JavaScript
JavaScript overview
summary
Is a scripting language that is parsed and executed directly by the browser
Development history
- In 1995, Netscape developed a client script language: LiveScript. Later, experts from SUN company were invited to modify LiveScript and name it JavaScript
- In 1996, Microsoft copied JavaScript and developed JScript language
- In 1997, ECMA (European Computer Manufacturers Association) formulated the standard of client script language: ECMAScript, which unifies the coding mode of all client script languages.
summary
JavaScript=ecmascript+bom+dom
html combination of ECMAScript
-
classification
1. Internal combination
Write js code directly in html2,External combination stay javas Prepared in the document js Code, and ton too script Label introduction **1,Internal combination**
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>ECMAScript of html combination</title>
<!--Internal combination-->
<script>
console.log("helloworld");
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
**2,External combination**
console.log("helloworld");------demo02.js"
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>ECMAScript of html combination</title>
<!-- External combination -->
<script src="demo02.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
summary
Internal links are used for your own script code
External script code for others
ECMAScript comments
Single line note:
//
Multiline comment:
/**/
ECMAScript variables and constants
-
grammar
var Variable name = value; const Constant name = value;
-
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>ECMAScript Variables and constants</title>
<script>
//Declare variable
var num = 1;
console.log("num = " + num);
num = 250;
console.log("num = " + num);
//declare constant
const num2 = 1;
console.log("num2 = " + num2);
num2 = 500;//Constants cannot be assigned
console.log("num2 = " + num2);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Data type of ECMAScript
-
Strongly typed language
- The data type has been determined when defining variables, such as java
-
Weakly typed language
- When defining variables, the data type can be uncertain, such as javascript
-
data type
- boolean
- null
- number
- string
- object
- Undefined: variable type is undefined
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>ECMAScript Data type</title>
<script>
/* - boolean
- null
- number
- string
- object
- undefined : Variable type undefined*/
// var a;
var flag =true;
console.log(typeof (flag));
//null
var obj = null;
console.log(typeof (obj))
//number
var num =1;
console.log(typeof(num));
//string
var str ="hello";
console.log(typeof(str));
//object
var date = new Date();
console.log(date);
//undefined
var a;
console.log(typeof (a));
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
ECMAScript operator
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>ECMAScript Operator of</title>
<script>
var num1 =1;
var num2=1;
//Compare content only
console.log(num1 == num2);
//Both comparison types have comparison contents
console.log(num1 === num2);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Process control of ECMAScript
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>ECMAScript Process control of</title>
<script>
100.
for (var i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
ECMAScript function
-
summary
Functions are similar to AV Some codes can be extracted to achieve the effect of reuse
-
grammar
function Function name (formal parameter list) { Function body; } //Anonymous function var Method name =function (Formal parameter list){ Function body; } -
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>ECMAScript Function of</title>
<script>
//Mode 1
function add(num1,num2,num3) {
console.log("num1 ="+num1);
console.log("num2 ="+num2);
console.log("num3 ="+num3);
}
//Mode II
var add2 =function (num1,num2,num3) {
console.log("num1 ="+num1);
console.log("num2 ="+num2);
console.log("num3 ="+num3);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
-
matters needing attention
Anonymous functions are usually used in event listening. There are three formal parameters when calling a function, and three arguments can not be passed when calling
Event overview
-
summary
- Functions that trigger javascript through some user actions
-
Noun interpretation
- Event source: the source of the event
- Listener: a javascript function used to listen to the component where the event occurs
- Event: an event that triggers a listener
- Event binding: associate an event source with a listener
Event binding
-
summary
- Associate event sources with listeners
-
classification
- ① Use event properties
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Event binding</title>
<script>
/**
* monitor
*/
function fn1() {
console.log("Point NIMA!!!")
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Event source -->
<!--onclick ="fn1()":Event binding-->
<button onclick="fn1()">
Click to send dragon killing Sabre!!!!
</button>
</body>
</html>
- ② Using dom assignment
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Event binding</title>
<!-- use dom distribution-->
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">
I'll send it at five o'clock!!!
</button>
</body>
<script>
//Get the button object with id=btn
var btnEle =document.getElementById("btn");
btnEle.onclick =function () {
console.log("Send the colored pen!!!!")
}
</script>
</html>
onload event
-
summary
- Listening element loading completed
-
demand
- After loading the listening page, set the click event for the button
-
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>onload event</title>
<script>
//Listening page loading completed
window.onload = function () {
console.log("Page loading complete");
var btnEle = document.getElementById("btn");
btnEle.onclick = function () {
console.log("Please~~~");
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">
Save me quickly!!!
</button>
</body>
</html>
focal event
-
summary
- The listening component obtains the focus (onfocus) and loses the focus (onblur)
-
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>focal event</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function fn1(){
console.log("1 Get focus");
}
function fn2(){
console.log("1 Lose focus");
}
function fn3(){
console.log("2 Get focus");
}
function fn4(){
console.log("2 Lose focus");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" onfocus="fn1()" onblur="fn2()"/><br/>
<input type="text" onfocus="fn3()" onblur="fn4()"/><br/>
</body>
</html>
onchange event
-
summary
- Monitoring content change
-
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>onchange event</title>
<script>
function fn1() {
console.log("The content has changed!");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" onchange="fn1()"/>
</body>
</html>
onsubmit event
-
summary
- Listening form submission
-
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>onsubmit event</title>
<script>
function fn1(){
console.log()
var flag = false;
if (flag) {
//If the input content is legal, the form submission is allowed
return true;
}else {
//If the input content is legal, submission is prohibited
return false;
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
< onsubmit ="return fn1()">
Message:<input type="text"name="msg">
<button type="submit">send out</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
dom introduction
summary
- The HTML DOM defines standard methods for accessing and manipulating HTML documents. DOM represents an HTML document as a tree structure.
- Let developers add, delete, modify and check the elements on the page through code
- dom tree
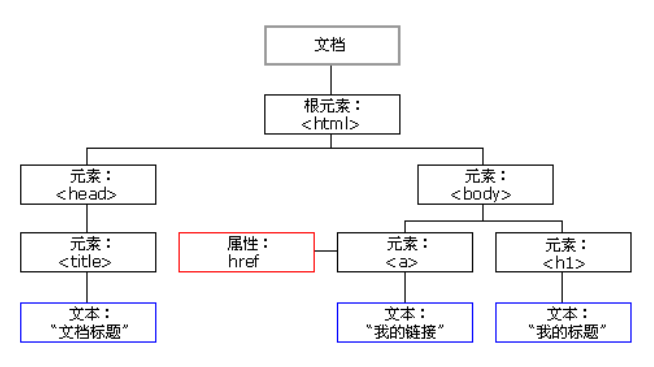
- summary
dom tree is generally composed of three types of nodes: element object, attribute node object and text node object
Get operation of Element element
common method
| method | explain |
|---|---|
| getElementByld | Gets the element object according to the id attribute value |
| getElementsByTagName | Get multiple element objects based on tag names |
| getElementsByName | Get multiple element objects according to the value of the name attribute |
| getElementsByClassName | Get multiple element objects according to the class attribute value |
| parentElement | Get parent element |
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Element Get operation of element</title>
</head>
<body>
<span id="spn" name="span1" class="spanClass">This is a span</span><br />
<button onclick="fn1()">getElementById</button><br />
<button onclick="fn2()">getElementsByTagName</button><br />
<button onclick="fn3()">getElementsByName</button><br />
<button onclick="fn4()">getElementsByClassName</button><br />
<button onclick="fn5()">parent</button><br />
</body>
<script>
function fn1(){
var spanEle = document.getElementById("spn");
console.log(spanEle);
}
function fn2(){
var spanEle = document.getElementsByTagName("span")[0];
console.log(spanEle);
}
function fn3(){
var spanEle = document.getElementsByName("span1")[0];
console.log(spanEle);
}
function fn4(){
var spanEle = document.getElementsByClassName("spanClass")[0];
console.log(spanEle);
}
function fn5(){
var spanEle = document.getElementsByClassName("spanClass")[0];
var bodyEle = spanEle.parentElement;
console.log(bodyEle);
}
</script>
</html>
Addition, deletion, query and modification of Element
common method
| method | explain |
|---|---|
| getElementByld | Gets the element object according to the id attribute value |
| getElementsByTagName | Get multiple element objects based on tag names |
| getElementsByName | Get multiple element objects according to the value of the name attribute |
| getElementsByClassName | Get multiple element objects according to the class attribute value |
| parentElement | Get parent element |
demand
- Add a Jingzhou option to the drop-down selection box
- Delete the last option in the drop-down selection box
- Change the last option in the drop-down selection box to Yichang
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Element Addition, deletion and modification of elements</title>
</head>
<body>
<select>
<option>Wuhan</option>
<option>Xiaogan City</option>
</select>
<button onclick="fn1()">add to</button>
<button onclick="fn2()">delete</button>
<button onclick="fn3()">modify</button>
</body>
<script>
/**
* Add a Jingzhou option to the drop-down selection box < option > Jingzhou < / option >
*/
function fn1(){
//1. Create an option object < option > < / option >
var optionEle = document.createElement("option");
//2. Create text object Jingzhou
var jingzhou = document.createTextNode("jingzhou ");
//3. Add Jingzhou City to option < option > Jingzhou City < / option >
optionEle.appendChild(jingzhou);
//4. Get the select object
var selectEle = document.getElementsByTagName("select")[0];
//5. Add < option > Jingzhou < / option > to select
selectEle.appendChild(optionEle);
}
/**
* Delete the last option in the drop-down selection box
*/
function fn2(){
//1. Get all option objects
var optionEles = document.getElementsByTagName("option");
//2. Obtain the length of all option s
var length = optionEles.length;
//3. Get the last option object
var lastOptionEle = optionEles[length-1];
//4. Get the select object
var selectEle = document.getElementsByTagName("select")[0];
//5. Delete the last option object from the select object
selectEle.removeChild(lastOptionEle);
}
/**
* Change the last option in the drop-down selection box to Yichang
*/
function fn3(){
//1. Get the last option object
var optionEles = document.getElementsByTagName("option");
var lastOptionEle = optionEles[optionEles.length - 1];
//2. Prepare < option > Yichang < / option >
var newOptionEle = document.createElement("option");
newOptionEle.appendChild(document.createTextNode("Yichang City"));
//3. Replace the last option object with < option > Yichang < / option >
var selectEle = document.getElementsByTagName("select")[0];
selectEle.replaceChild(newOptionEle,lastOptionEle);
}
</script>
</html>
Attribute action
common method
| method | explain |
|---|---|
| setAtrribute | set a property |
| getAtrribute | get attribute |
| removeAtrribute | Remove Attribute |
| style | Set css Style |
-
demand
- Set the href attribute of a tag to“ http://www.baidu.com "
- Gets the href attribute of the a tag
- Remove the href attribute of a tag
- Set the style of text content in a label: color = "blue", fontsize = "100px", fontFamily = "italics"
-
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Attribute Operation of property</title>
</head>
<body>
<a>use Baidu Search</a><br />
<button onclick="fn1()">set a property</button>
<button onclick="fn2()">get attribute</button>
<button onclick="fn3()">Remove Attribute </button>
<button onclick="fn4()">Set style</button>
</body>
<script>
/**
* Set the href attribute of a tag to“ http://www.baidu.com "
*/
function fn1(){
//1. Get a object
var aEle = document.getElementsByTagName("a")[0];
//2. Set href attribute
aEle.setAttribute("href","http://www.baidu.com");
}
/**
* Gets the href attribute of the a tag
*/
function fn2(){
//1. Get a object
var aEle = document.getElementsByTagName("a")[0];
//2. Get href attribute
var href = aEle.getAttribute("href");
//3. Print href
console.log(href);
}
/**
* Remove the href attribute of a tag
*/
function fn3(){
//1. Get a object
var aEle = document.getElementsByTagName("a")[0];
//2. Remove the href attribute
aEle.removeAttribute("href");
}
/**
* Set the style of text content in a label: color = "blue", fontsize="100px", fontFamily = "italics"
*/
function fn4(){
//1. Get a object
var aEle = document.getElementsByTagName("a")[0];
//2. Set style
aEle.style.color = "blue";
aEle.style.fontSize = "100px";
aEle.style.fontFamily = "Regular script";
}
</script>
</html>
Operation of Text
common method
| method | explain |
|---|---|
| innerText | Add / get text, cannot parse html tag |
| innerHTML | Add / get text to parse html tags |
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Text Operation of text</title>
</head>
<body>
<span id="spn">
This is span
</span><br>
<button onclick="fn1()">innerText1</button>
<button onclick="fn2()">innerText2</button>
<button onclick="fn3()">innerHTML1</button>
<button onclick="fn4()">innerHTML2</button>
</body>
<script>
/**
* Add the text "helloworld" to span
*/
function fn1() {
//1. Get span object
var spanEle = document.getElementById("spn");
//2. Add the text "helloworld" to span
spanEle.innerText = "<font color='red'>helloworld</font>";
}
/**
* Get the text content in span
*/
function fn2() {
//1. Get span object
var spanEle = document.getElementById("spn");
//2. Get the text content in span
var content = spanEle.innerText;
//3. Print text content
console.log(content);
}
/**
* Add the text "helloworld" to span
*/
function fn3() {
//1. Get span object
var spanEle = document.getElementById("spn");
spanEle.innerHTML = "<font color='red'>helloworld</font>";
}
/**
* Get the text content in span
*/
function fn4() {
//1. Get span object
var spanEle = document.getElementById("spn");
console.log(spanEle.innerHTML);
}
</script>
</html>
dom comprehensive case effect
Case effect
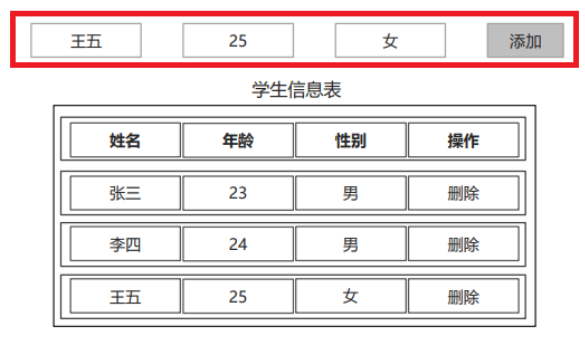
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>dom Comprehensive case</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" placeholder="Please enter your name">
<input type="text" placeholder="Please enter age">
<button>add to</button><br><br><br>
<table border="1px" rules="all" cellpadding="10px" cellspacing="0px" width="300px">
<tr>
<td>full name</td>
<td>Age</td>
<td>operation</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Zhang San</td>
<td>18</td>
<td>
<button>delete</button>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Li Si</td>
<td>19</td>
<td>
<button>delete</button>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
dom comprehensive case deletion function
code implementation
//The node to be removed is not a child of this node
function deleteUser(obj) {
console.log("deleteUser..." + obj);
//obj is a button object
//1. Get the tr object where the button is located
var trEle = obj.parentElement.parentElement;
//2. Get the table object
var tableEle = document.getElementsByTagName("table")[0];
//3. Remove the tr object from the table object
tableEle.removeChild(trEle);
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>dom Comprehensive case</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" placeholder="Please enter your name">
<input type="text" placeholder="Please enter age">
<button>add to</button><br><br><br>
<table border="1px" rules="all" cellpadding="10px" cellspacing="0px" width="300px">
<tr>
<td>full name</td>
<td>Age</td>
<td>operation</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Zhang San</td>
<td>18</td>
<td>
<button onclick="deleteUser2()">delete</button>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Li Si</td>
<td>19</td>
<td>
<button onclick="deleteUser2()">delete</button>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
<script>
/**
* Deletion method 1
* @param obj
*/
function deleteUser1(obj) {
console.log("deleteUser..." + obj);
//obj is a button object
//1. Get the tr object where the button is located
var trEle = obj.parentElement.parentElement;
//2. Get the table object
var tableEle = trEle.parentElement;
//3. Remove the tr object from the table object
tableEle.removeChild(trEle);
}
/**
* Deletion method 2
* @param obj
*/
function deleteUser2() {
//Event: the current click event object
var buttonEle = event.target;
console.log(buttonEle);
//1. Get the tr object where the button is located
var trEle = buttonEle.parentElement.parentElement;
//2. Get the table object
var tableEle = trEle.parentElement;
//3. Remove the tr object from the table object
tableEle.removeChild(trEle);
}
</script>
</html>
summary
- Method 1: pass the button object through the parameter this object of deleteUser1.
- Method 2: get the button object through event.target
dom comprehensive case addition
code implementation
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>dom Comprehensive case</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" placeholder="Please enter your name" id="name">
<input type="text" placeholder="Please enter age" id="age">
<button onclick="addUser2()">add to</button>
<br><br><br>
<table border="1px" rules="all" cellpadding="10px" cellspacing="0px" width="300px">
<tr>
<td>full name</td>
<td>Age</td>
<td>operation</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Zhang San</td>
<td>18</td>
<td>
<button onclick="deleteUser1(this)">delete</button>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Li Si</td>
<td>19</td>
<td>
<button onclick="deleteUser2()">delete</button>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
<script>
/*
<tr>
<td>Wang Wu</td>
<td>20</td>
<td>
<button οnclick="deleteUser1(this)">Delete < / button >
</td>
</tr>
*/
function addUser1() {
console.log("addUser1..");
//Gets the contents of the input box
var nameInputEle = document.getElementById("name");
var ageInputEle = document.getElementById("age");
var name = nameInputEle.value;
var age = ageInputEle.value;
//1. Create tr object
var trEle = document.createElement("tr");
//2. Create td object with name
//2.1, td of name
var nameTdEle = document.createElement("td");
nameTdEle.appendChild(document.createTextNode(name));
//2.2, age td
var ageTdEle = document.createElement("td");
ageTdEle.appendChild(document.createTextNode(age));
//2.3. td of button
var buttonTdEle = document.createElement("td");
var buttonEle = document.createElement("button");
buttonEle.setAttribute("onclick", "deleteUser1(this)");
buttonEle.appendChild(document.createTextNode("delete"));
buttonTdEle.appendChild(buttonEle);
//3. Add all td to tr object
trEle.appendChild(nameTdEle);
trEle.appendChild(ageTdEle);
trEle.appendChild(buttonTdEle);
//4. Add tr to the table object
var tableEle = document.getElementsByTagName("table")[0];
tableEle.appendChild(trEle);
}
/*
<tr>
<td>Wang Wu</td>
<td>20</td>
<td>
<button οnclick="deleteUser1(this)">Delete < / button >
</td>
</tr>
*/
function addUser2() {
//Gets the contents of the input box
var nameInputEle = document.getElementById("name");
var ageInputEle = document.getElementById("age");
var name = nameInputEle.value;
var age = ageInputEle.value;
var tableEle = document.getElementsByTagName("table")[0];
//Gets the text content of the table tag
var content = tableEle.innerHTML;
tableEle.innerHTML = content + "<tr>\n" +
" <td>" + name + "</td>\n" +
" <td>" + age + "</td>\n" +
" <td>\n" +
" <button οnclick=\"deleteUser1(this)\">delete</button>\n" +
" </td>\n" +
" </tr>";
}
</script>
</html>