This article describes in detail how to install Gitlab, Gitlab-Runner and implement CICD of the project using Docker in Linux system.
Installation of Gitlab
1. Pull up the mirror and start it
Since port 80 of the server may be occupied, we have changed to other ports to start it here.
docker run -d -p 2443:443 -p 5678:80 -p 2222:22 --name gitlab --restart always -v/srv/gitlab/config:/etc/gitlab -v /srv/gitlab/logs:/var/log/gitlab -v /src/gitlab/data:/var/opt/gitlab docker.io/gitlab/gitlab-ce
2. Modifying configuration files
Modify gitlab.yml file
vim /src/gitlab/data/gitlab-rails/etc/gitlab.yml
Find the following configuration, modify the IP or domain name that host s serve for you (can't add http://), save and exit after modification.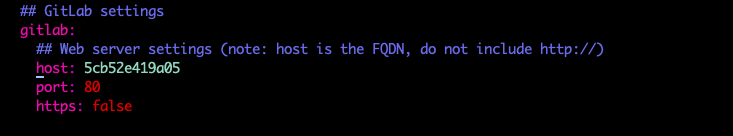
Modify the gitlab.rb file
vim /srv/gitlab/config/gitlab.rb
Find external_url, which is annotated by default. Open it and fill in the exposed http://ip:port. IP must be the same as the gitlab.yml file configuration. Port is specified for you when you start up. We have 5678 here, and finally add the IP and port used under ssh protocol (where the port is specified when you start up, we have 222 here). Finally save and exit.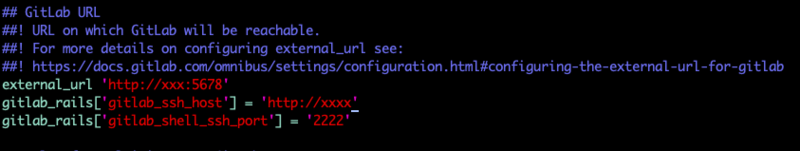
Stop and remove the gitlab that was started before
# Stop it docker stop gitlab # remove docker rm gitlab
Restart gitlab
Here, change the container port to 5678
docker run -d -p 2443:443 -p 5678:5678 -p 2222:22 --name gitlab --restart always -v/srv/gitlab/config:/etc/gitlab -v /srv/gitlab/logs:/var/log/gitlab -v /src/gitlab/data:/var/opt/gitlab docker.io/gitlab/gitlab-ce
Installation of Gitlab-Runner
You can configure `settings --> CICD --> Runner in a project, or install shared Runner on the GitLab home settings page with the same installation method.
1. Pull Runner Image and Start
docker run -d --name gitlab-runner --restart always -v /srv/gitlab-runner/config:/etc/gitlab-runner -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock gitlab/gitlab-runner:latest
2. Enter Runner Container
docker exec -it gitlab-runner bash
3. Run the following commands
gitlab-runner register
Enter the address of the Gitlab instance
Please enter the gitlab-ci coordinator URL (e.g. https://gitlab.com ) http://xxx
Input token
Please enter the gitlab-ci token for this runner xxx
Input Runner's description
Please enter the gitlab-ci description for this runner [hostname] my-runner
Enter labels associated with Runner
Please enter the gitlab-ci tags for this runner (comma separated): my-tag,another-tag
Enter Ruuner Executor
Please enter the executor: ssh, docker+machine, docker-ssh+machine, kubernetes, docker, parallels, virtualbox, docker-ssh, shell: docker
If the above executor is docker, you need to specify the docker version in. gitlab-ci.yml
Please enter the Docker image (eg. ruby:2.1): alpine:latest
With the above commands, you can see the newly created runner in gitlab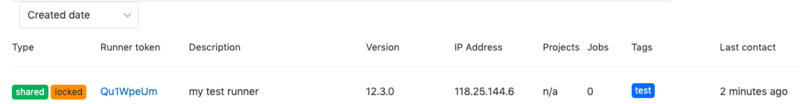
4. Modify Runner configuration file
vim /srv/gitlab-runner/config/config.toml
Find the volume configuration and modify it as follows: mount the docker of the host and configure the cache of Maven to improve efficiency
volumes = ["/cache","/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock","/data/.m2/:/.m2/"]
Add a row configuration under volume configuration to prevent Runner from repeatedly pulling mirrors
pull_policy = "if-not-present"
Restart Runner
docker restart gitlab-runner
Create SpringBook Project to Test CICD
Instead of demonstrating how to create a project and learning by SpringBoot itself, the. gitlab-ci.yml file is shown here.
1. Create a Docker file in the project root directory
FROM openjdk:8-jdk COPY target/*.jar swarm-test.jar EXPOSE 8000 ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","swarm-test.jar"]
2. Project root directory creation. gitlab-ci.yml file
# Because our Runner executor is set to docker, we need to specify the version of docker here. image: docker:stable # Define three stages stages: - compile - build - run # Define a variable to specify where the jar package downloaded by maven will be stored variables: MAVEN_OPTS: "-Dmaven.repo.local=/.m2" # Stage one compile: # maven is used for packaging, and all the maven images need to be pulled out. This is the maven image I built for my Aliyun maven private clothes. image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/gjing/maven:1.0 # Designated stage stage: compile # To run the script, use the $symbol when using variables script: - mvn $MAVEN_OPTS clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true # Act only on the master branch only: - master # tag specified when creating runner tags: - test # There are products after compilation, so specify the next expiration time and path for use at other stages artifacts: expire_in: 1 days paths: - target/*.jar # The second stage, which is no longer introduced here, is similar to the first stage. build: stage: build script: - docker build -t registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/gjing/test:1.0 . - docker login --username xxx --password xxx registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com - docker push registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/gjing/test:1.0 only: - master tags: - test run: stage: run script: - docker run -d --name my-test -p 8000:8000 registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/gjing/test:1.0 only: - master tags: - test
3. Submit the project to Gitlab warehouse
After submitting to the master branch of the warehouse, CICD will be automatically executed, which will be slower for the first time because some mirrors will be pulled and jar packages that are not currently available in the local library will be downloaded as follows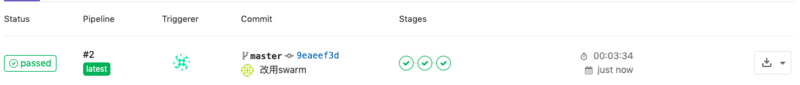
This is the end of this article. Any questions can be commented on in the comments section, or any better suggestions can be explained in the comments section.