1. Comparison between docker and virtual machine
Compared with traditional virtual machines, Docker has fast startup speed and small footprint.
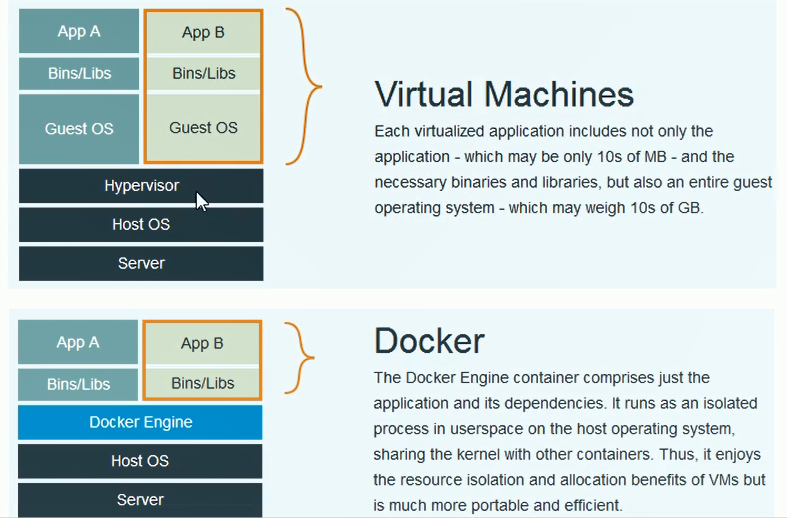
2. Docker component
2.1 docker server and client

2.2 docker image and container
Mirroring is the foundation for building containers.
2.3 Registry registry
Used to save user built images. It is divided into public and private.
3. Docker installation and startup
3.1 installation
Installation steps
# Update yum package sudo yum update # Install the required packages. Yum util provides the yum config manager function. The other two functions are dependent on the devicemapper driver. sudo yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 # Set the yum source to alicloud sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo # Install docker sudo yum install docker-ce # Check docker version after installation docker -v
Set as domestic image
Steps:
# Edit the daemon.json file
vi /etc/docker/daemon.json
# Enter the following in this file:
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://tnxkcso1.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
# Or http://docker.mirrors.ustc.edu.cm
3.2 viewing the start and stop status of docker service
The systemctl command is a command of the system service manager
# Start docker systemctl start docker # Stop docker systemctl stop docker # Restart docker systemctl restart docker # View docker status systemctl status docker # Set docker startup self startup systemctl enable docker # View docker profile docker info # View docker help documentation docker --help
4. Common docker commands
4.1 image related commands
4.1.1 view image [docker images]
docker images Image name Label (version) image ID Creation time Occupancy size REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE consul latest b74a0a01afc4 8 weeks ago 116MB
There is a problem when using docker images here. The questions are as follows:

I then used the service docker status to check the running status of dockers and found that dockers are active (running).
When I restart docker with sudo service docker restart command, I find the docker images command. Success!
4.1.2 search image [docker search [imageName]]
docker search <imageName> # Example: [root@localhost ~]# docker search eureka #Image name Mirror description stars Is it official Created by dockerHub auto build flow NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED springcloud/eureka Spring Cloud Eureka Server 74 netflixoss/eureka Eureka NetflixOSS container image 69 [OK]
4.1.3 pull image [docker pull [imageName]]
docker pull <imageName> # Download centos7 image docker pull centos:7
4.1.4 delete image [docker rmi imageId]
# Delete image by image id docker rmi imageId # Delete all mirrors docker rmi `docker images -q`
4.2 container related commands
4.2.1 viewing containers [ docker ps ]
docker ps # Viewing stopped containers docker ps -f status=exited
4.2.2 create and start container [docker run]
# Create container docker run
Command parameters:
-i: Represents a running container
-t: Indicates that the container enters its command line after it is started. After adding these two parameters, the container creation can log in. That is, a pseudo terminal is assigned.
--Name: name the created container.
-v: Indicates the directory mapping relationship (the former is the host directory, and the latter is the directory mapped to the host). You can use multiple "- V" to map multiple directories or files. Note: it's best to do directory mapping, modify it on the host, and then share it on the container.
-d: Add "- D" parameter after run to create a daemon container to run in the background (so that the container will not be logged in automatically after the container is created. If only "- i-t" parameter is added, it will automatically enter the container after creation).
-p: Represents port mapping. The former is the host port and the latter is the port in the container. You can do multiple port mapping.
Note: all hosts here are relative to docker.
- Create containers interactively
## Example: observe the address in the second line and find that it has changed from localhost to the command line of docker container. And it is useless to enter docker ps here. [root@localhost ~]# docker run -it --name=mycentos centos:7 /bin/bash [root@18ae6d4771c0 /]# docker ps bash: docker: command not found #### Use the exit command to exit the container [root@18ae6d4771c0 /]# exit exit # Note: for containers that run interactively, when you exit with the exit command, the container will also exit. [root@localhost ~]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 18ae6d4771c0 centos:7 "/bin/bash" 4 minutes ago Exited (127) About a minute ago mycentos
- Create containers in a guarded manner
# Create container [root@localhost ~]# docker run -di --name mycentos2 centos:7 299409ff68afa7be21e2e7573c6e9e7e55624f567cfdd2db8c55e673909d097e # View container status [root@localhost ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 299409ff68af centos:7 "/bin/bash" 29 seconds ago Up 29 seconds mycentos2 # Enter container [root@localhost ~]# docker exec -it mycentos2 /bin/bash [root@299409ff68af /]# exit exit # Note: containers created in a guard mode are still running after exiting. [root@localhost ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 299409ff68af centos:7 "/bin/bash" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes mycentos2