1, docker: container based Virtualization (hosting applications to application containers) implements an application level resource isolation and quota.
What is a container?
Container: lightweight Virtualization (sharing the same system kernel). The container is run by the container image.
Advantages: high container density, fast startup, no extra overhead; disadvantages: only in linux operating system
What's the difference between virtualization and containers?
Differences: both pay attention to isolation. Virtualization is to install virtual machines on physical machines and then install a variety of operating systems (commonly used vmword, openstack and kvm are virtualization technologies); container is to directly install the container layer on the linux operating system to achieve various plate isolation
1.docker installation
Method 1: use the official installation script to install automatically
In fact, download an installation script, and then perform the installation (not recommended, because the version installation cannot be selected)
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | bash -s docker --mirror Aliyun
Method 2: install using yum, not recommended
yum install docker
In this way, you can install it directly from the CD or yum warehouse. The version is lower
Method 3: use yum add source to install the specified version, recommended
(1) Add docker CE source information
yum-config-manager --add-repo=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
(2) Update yum source: to cache the package information locally in advance, so as to improve the speed of installing search software
yum makecache fast
(3) Install docker CE
yum -y install docker-ce #The latest version is downloaded by default
① Check which docker versions are available
yum list docker-ce.x86_64 --showduplicates | sort -r
② Download the specified version, the stable version downloaded here
yum -y install docker-ce-17.03.2.ce
Test: docker version / docker -v
[root@manager yum.repos.d]# docker version Client: Docker Engine - Community Version: 19.03.12 API version: 1.40 Go version: go1.13.10 Git commit: 48a66213fe Built: Mon Jun 22 15:46:54 2020 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Experimental: false Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running? #Description the docker service is not enabled [root@manager yum.repos.d]# docker -v Docker version 1.13.1, build 64e9980/1.13.1s
2. Start service: systemctl enable --now docker
Note 1: possible problems during installation:
The reason is that the old version of docker may have been installed before. When installing, an error is reported as follows
Transaction check error: file /usr/bin/docker from install of docker-ce-cli-1:19.03.12-3.el7.x86_64 conflicts with file from package docker-common-2:1.13.1-161.git64e9980.el7_8.x86_64 file /usr/bin/dockerd from install of docker-ce-3:19.03.12-3.el7.x86_64 conflicts with file from package docker-common-2:1.13.1-161.git64e9980.el7_8.x86_64
Resolution: uninstall the old version of the package
yum remove docker-common-2:1.13.1-161.git64e9980.el7_8.x86_64
Install docker again and it will be installed successfully!
Note 2:[ root@manager ~]#Docker -- help command
2, Three cores of docker: image, container and warehouse
Image: similar to virtual machine image
Container: similar to linux system environment, running and isolating applications. When the container starts from the image, docker will create a writable layer at the top layer of the image. The image itself is read-only and remains unchanged
Warehouse: each warehouse stores a certain type of image. There are two types: docker hub shared warehouse and docker registry private warehouse. (build docker warehouse graphically)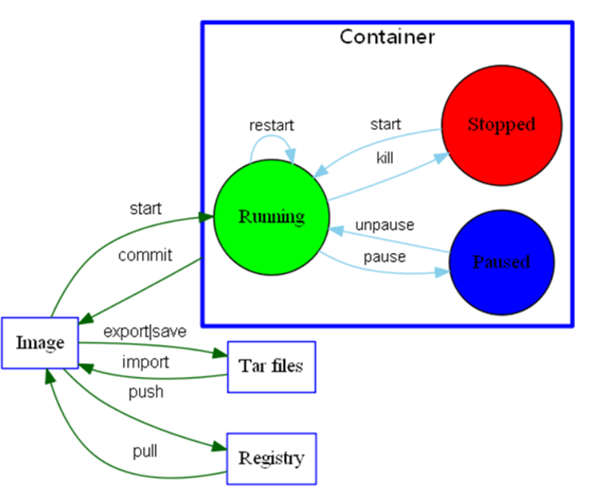
3, docker operation
1. Warehouse related orders
| docker search image name | Search image from warehouse |
|---|---|
| docker pull image name | Pull the image from the warehouse. The latest version is pulled by default |
| docker push image name | Push image to warehouse[ hub.docker.com You must register an account (docker hub registration account) on the web page to push the image to the warehouse; then use docker login on the command line to log in] |
eg1. Search image centos from warehouse
[root@manager ~]# docker search centos NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED centos The official build of CentOS. 6061 [OK] ansible/centos7-ansible Ansible on Centos7 130 [OK] consol/centos-xfce-vnc Centos container with "headless" VNC session... 116 [OK] jdeathe/centos-ssh OpenSSH / Supervisor / EPEL/IUS/SCL Repos - ... 114 ...................
eg2: pull image busybox from warehouse
[root@manager ~]# docker pull busybox Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/busybox 76df9210b28c: Pull complete Digest: sha256:95cf004f559831017cdf4628aaf1bb30133677be8702a8c5f2994629f637a209 Status: Downloaded newer image for busybox:latest docker.io/library/busybox:latest
eg3: push the image to the warehouse
hub.docker.com You must register an account (docker hub registration account) on the web page to push the image to the warehouse
docker push Image name docker login
2. Image related commands
| docker search image name | Search image |
|---|---|
| docker pull image name | Pull out image, the latest version pulled by default |
| docker image save image name > name.tar.gz | Export image |
| docker image rm image name | Delete image (to delete a running image plus - f) |
| docker image load -i filename | Import image |
| docker image ls | View the current image list |
| Docker image inspection image name | View image details |
| docker image tag image name: latest image name: tag name | Mark the image, which is usually used to push the image into the warehouse |
eg1: view the current image list, view image details, and view busybox image history
[root@manager ~]# docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE busybox latest 1c35c4412082 3 weeks ago 1.22MB [root@manager ~]# docker image inspect busybox [root@manager ~]# docker image history busybox IMAGE CREATED CREATED BY SIZE COMMENT 1c35c4412082 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) CMD ["sh"] 0B <missing> 3 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) ADD file:a84c53d2fe5207d17... 1.22MB
eg2: export image:
Method 1: docker image save image name > path location information( name.tar.gz)
[root@manager ~]# docker image save busybox > busybox1.tar.gz
Method 2: docker image save -o path location information( name.tar.gz )Image name: latest
[root@manager ~]# docker image save -o busybox2.tar.gz busybox:latest
eg3: delete image: docker image rm image name
[root@manager ~]# docker image rm busybox Untagged: busybox:latest Untagged: busybox@sha256:95cf004f559831017cdf4628aaf1bb30133677be8702a8c5f2994629f637a209 Deleted: sha256:1c35c441208254cb7c3844ba95a96485388cef9ccc0646d562c7fc026e04c807 Deleted: sha256:1be74353c3d0fd55fb5638a52953e6f1bc441e5b1710921db9ec2aa202725569 [root@manager ~]# docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE centos 7 b5b4d78bc90c 7 weeks ago 203MB
eg4: import image: docker image load -i path location information
[root@manager ~]# docker image load -i busybox1.tar.gz 1be74353c3d0: Loading layer 1.437MB/1.437MB Loaded image: busybox:latest [root@manager ~]# docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE busybox latest 1c35c4412082 3 weeks ago 1.22MB centos 7 b5b4d78bc90c 7 weeks ago 203MB
perhaps
[root@manager ~]# docker image import busybox1.tar.gz busybox:v1 sha256:70fe82f93ddc2f501380d3749e743be3e9afd3d9dfc106ae2e22c92d830f91df [root@manager ~]# docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE busybox v1 70fe82f93ddc 6 seconds ago 1.44MB centos 7 b5b4d78bc90c 7 weeks ago 203MB
eg5: mark the image: tag is generally used to push the image into the warehouse
docker image tag image name: latest image name: tag name
[root@manager ~]# docker image tag busybox:latest busybox:v1.1 [root@manager ~]# docker image tag busybox:latest busybox:v1.2 [root@manager ~]# docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE busybox latest 1c35c4412082 3 weeks ago 1.22MB busybox v1.1 1c35c4412082 3 weeks ago 1.22MB busybox v1.2 1c35c4412082 3 weeks ago 1.22MB centos 7 b5b4d78bc90c 7 weeks ago 203MB [root@manager ~]# docker image rm busybox:v1.1 busybox:v1.2 Untagged: busybox:v1.1 Untagged: busybox:v1.2 [root@manager ~]# docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE busybox latest 1c35c4412082 3 weeks ago 1.22MB centos 7 b5b4d78bc90c 7 weeks ago 203MB
docker image help command
[root@manager ~]# docker image --help Usage: docker image COMMAND Manage images Commands: build Build an image from a Dockerfile history Show the history of an image import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image inspect Display detailed information on one or more images load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN ls List images prune Remove unused images pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry push Push an image or a repository to a registry rm Remove one or more images save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default) tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE Run 'docker image COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
3. Container related orders:
| docker run image name [- i/-d/-t / – name] | Start container |
|---|---|
| docker stop container name / container ID | Stop container |
| docker kill container name / container ID | Kill running containers |
| docker rm container name / container ID | Delete container (add - f to delete running) |
| docker start container name / container ID | Activate closed container |
| docker ps | View information (status) of running containers |
| docker ps -a | View information (status) for all containers |
| docker ps -q | View the ID number of the running container |
| docker ps -aq | View ID numbers for all containers |
| Docker inspection container name / container ID | View details of a container |
| Docker exec - shell specified by it container name | Execute the specified command exec on the running container |
eg1: start container
Method 1 (not recommended):
First create a container: docker create image name
Restart container: docker start container name
[root@manager ~]# docker create busybox:latest 47f2de8f995999651498e6f0b58764214817e182ad8eff32b2b0b231f5fd3628 [root@manager ~]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 47f2de8f9959 busybox:latest "sh" 16 seconds ago Created recursing_galileo [root@manager ~]# docker start recursing_galileo recursing_galileo [root@manager ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES [root@manager ~]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 47f2de8f9959 busybox:latest "sh" 58 seconds ago Exited (0) 9 seconds ago recursing_galileo
Method 2: docker run image name [- d/-i/-t / – name], the status will be Exited if you enter and exit when you start
[root@manager ~]# docker run -it busybox:latest / # ls bin dev etc home proc root sys tmp usr var / # exit [root@manager ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES [root@manager ~]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 1fcc320d6f11 busybox:latest "sh" 23 seconds ago Exited (0) 10 seconds ago gracious_hopper 47f2de8f9959 busybox:latest "sh" 3 minutes ago Exited (0) 2 minutes ago recursing_galileo
The docker run image name [- d/-i/-t / – name], press CTRL+p, CTRL+Q, and the status is UP
[root@manager ~]# docker run -it busybox:latest / # [root@manager ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 328a8dbff50f busybox:latest "sh" 9 seconds ago Up 8 seconds vigorous_easley
Or execute in the background (- d) to make the status UP [recommended]
[root@manager ~]# docker run -idt --name c1 busybox:latest baafbd0b1a3dfe19692929cac68e29096652c277140ccdc48f2ec8bd331631ac [root@manager ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES baafbd0b1a3d busybox:latest "sh" 10 seconds ago Up 9 seconds c1
eg2: container stopped:
[root@manager ~]# docker stop vigorous_easley vigorous_easley [root@manager ~]# docker stop baafbd0b1a3d baafbd0b1a3d [root@manager ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
eg3: kill the running container
[root@manager ~]# docker kill competent_robinson competent_robinson
eg4: activate closed container:
[root@manager ~]# docker start competent_robinson competent_robinson
eg5: View container details:
[root@manager ~]# docker inspect 9f91c7213a7d [ { "Id": "9f91c7213a7dda367f8fe152403eb2b6612c2849bb9a06299e360378db3c9f8e", "Created": "2020-06-25T09:34:09.421984223Z", "Path": "/bin/sh", "Args": [], "State": { "Status": "exited", "Running": false, "Paused": false, "Restarting": false, "OOMKilled": false, "Dead": false, "Pid": 0, "ExitCode": 0,
View the ID number of the running container
[root@manager ~]# docker ps -q f658dc1f9c9f
View ID numbers of all containers
[root@manager ~]# docker ps -aq f658dc1f9c9f 328a8dbff50f baafbd0b1a3d 1fcc320d6f11 47f2de8f9959
eg6: delete container: docker rm container name or container ID
Delete all containers: query all containers IDdocker ps -aq, and add - f to delete the running
[root@manager ~]# docker rm -f `docker ps -aq` f658dc1f9c9f 328a8dbff50f baafbd0b1a3d 1fcc320d6f11 47f2de8f9959 [root@manager ~]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
eg7: execute the specified command exec on the running container:
[root@manager ~]# docker exec -it centos7 /bin/bash [root@73e57bae16bf /]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.8.2003 (Core) [root@73e57bae16bf /]# exit
Query container internal log:
docker logs
4, External access to the docker container: docker run -p (- p represents port mapping); that is, the application is hosted on the application container
1. Pull Mysql image from the warehouse
[root@manager ~]# docker pull mysql:5.6 5.6: Pulling from library/mysql 7d2977b12acb: Pull complete 5fb8400e7f07: Pull complete 234877fbb165: Pull complete 6fe1021f12f3: Pull complete 7e36fe6b53f0: Pull complete 996ec709c11b: Pull complete 5198b7523387: Pull complete cc9bdad4dcc0: Pull complete 380cd37ad979: Downloading 6.446MB/64.2MB d64465acf034: Download complete d4ee6606b3ab: Download complete 380cd37ad979: Downloading 18.26MB/64.2MB 380cd37ad979: Downloading 29.01MB/64.2MB 380cd37ad979: Pull complete d64465acf034: Pull complete d4ee6606b3ab: Pull complete Digest: sha256:2bf1a0a05a6ad437dcac6689e48a9c33774ac92c6213fce2c4196343210592f3 Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:5.6 docker.io/library/mysql:5.6
2. Start the container MySQL (and set the root password), and set the external port mapping
[root@manager ~]# docker run --name mysql -itd -p 3305:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 mysql:5.6 97be89fd63737771d36882d512f86cf484c5518de9a56848d68ca8ed31edc42c
3. Install mysql5.6 externally and check whether port 3305 listens
yum whatprovides mysql
yum install mariadb -y
[root@manager ~]# netstat -ltunp | grep 3305 tcp6 0 0 :::3305 :::* LISTEN 6379/docker-proxy
4. Access mysql container from outside
Method 1: docker exec - it MySQL - uroot - p123456
[root@manager ~]# docker exec -it mysql mysql -uroot -p123456 Warning: Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 1 Server version: 5.6.48 MySQL Community Server (GPL) Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql> select version(); +-----------+ | version() | +-----------+ | 5.6.48 | +-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> exit Bye
Method 2: mysql-uroot-p-h172.17.0.2
[root@manager ~]# mysql -uroot -p -h172.17.0.2 Enter password: Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 2 Server version: 5.6.48 MySQL Community Server (GPL) Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MySQL [(none)]> exit Bye
Note: external users cannot access mysql directly because they do not have permission