docker storage volume
Data Volume
-
Why data volumes (storage volumes) are needed
- The docker image is made up of multiple read-only layers. When the container is started, the docker loads the read-only layer and adds a read-write layer to the mirror layer.
-
If the running container modifies an existing file, the file will be copied from the read-only layer below the read-write layer to the read-write layer. The read-only version of the file still exists, but has been hidden by a copy of the file in the read-write layer, which is the COW mechanism.
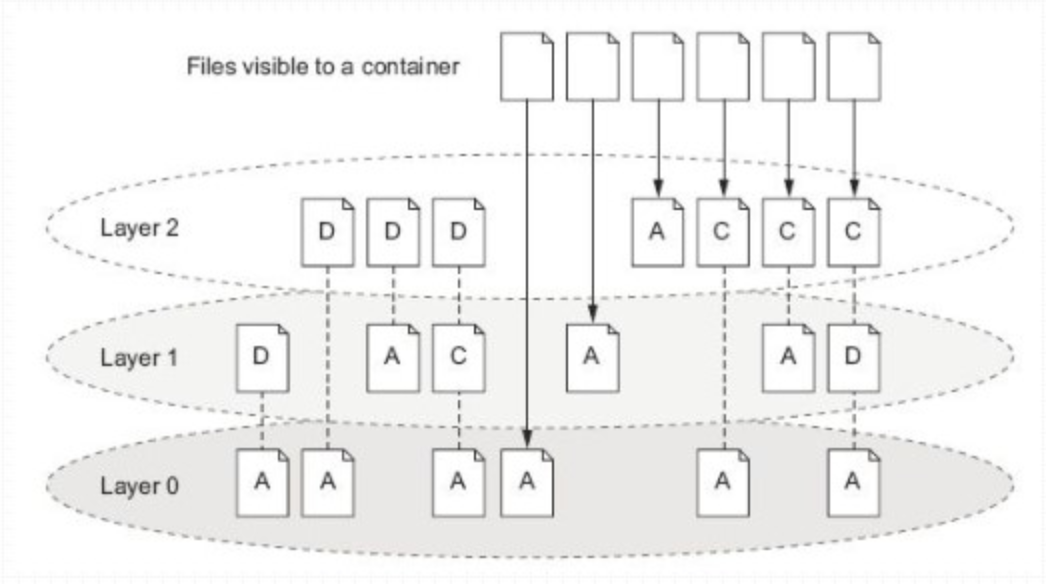
- Close and restart the container without affecting its data, but delete the container and all its changes will be lost
- Problems:
- Storage and Federation file systems are not easily accessible by hosts
- Container key data sharing is inconvenient
- Deleting a container loses its data
volume
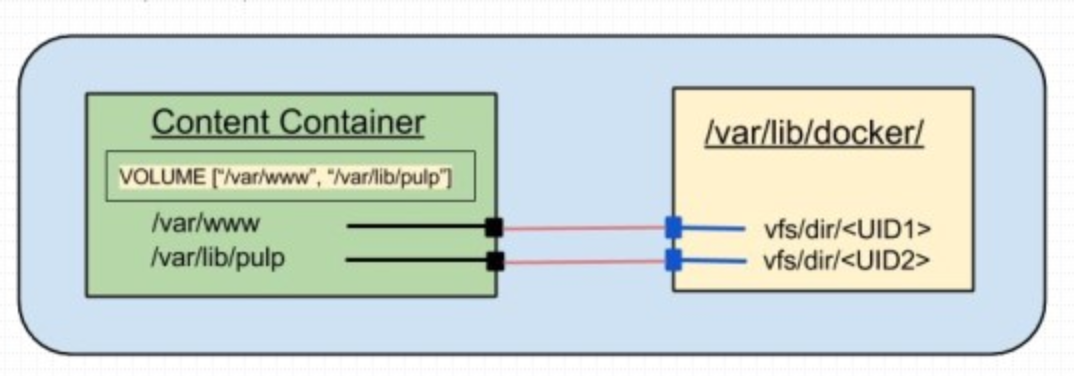
- What is a volume
- Volumes are one or more directories on containers that bypass the federated file system and can be bound (associated) to a directory on the host machine.
Setting up random volumes
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker run --name mybbox5 -it -v /mydata --rm busybox /bin/sh #Specify a container volume, which is automatically created if it does not exist
/ # cd /mydata/
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker inspect mybbox5 # Start another window to view mounts
"Mounts": [
{
"Type": "volume",
"Name": "a39b4a68fc51d83900093f35b05b4e29085b2d45d1fa9a19f63f75130dbf1d0c",
"Source": "/data/docker/volumes/a39b4a68fc51d83900093f35b05b4e29085b2d45d1fa9a19f63f75130dbf1d0c/_data",
"Destination": "/mydata",
"Driver": "local",
"Mode": "",
"RW": true,
"Propagation": ""
}
],Bind mounted volume
- Bind volumes from locally specified directories to containers
- Characteristic:
- The local directory will not be deleted after the container is deleted, and the data is still there
- Can exist without the life cycle of the container
- With NFS storage, data can also exist natively
- Sharing data between containers is possible
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# mkdir /data/volumes/v1 -p [root@centos7-node1 v1]# echo "hello" > /data/volumes/v1/my.txt [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker run --name mybox -it -v /data/volumes/v1:/mydata busybox /bin/sh [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker rm mybox mybox [root@centos7-node1 ~]# ls /data/volumes/v1/ my.txt
Cases of data sharing between containers
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker run --name box6 -it -d -v /data/volumes/v1:/mydata busybox /bin/sh [root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker run --name box7 -it --rm --volumes-from box6 busybox
inspect data display
[root@centos7-node1 v1]# docker inspect box7 #View containers to find corresponding fields
[root@centos7-node1 v1]# docker inspect -f {{.Mounts}} box6 #.Mounts is a top-level field
[root@centos7-node1 v1]# docker inspect -f {{.NetworkSettings.Networks.bridge}} box7 #Connection between multilevel fieldsactual combat
-
Containerized deployment of wordpress
- php+http
- nginx profile local storage
- mysql
- Web page data and mysql data stored locally
- mysql needs to pass in-e mysql_at startupROOTPASSWORD=hello
- thinking
- The three application containers are on the same network layer
- Configuration files and data files need to be stored locally using bound volumes
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# mkdir /data/volumes/mysql
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker pull mysql:5.5
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker run --name db -d -v /data/volumes/mysql:/var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=qwer1234 mysql:5.5
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker exec -it db /bin/bash #Enter the database, create users and databases
root@38b54e3d76cf:/# mysql -uroot -p
mysql> create database wordpress charset utf8;
mysql> grant all on wordpress.* to 'wordpress'@'127.0.0.1' identified by 'wpss2020';
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker pull php:5.6-fpm
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker pull nginx:1.18-alpine
[root@centos7-node1 ~]#mkdir /data/volumes/nginx_conf -p #nginx profile directory
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# cat /data/volumes/nginx_conf/nginx_php.conf #Define the Nginx-php configuration file
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /www/wordpress;
index index.php;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass php:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /www/wordpress/$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker run --name php-fpm -d -v /data/volumes/web:/www php:5.6-fpm #Start php
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker run --name nginx_php -d -p 80:80 -v /data/volumes/nginx_conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d --volumes-from php-fpm --link php-fpm:php nginx:1.18-alpine #start nginx
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# cd /data/volumes/web && wget https://wordpress.org/latest.zip
root@centos7-node1 web]# unzip wordpress-5.4.1.zip
[root@centos7-node1 ~]# docker exec nginx_php nginx -s reload