Getting started with Docker
Definition of container
- Stand alone processes running in user space
- Isolated from other user space programs
- A container runs in a separate user space
- At the bottom is a separate kernel space
History of development
- FreeBSD jail, 2000
- Linux VServer ,2001
- CGroups
- NameSpace
- LXC
- Docker ,2010
- libcontainer
- runC
docker container arrangement three swordsmen
- docker-mechine
- docker-swarm
- docker-compose
Linux NameSpace
- It is used to encapsulate a global level of system resources that can be segmented on an abstraction layer, mainly including the following seven levels of system resources
| NameSpaces | Constant | Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| Cgroup | CLONE_NEWCGROUP | Cgroup root directory, dispatch the underlying cpu, memory and IO resources to the container |
| IPC | CLONE_NEIPC | System V IPC,POSIX message queues |
| NETWORK | COLNE_NENET | NetWork devices,stacks,ports,etc |
| Mount | ClONE_NEWNS | MountPoints |
| PID | COLNE_NEW_PID | Process PID |
| Users | COLNE_USER | User and Group IDs |
| UTS | CLONE_NEW_UTS | Hostname and NIS domain name |
Version of docker
- docker-ee
- docker-ce
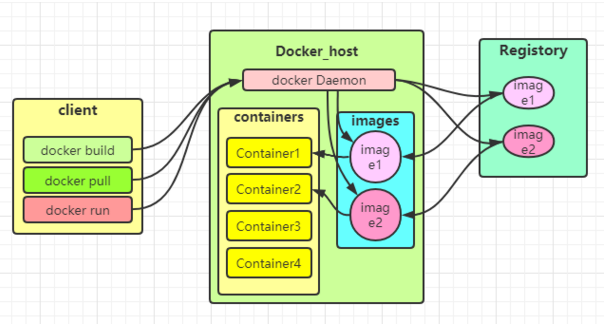
Docker architecture
Installation of docker
- System: centos7+
- Initialization: configure host name & IP bypass
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalld [root@centos7-node1 ~]# sed -i "s/SELINUX=permissive/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/selinux/config && reboot -f [root@centos7-node1 ~]# yum install chrony wget curl git -y && systemctl enable chronyd && systemctl start chronyd && timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai && timedatectl set-ntp yes #time synchronization [root@centos7-node1 ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo [root@centos7-node1 ~]# yum -y install epel-release [root@centos7-node1 ~]# echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf && sysctl -p
- Installation and configuration of docker
# step 1: install some necessary system tools
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
# Step 2: add software source information
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# Step 3: update and install docker CE
yum makecache fast
yum -y install docker-ce
# New profile
mkdir -p /etc/docker
tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://0b8hhs68.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
"storage-driver": "overlay2",
"graph":"/data/docker",
"storage-opts": [
"overlay2.override_kernel_check=true"
]
}
EOF
# Overloaded service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart dockerdocker environment related commands
docker info #View docker information docker version #View version information
Mirror related commands
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker image -h Flag shorthand -h has been deprecated, please use --help Usage: docker image COMMAND Manage images Commands: build Build an image from a Dockerfile history Show the history of an image import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image inspect Display detailed information on one or more images load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN ls List images prune Remove unused images pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry push Push an image or a repository to a registry rm Remove one or more images save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default) tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
Container related commands
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker container -h Flag shorthand -h has been deprecated, please use --help Usage: docker container COMMAND Manage containers Commands: attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container commit Create a new image from a container's changes cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem create Create a new container diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem exec Run a command in a running container export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive inspect Display detailed information on one or more containers kill Kill one or more running containers logs Fetch the logs of a container ls List containers pause Pause all processes within one or more containers port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container prune Remove all stopped containers rename Rename a container restart Restart one or more containers rm Remove one or more containers run Run a command in a new container start Start one or more stopped containers stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics stop Stop one or more running containers top Display the running processes of a container unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers update Update configuration of one or more containers wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
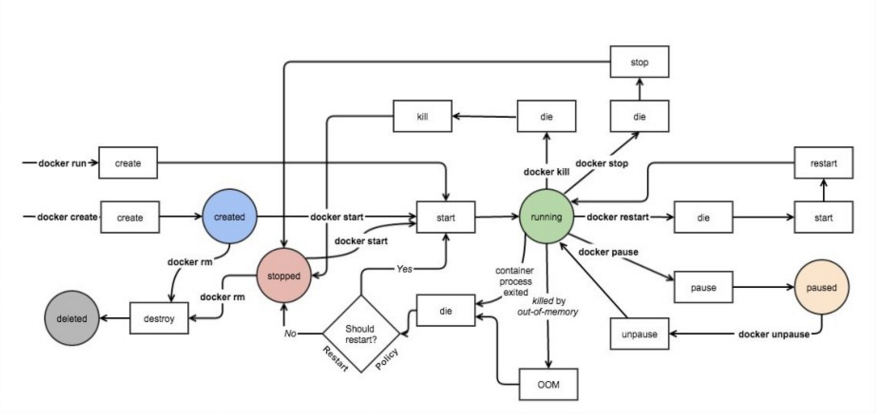
practice
Mirror practice
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker search redis #Find redis image [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker pull redis:4-alpine #Drag image [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker images #View all mirrors [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker inspect redis:4-alpine #View image details [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker rmi redis:4-alpine #delete mirror [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker image save redis:4-alpine -o redis.tar #Export image [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker image load -i redis.tar #Import image
Log in to Alibaba cloud container image console, create a namespace, and then create a redis local image warehouse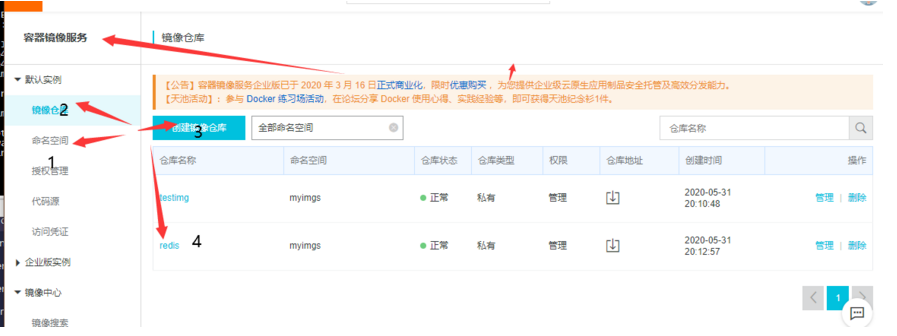
The next step is to upload images to Alibaba cloud redis image warehouse
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker login --username=valiente0822 registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com #Log in to my alicloud docker image warehouse [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker image tag redis:4-alpine registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/myimgs/redis:4-alpine #Copy and modify tag [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker push registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/myimgs/redis:4-alpine #Upload image [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/myimgs/redis:4-alpine #Download Image
matters needing attention:
- If you create a private Alibaba cloud warehouse, you need docker login to pull the image
Container practice
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker image pull centos:7 #Pull image [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker container run -it --name c1 centos:7 /bin/bash #Interactive run container [root@centos7-node1 ~]# iptables -t nat -vnL #New terminal found nat iptables rule [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker ps -a #View containers in run or stop state [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker start c1 #Start container [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker ps #Container for viewing the running state