I. Installation
1.1 Install docker-ce on centos7
- Check system and kernel version
[root@myhost img1]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.3.1611 (Core)[root@myhost img1]# uname -r #Kernel version must be above 3.10, centos7 just meets. 3.10.0-514.21.1.el7.x86_64
- Execute the following commands in turn
#Adding Package Sources
cd /etc/yum.repo.d/ wget https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo sed -i 's//https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/docker-ce/g' docker-ce.repo
#Check to see if it works [root@myhost yum.repos.d]# yum repolist //Loaded plug-ins: fastest mirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile //Source Identifies Source Name Status docker-ce-stable/x86_64 Docker CE Stable - x86_64 46
#install [root@myhost yum.repos.d]# yum install docker-ce -y
At this point, the Docker installation is complete.
1.2 Configure Docker Image Acceleration
- Specify the mirror source address when pulling the image (only the current command is valid)
docker pull registry.docker-cn.com/myname/myrepo:mytag
- Configure the Docker daemon using registry-mirror (only the current process is valid)
docker --registry-mirror=https://registry.docker-cn.com daemon
- Modify the / etc/docker/daemon.json file (permanent)
Add the following:
{
"registry-mirrors": ["http://hub-mirror.c.163.com"]
}
# Need to restart service to take effect
systemctl restart docker.service
II. Basic Usage
2.1 State Machine of Docker Container
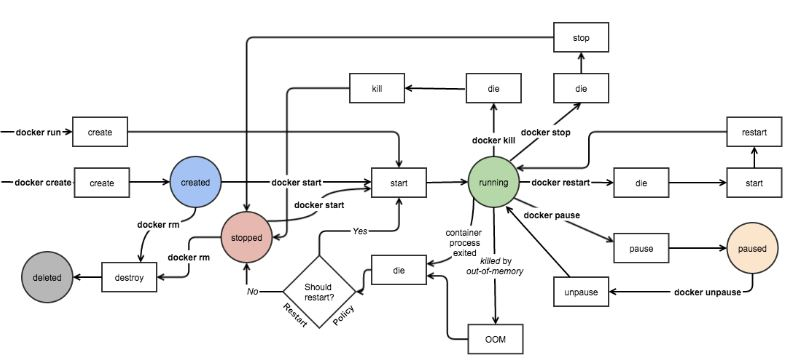
A container may be in the following states:
- created: created, but not yet started (listed using docker PS-A command)
- Running: running (listed using docker ps command)
- paused: The container's process has been suspended
- Restarting: The container process is in the process of restarting
- Existing: The stopped state in the figure above indicates that the container has been running before but is now in a stop state (unlike the created state, it refers to a newly created container that has not yet been run). It can be restarted to running state by the start command
- destroyed: The container has been removed and no longer exists
Its status can be viewed by following commands:
docker inspect Container name
"State": {
"Status": "exited",
"Running": false,
"Paused": false,
"Restarting": false,
"OOMKilled": false,
"Dead": false,
"Pid": 0,
"ExitCode": 0,
"Error": "",
"StartedAt": "2019-07-24T02:00:25.879483514Z",
"FinishedAt": "2019-07-24T02:00:28.685934396Z"
},
2.2 Summary of Commands
- Overall operation
[root@myhost ~]# docker --help
Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND #Grammatical Format
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default "/root/.docker")
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
-H, --host list Daemon socket(s) to connect to
-l, --log-level string Set the logging level ("debug"|"info"|"warn"|"error"|"fatal") (default "info")
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default "/root/.docker/ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default "/root/.docker/cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default "/root/.docker/key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
-v, --version Print version information and quit
Management Commands:
builder Manage builds #Management Creation
config Manage Docker configs #Management Configuration
container Manage containers #Management container
engine Manage the docker engine #Manage Container Engine
image Manage images #Management Mirror
network Manage networks #Management Network
node Manage Swarm nodes
plugin Manage plugins
secret Manage Docker secrets
service Manage services
stack Manage Docker stacks
swarm Manage Swarm
system Manage Docker
trust Manage trust on Docker images
volume Manage volumes
- Operation of Mirror Image
[root@myhost ~]# docker image --help Usage: docker image COMMAND #Grammatical Format Manage images Commands: build Build an image from a Dockerfile #Read the Dockerfile and create a mirror history Show the history of an image #Show the history of a mirror import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image inspect Display detailed information on one or more images #Get detailed information about the mirror load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN ls List images prune Remove unused images pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry push Push an image or a repository to a registry rm Remove one or more images save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default) tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE Run 'docker image COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
- Operation of containers
[root@myhost ~]# docker container --help Usage: docker container COMMAND #Grammatical Format Manage containers Commands: attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container commit Create a new image from a container's changes cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem create Create a new container #Create a container diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem exec Run a command in a running container export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive inspect Display detailed information on one or more containers kill Kill one or more running containers logs Fetch the logs of a container #Get container logs ls List containers pause Pause all processes within one or more containers port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container prune Remove all stopped containers rename Rename a container restart Restart one or more containers rm Remove one or more containers run Run a command in a new container #Create and run a container start Start one or more stopped containers #Start a stop state container stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics #Display container real-time resource consumption information stop Stop one or more running containers #Stop a running container top Display the running processes of a container unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers update Update configuration of one or more containers wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
2.1 Composition of Docker Platform
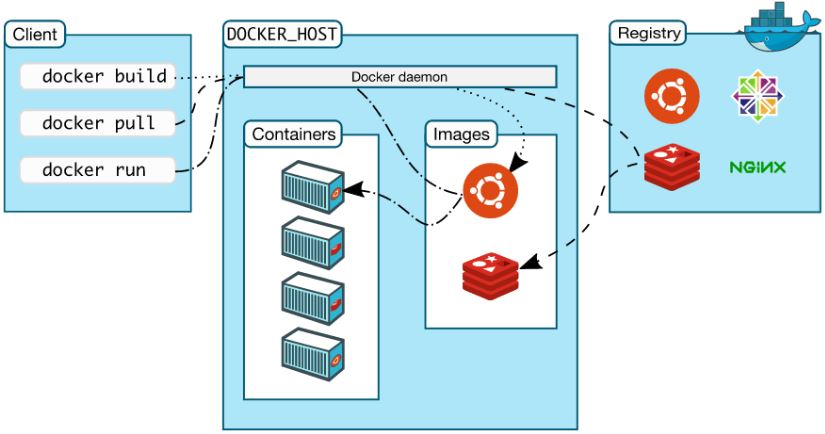
Docker platform basically consists of three parts:
- Client: Users use tools provided by Docker (CLI, API, etc.) to build, upload images and issue commands to create and start containers.
- Docker host: Download the image from Docker registry and start the container
- Docker registry: Docker image repository for storing images and providing image upload and download