Currently, docker is very popular. Of course, compared with k8s, docker is slightly less powerful, but it is still widely used and convenient. Here are two ways to install docker
First type: yum source installation
This method is relatively simple to install, but first make sure that yum is installed on the server (usually comes with it).
First, check whether there is a docker
yum list installed | grep docker
Install directly if it doesn't exist
yum -y install docker
Start docker
systemctl start docker #Stop is stop
View docker status
systemctl status docker
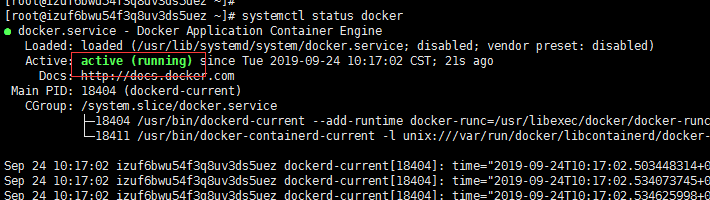

You can see the activation status, indicating that the installation is successful
The second way is to install offline:
Official installation package address: https://download.docker.com/linux/static/stable/x86_64/
wget https://download.docker.com/linux/static/stable/x86_64/docker-18.06.3-ce.tgz
decompression
tar -zxvf docker-18.06.3-ce.tgz
Copy the extracted docker file to the directory / usr/bin /
cp docker/* /usr/bin/
Add the docker.service file in the directory / etc/systemd/system /. The content is as follows. In this way, you can register the docker as a service
[Unit] Description=Docker Application Container Engine Documentation=https://docs.docker.com After=network-online.target firewalld.service Wants=network-online.target [Service] Type=notify # the default is not to use systemd for cgroups because the delegate issues still # exists and systemd currently does not support the cgroup feature set required # for containers run by docker ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd --selinux-enabled=false --insecure-registry=127.0.0.1 ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID # Having non-zero Limit*s causes performance problems due to accounting overhead # in the kernel. We recommend using cgroups to do container-local accounting. LimitNOFILE=infinity LimitNPROC=infinity LimitCORE=infinity # Uncomment TasksMax if your systemd version supports it. # Only systemd 226 and above support this version. #TasksMax=infinity TimeoutStartSec=0 # set delegate yes so that systemd does not reset the cgroups of docker containers Delegate=yes # kill only the docker process, not all processes in the cgroup KillMode=process # restart the docker process if it exits prematurely Restart=on-failure StartLimitBurst=3 StartLimitInterval=60s [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
The setting of -- secure registry = 127.0.0.1 (changed to your private ip here) here is to allow the docker to have insecure access when you have set up your own private Harbor, otherwise the access will be denied
Start docker
Add execution permission to docker.service file
chmod +x /etc/systemd/system/docker.service
Reload the configuration file (reload every time you modify the docker.service file)
systemctl daemon-reload
start-up
systemctl start docker
Set startup
systemctl enable docker.service
View docker service status
systemctl status docker
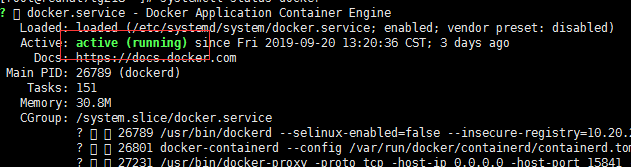
The above figure shows that docker has been installed successfully
It may be said that for the simple installation of Yum source, you need to see the offline installation. In fact, I want to say that it's only for standby. In case of any problem with the yum installation, you can try the offline installation. No matter what kind of installation is successful, it's ok!

