Implementation principle reference: Asynchronous fifo -- Verilog implementation_ Alan aixiao's blog - CSDN blog_ Asynchronous fifo
Code reference: IC Foundation (I): asynchronous fifo_ Maochuang an's blog - CSDN blog_ Asynchronous fifo
1. Key points of asynchronous FIFO design:
(1) Conversion from binary code to gray code:
The highest bit of the binary code remains unchanged, and the other bits are XOR with the left bit to get the gray code. That is, move the binary code one bit to the right and XOR with yourself to get the corresponding gray code.
Namely: assign gray = ( bin >> 1 ) ^ bin ;
(2) Synchronization of clock domain:
The gray code corresponding to the binary address is delayed by the synchronization module from the FIFO empty module to the FIFO full module to complete the clock synchronization. The same goes for the full module to the empty module.
(3) Logic of FIFO full and empty judgment through gray code:
Full judgment: the highest and second highest positions are different, and others are the same. Namely:
assign wfull_val = ( wgraynext == { ~wq2_rptr [ ADDR_SIZE: ADDR_SIZE - 1 ], wq2_rptr [ ADDR_SIZE-2: 0 ] } )Full judgment: Gray code is exactly the same. Namely:
assign rempty_val = ( rgraynext == rq2_wptr );
2. Function of each module and detailed explanation of Verilog code:
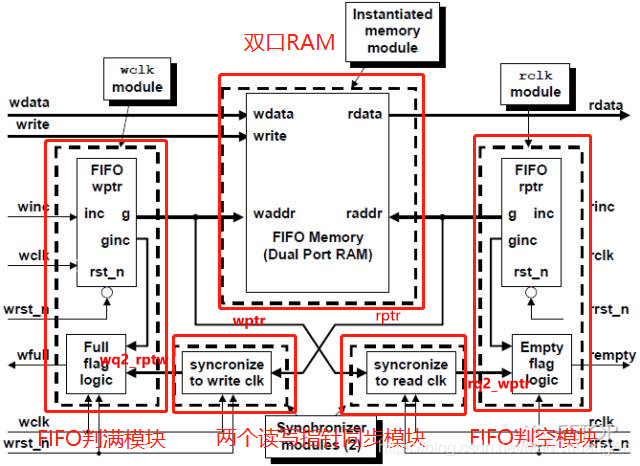
(the picture is taken from the blog at the beginning, with changes)
(1) Dual port RAM module
Function: as an enclosure, the input read and write addresses are binary. The highest bit is used to store empty / full signals.
Port Description:
wclken: Write enable
wclk: Write clock
raddr: Read address
waddr: Write address
wdata: Data written to RAM
rdata: Data read from RAM
module DualRAM #(
parameter DATA_SIZE = 8, // Data bit width
parameter ADDR_SIZE = 4 // FIFO address depth
)(
input wclken, // Write enable
input wclk, // Write clock
input [ADDR_SIZE - 1: 0] raddr, // Read address
input [ADDR_SIZE - 1: 0] waddr, // Write address
input [DATA_SIZE - 1: 0] wdata, // Data written to RAM
output [DATA_SIZE - 1: 0] rdata // Data read from RAM
);
localparam RAM_DEPTH = 1 << ADDR_SIZE; // RAM depth, the highest bit stores the empty and full signal pointer
reg [DATA_SIZE-1: 0] mem [0:RAM_DEPTH-1];// Open up memory
// Write timing
always @ ( posedge wclk ) begin
if ( wclken == 1'b1 ) begin
mem[ waddr ] <= wdata; // Write enable signal is high, write data
end
else begin
mem[ waddr ] <= mem[ waddr ]; // Write enable didn't come, keep it
end
end
assign rdata = mem [ raddr ]; // Read the address and give the data directly
endmodule(2) FIFO empty module
Function: input the read enable signal, generate the corresponding binary address and output it to the RAM module, convert the binary address into the corresponding gray code and output it to the synchronization module, which synchronizes the read address to the write clock domain.
Note that the signal transmitted from the module to the synchronization module in the figure is the gray code corresponding to the binary address.
Port Description:
rclk : Read clock signal
rinc : Read enable signal. For each read enable signal, add one to the read address
rrst_n: Reset signal
rq2_wptr: write pointer code passed in by synchronization module
rempty : Output FIFO null signal
raddr : Binary read address output to RAM
rptr : Gray code output to write clock field
module rptr_empty # (
parameter ADDR_SIZE = 4
)
(
input rclk,
input rinc, // Read enable signal: add one to the read address for each read enable signal
input rrst_n,
input [ ADDR_SIZE :0 ] rq2_wptr, // Write pointer code passed in by synchronization module
output reg rempty,
output [ ADDR_SIZE - 1:0 ] raddr, // Read address output to RAM
output reg [ ADDR_SIZE :0 ] rptr // Gray code output to the write clock field: one more bit than the address, and the highest bit is used to judge the empty and full state
);
reg [ ADDR_SIZE: 0 ] rbin; // Binary address
wire [ ADDR_SIZE: 0 ] rgraynext, rbinnext; // Binary and gray code addresses
wire rempty_val;
//----------Address logic-------------//
always @ ( posedge rclk or negedge rrst_n ) begin
if ( !rrst_n ) begin
rbin <= 0;
rptr <= 0;
end
else begin
rbin <= rbinnext; // Clock to update the binary address
rptr <= rgraynext; // Update the gray code of the corresponding address
end
end
// Address generation logic
assign rbinnext = !rempty ? ( rbin + rinc ): rbin; // Binary address update logic: if FIFO is not empty, the address is current address + read enable (i.e. address plus one); If FIFO is empty, the address will not be updated
assign rgraynext = ( rbinnext >> 1 ) ^ ( rbinnext ); // Gray code address generation: XOR after binary is shifted one bit to the right
assign raddr = rbin[ ADDR_SIZE - 1: 0 ]; // Read address into RAM
// FIFO empty judgment
assign rempty_val = ( rgraynext == rq2_wptr ); // Null determination logic: if the gray code of the write pointer is exactly the same as the gray code of the read pointer, it is null
// Judgment sequence of empty signal rempty
always @ ( posedge rclk or negedge rrst_n ) begin
if ( !rrst_n )
rempty <= 1'b1; // When reset, FIFO is empty
else
rempty <= rempty_val; // Need another signal rempty_val write timing logic
end
endmodule(3) Read clock domain to write clock domain synchronization module
Function: delay the gray code address generated by FIFO blank judgment module by one beat, and then output the address to the write clock field.
Port Description:
rptr : Gray code address pointer passed in by null determination module
wclk : External incoming write clock signal
wrst_n: External incoming write reset signal
wq2_rptr: Gray code address pointer output to the full judgment module
module sync_r2w # (
parameter ADDR_SIZE = 4
)
(
input [ ADDR_SIZE: 0 ] rptr, // Gray code address pointer passed in by null determination module
input wclk, // External incoming write clock signal
input wrst_n, // External incoming write reset signal
output reg [ ADDR_SIZE: 0 ] wq2_rptr // Gray code address pointer output to full judgment module
);
reg [ ADDR_SIZE: 0 ] wq1_rptr; // This register is used to generate a delay of one beat
// D trigger, two-stage synchronization
always @ ( posedge wclk or negedge wrst_n ) begin
if ( !wrst_n )
{ wq2_rptr, wq1_rptr } <= 0;
else // It is equivalent to delaying the input address by one clock cycle:
{ wq2_rptr, wq1_rptr } <= { wq1_rptr, rptr }; // In the first cycle, the address pointer of the empty judgment module is given to the beat register, and in the second cycle, it is taken out to the output signal
end
endmodule(4) The full rating module is the same as another synchronization module, and the code is pasted directly:
Full rating module:
module wptr_full# (
parameter ADDR_SIZE = 4
)
(
input wclk,
input winc,
input wrst_n,
input [ ADDR_SIZE :0 ] wq2_rptr,
output reg wfull,
output [ ADDR_SIZE - 1:0 ] waddr, // Read address output to RAM
output reg [ ADDR_SIZE :0 ] wptr // Gray code output to write clock field
);
reg [ ADDR_SIZE: 0 ] wbin; // Binary address
wire [ ADDR_SIZE: 0 ] wgraynext, wbinnext; // Binary and gray code addresses
wire wfull_val;
//----------Address logic-------------//
always @ ( posedge wclk or negedge wrst_n ) begin
if ( !wrst_n ) begin
wbin <= 0;
wptr <= 0;
end
else begin
wbin <= wbinnext;
wptr <= wgraynext;
end
end
// Address generation logic
assign wbinnext = !wfull ? ( wbin + winc ): wbin;
assign wgraynext = ( wbinnext >> 1 ) ^ ( wbinnext );
assign waddr = wbin[ ADDR_SIZE - 1: 0 ];
// FIFO full
assign wfull_val = ( wgraynext == { ~wq2_rptr [ ADDR_SIZE: ADDR_SIZE - 1 ], wq2_rptr [ ADDR_SIZE-2: 0 ] } );//The highest two digits are reversed and then judged
always @ ( posedge wclk or negedge wrst_n ) begin
if ( !wrst_n )
wfull <= 1'b0;
else
wfull <= wfull_val;
end
endmoduleSynchronization module:
// The write pointer is synchronized to the read clock module
module sync_w2r # (
parameter ADDR_SIZE = 4
)
(
input [ ADDR_SIZE: 0 ] wptr, // Write address gray code generated by full judgment module
input rclk,
input rrst_n,
output reg [ ADDR_SIZE: 0 ] rq2_wptr // Write address code output to read clock field
);
reg [ ADDR_SIZE: 0 ] rq1_wptr; // One shot delay
// D trigger, two-stage synchronization
always @ ( posedge rclk or negedge rrst_n ) begin
if ( !rrst_n )
{ rq2_wptr, rq1_wptr } <= 0;
else
{ rq2_wptr, rq1_wptr } <= { rq1_wptr, wptr }; // It is equivalent to delaying the input address by one clock cycle
end
endmodule(5) Connect the top module:
module AsyncFIFO # (
parameter ADDR_SIZE = 4,
parameter DATA_SIZE = 8
)
(
input [ DATA_SIZE - 1: 0 ] wdata,
input winc,
input wclk,
input wrst_n,
input rinc,
input rclk,
input rrst_n,
output [ DATA_SIZE - 1: 0 ] rdata,
output wfull,
output rempty
);
wire [ ADDR_SIZE - 1: 0 ] waddr, raddr;
wire [ ADDR_SIZE : 0 ] wptr, rptr, wq2_rptr, rq2_wptr;
sync_r2w # (
.ADDR_SIZE ( ADDR_SIZE )
)
I1_sync_r2w (
.rptr ( rptr ),
.wclk ( wclk ),
.wrst_n ( wrst_n ),
.wq2_rptr ( wq2_rptr )
);
sync_w2r # (
.ADDR_SIZE ( ADDR_SIZE )
)
I2_sync_w2r (
.wptr ( wptr ),
.rclk ( rclk ),
.rrst_n ( rrst_n ),
.rq2_wptr ( rq2_wptr )
);
DualRAM # (
.DATA_SIZE ( DATA_SIZE ), // Data bit width
.ADDR_SIZE ( ADDR_SIZE ) // FIFO address depth
)
I3_DualRAM (
.wclken ( winc ), // Write enable
.wclk ( wclk ), // Write clock
.raddr ( raddr ), // Read clock
.waddr ( waddr ), // Write address
.wdata ( wdata ), // Data written to RAM
.rdata ( rdata ) // Data read from RAM
);
rptr_empty # (
.ADDR_SIZE ( ADDR_SIZE )
)
I4_rptr_empty (
.rclk ( rclk ),
.rinc ( rinc ),
.rrst_n ( rrst_n ),
.rq2_wptr ( rq2_wptr ),
.rempty ( rempty ),
.raddr ( raddr ), // Read address output to RAM
.rptr ( rptr ) // Gray code output to write clock field
);
wptr_full# (
.ADDR_SIZE ( ADDR_SIZE )
)
I5_wptr_full (
.wclk ( wclk ),
.winc ( winc ),
.wrst_n ( wrst_n ),
.wq2_rptr ( wq2_rptr ),
.wfull ( wfull ),
.waddr ( waddr ), // Read address output to RAM
.wptr ( wptr ) // Gray code output to write clock field
);
endmodule(6)testbench
module tb();
parameter DATA_SIZE = 16;
parameter ADDR_SIZE = 16;
reg [ DATA_SIZE - 1: 0] wdata;
reg winc, wclk, wrst_n;
reg rinc, rclk, rrst_n;
wire [ DATA_SIZE - 1: 0 ] rdata;
wire wfull;
wire rempty;
integer i=0;
AsyncFIFO # (
.ADDR_SIZE ( ADDR_SIZE ),
.DATA_SIZE ( DATA_SIZE )
)
u_fifo (
.rdata ( rdata ),
.wfull ( wfull ),
.rempty ( rempty ),
.wdata ( wdata ),
.winc ( winc ),
.wclk ( wclk ),
.wrst_n ( wrst_n ),
.rinc ( rinc ),
.rclk ( rclk ),
.rrst_n ( rrst_n )
);
localparam CYCLE = 20;
localparam CYCLE1 = 40;
initial begin
wclk = 0;
forever
# ( CYCLE / 2 )
wclk =~ wclk;
end
initial begin
rclk = 0;
forever
# ( CYCLE1 / 2)
rclk =~ rclk;
end
initial begin
wrst_n = 1;
#2;
wrst_n = 0;
# ( CYCLE * 3 );
wrst_n = 1;
end
initial begin
rrst_n = 1;
#2;
rrst_n = 0;
# ( CYCLE * 3 );
rrst_n = 1;
end
always @ ( posedge wclk or negedge wrst_n ) begin
if ( wrst_n == 1'b0 ) begin
i <= 0;
end
else if ( !wfull ) begin
i = i+1;
end
else begin
i <= i;
end
end
always @ ( rempty or rrst_n ) begin
if ( rrst_n == 1'b0 ) begin
rinc = 1'b0;
end
else if ( !rempty ) begin
rinc = 1'b1;
end
else
rinc = 1'b0;
end
always @ ( wfull or wrst_n ) begin
if ( wrst_n )
winc = 1'b0;
if ( !wfull )
winc = 1'b1;
else
winc = 1'b0;
end
always @ ( * ) begin
if ( !wfull )
wdata = i;
else
wdata = 0;
end
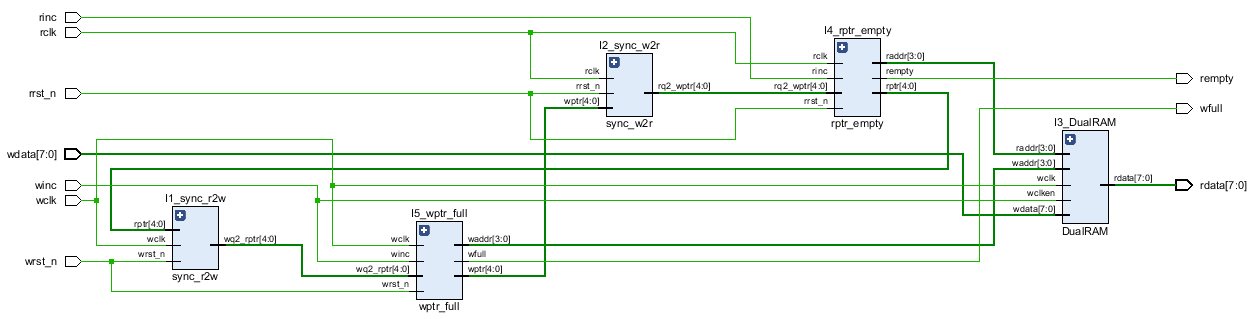
endmoduleRTL diagram:
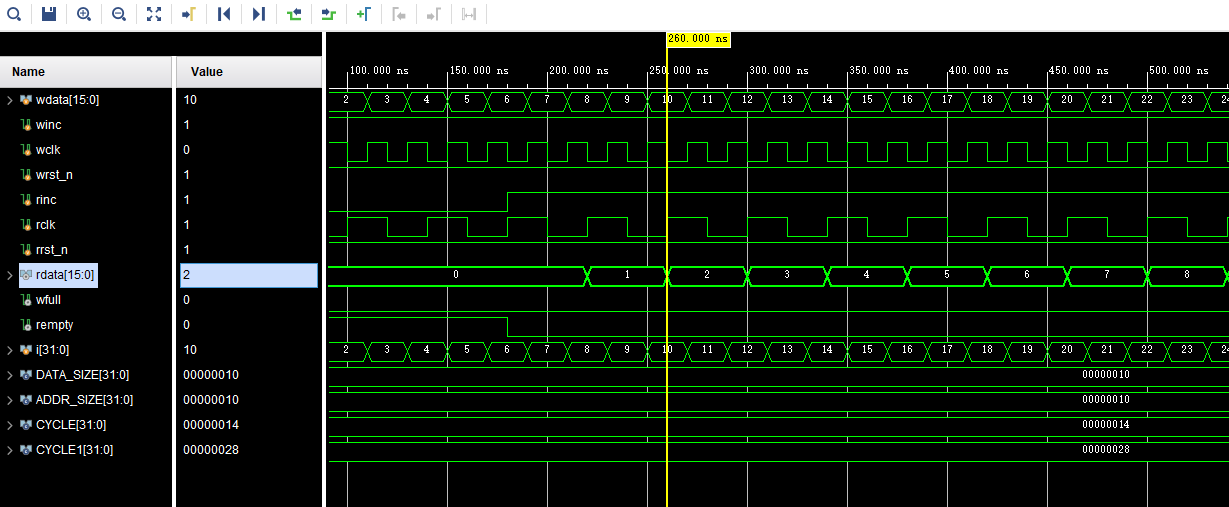
Simulation diagram: