This article is shared from Huawei cloud community< This article takes you to understand JDK dynamic agent and CGLIB dynamic agent >, author: skin shrimp.
What's the difference between the two
1, Jdk dynamic proxy: use the interceptor (to implement InvocationHandler interface) and add the reflection mechanism to generate an anonymous class of the proxy interface, and call InvokeHandler before calling the specific method.
2, Cglib dynamic proxy: use ASM framework to load the class file generated by proxy object class, and generate subclasses by modifying its bytecode to proxy
So:
- If you want to implement JDK dynamic proxy, the proxy class must implement the interface, otherwise it cannot be used;
- If you want to use CGlib dynamic proxy, the proxy class cannot use final to modify classes and methods;
Also: after jdk6, jdk7 and jdk8 gradually optimize the JDK dynamic agent, the JDK agent efficiency is higher than the CGLIB agent efficiency when the number of calls is small. Only when a large number of calls are made, the jdk6 and jdk7 are a little lower than the CGLIB agent efficiency, but when jdk8, the JDK agent efficiency is higher than the CGLIB agent efficiency.
How
JDK dynamic agent
UserService interface
public interface UserService { void addUser(); void updateUser(String str); }
UserServiceImpl implementation class
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Override public void addUser() { System.out.println("Add user"); } @Override public void updateUser(String str) { System.out.println("Update user information" + str); } }
The UserProxy proxy class implements the InvocationHandler interface and overrides the invoke method
public class UserProxy implements InvocationHandler { private Object target; public UserProxy(Object target) { this.target = target; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object res = method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("Log"); return res; } }
Test test class
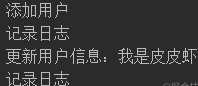
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { UserServiceImpl impl = new UserServiceImpl(); UserProxy userProxy = new UserProxy(impl); UserService userService = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(impl.getClass().getClassLoader(),impl.getClass().getInterfaces(),userProxy); userService.addUser(); userService.updateUser(": I'm Pipi shrimp"); } }
It can be seen that the enhancement is realized and the log is printed out
CGlib dynamic proxy
CGlib is not like JDK dynamic proxy. CGlib needs to import Jar package, so I use SpringBoot to import dependencies directly
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>
UserServiceImpl proxy class
public class UserServiceImpl { public void addUser() { System.out.println("Added a user"); } public void deleteUser() { System.out.println("A user was deleted"); } }
UserServiceCGlib proxy
public class UserServiceCGlib implements MethodInterceptor { private Object target; public UserServiceCGlib() { } public UserServiceCGlib(Object target) { this.target = target; } //Returns a proxy object: yes target Object's proxy object public Object getProxyInstance() { //1. Create a tool class Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer(); //2. Set parent class enhancer.setSuperclass(target.getClass()); //3. Set callback function enhancer.setCallback(this); //4. Create a subclass object, the proxy object return enhancer.create(); } @Override public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { System.out.println("Enhancement start~~~"); Object result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects); System.out.println("Enhancement end~~~"); return result; } }
Test test class
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { UserServiceCGlib serviceCGlib = new UserServiceCGlib(new UserServiceImpl()); UserServiceImpl userService = (UserServiceImpl)serviceCGlib.getProxyInstance(); userService.addUser(); System.out.println(); userService.deleteUser(); } }
It can be seen that the enhancement is realized and the log is printed out

Usage scenario
Here, I believe you have basically mastered the difference and implementation between JDK dynamic agent and CGlib dynamic agent
However, in the interview process, in addition to answering the above points, you should also answer their use scenarios, which is actually the bonus of the interview
So, what are the usage scenarios of these two dynamic agents???
Answer: Spring AOP
The following is how Spring AOP creates a proxy
@Override public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation."); } //If if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } }
1. If the target object implements the interface, the dynamic proxy of JDK will be adopted by default
2. CGLIB can also be enforced if the target object implements an interface
3. If the target object does not implement the interface, the CGLIB library must be used, and spring will automatically convert between JDK dynamic agent and CGLIB
If you need to force CGLIB to implement AOP, you need to configure spring. AOP. Proxy target class = true or @ EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true
Click focus to learn about Huawei cloud's new technologies for the first time~