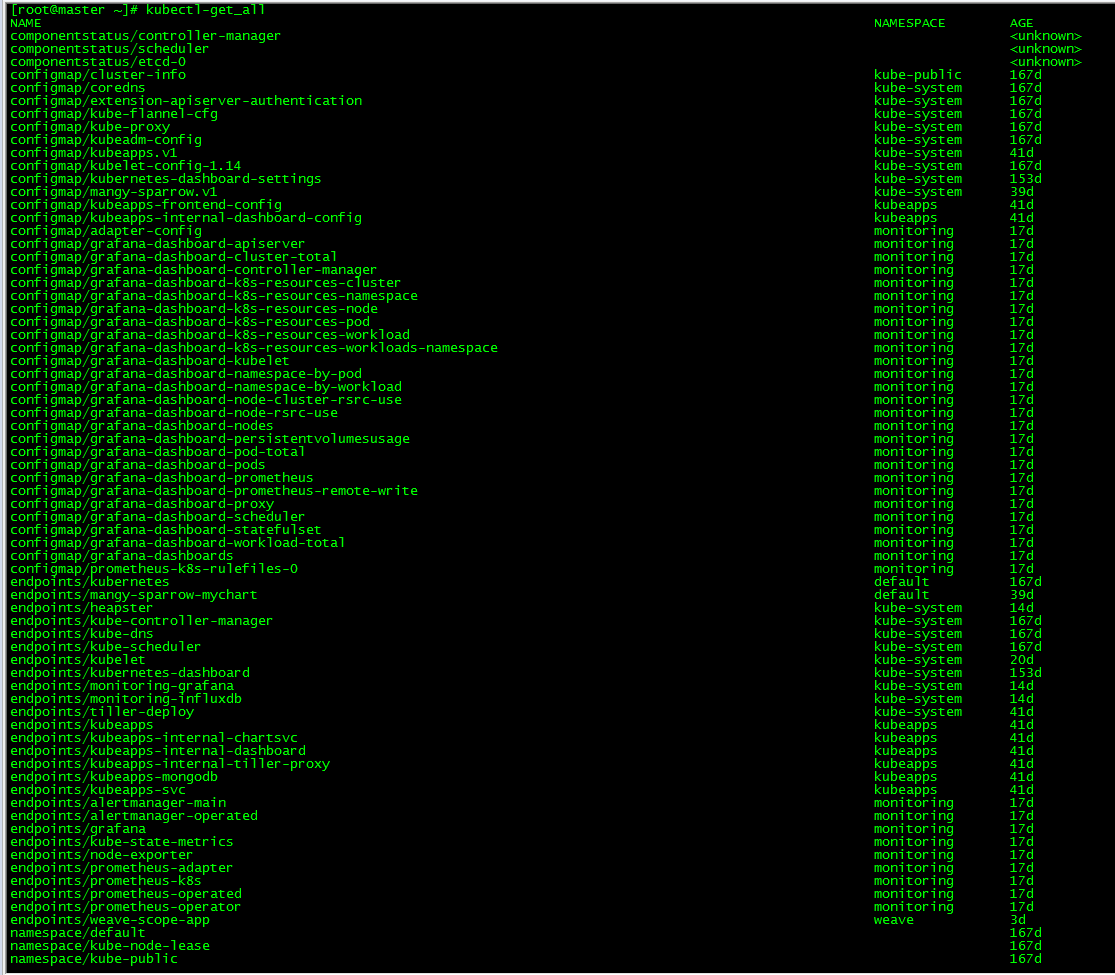
This command is similar to 'kubectl get all -- all namespaces', but more complete.
9. Use plug-in -- tail
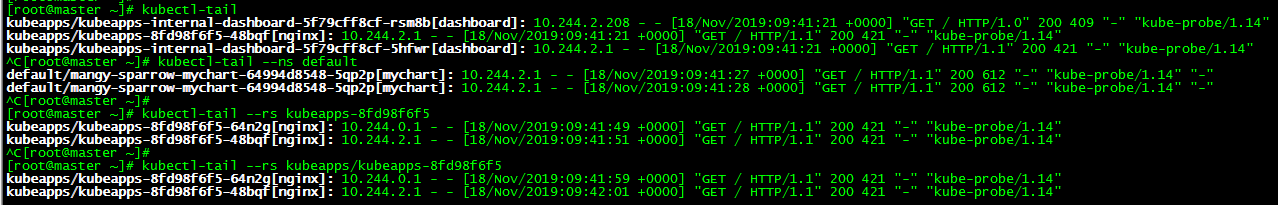
[root@master ~]# kubectl-tail [root@master ~]# kubectl-tail --ns default [root@master ~]# kubectl-tail --rs kubeapps-8fd98f6f5 [root@master ~]# kubectl-tail --rs kubeapps/kubeapps-8fd98f6f5
tail is to output pod logs. The above commands are: output all pod logs, output all pod logs with default namespace, output all pod logs with kubeapps-8fd98f6f5 replicaset, and output pod logs with kubeapps-8fd98f6f5 replicaset.
10. Uninstall plug-ins
[root@master ~]# kubectl krew uninstall tail Uninstalled plugin tail
Uninstall plug-in tail
V. krew unloading
1. View the installation directory
rm -rf ~/.krew [root@master ~]# kubectl krew version OPTION VALUE GitTag v0.3.2 GitCommit bd754e1 IndexURI https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/krew-index.git BasePath /root/.krew IndexPath /root/.krew/index InstallPath /root/.krew/store DownloadPath /tmp/krew-downloads BinPath /root/.krew/bin
2. uninstall
[root@master ~]# rm -rf /root/.krew
All scripts and configuration files of this article have been uploaded: k8s practice (XIII): kubectl plug-in management tool krew