1. Basic Commands
1.Help Command
# Display docker version information docker version # Show docker system information docker info # Show help commands (optional fill-in commands for more detailed information) docker help [command] perhaps docker [COMMAND] --help
"Explanation"
- []: Omittable
- COMMAND: Command
2.Mirror Command
2.1 View all mirrors
#View all mirroring information on the local host
docker images [OPTIONS] [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
Options:
-a, --all List all local mirrors (with intermediate layers)
--digests Display summary information for the mirror
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print images using a Go template
--no-trunc Show complete mirror information
-q, --quiet Show only mirrors ID
#View all mirror IDs on the local host
docker images -aq 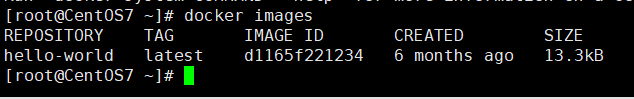
"List Explanation"
- "REPOSITORY: Mirrored repository source"
- "TAG: Mirrored Label"
- "IMAGE ID: id of the mirror"
- "CREATE: Creation time of mirror"
- "SIZE: Size of Mirror"
"Explanation"
- OPTIONS: Optional
There can be multiple TAGs for the same warehouse source, representing different versions of this warehouse source. We use REPOSITORY:TAG to define different mirrors.
If you do not specify a version label for a mirror, such as if you only use ubuntu, docker will default to the ubuntu:latest image.
2.2 Search Mirror
# Search for Mirrors (Search on Docker Hub)
docker search [OPTIONS] Mirror Name
Options:
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print search using a Go template
--limit int Max number of search results (default 25)
--no-trunc Show full mirror description
# Conditional Filter Search Results (Lists mirrors with no less than a specified number of collections)
docker search --filter=STARS=50 Mirror Name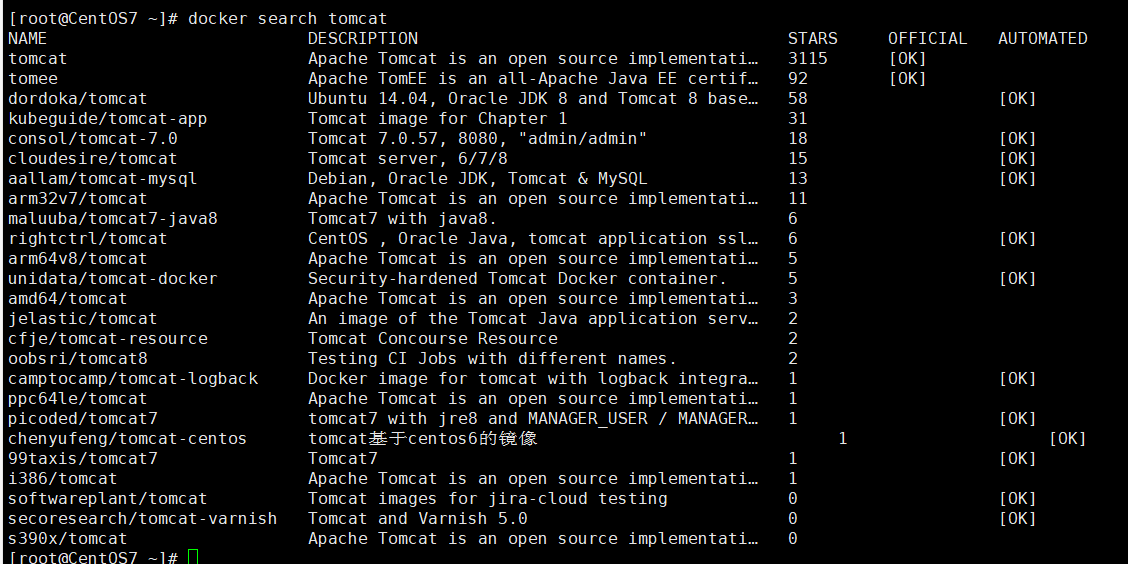
"List Explanation"
- "NAME: Mirror Name"
- "DESCRIPTION: Introduction to Mirrors"
- "stars: Mirrored stars"
- "OFFICIAL: Official or not"
- "AUTOMATED: Is it automated"
2.3 Pull mirror
# Pull the latest mirror by default
docker pull [OPTIONS] NAME[:TAG|@DIGEST]
Options:
-a, --all-tags Download all tagged images in the repository
--disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true)
--platform string Set platform if server is multi-platform capable
-q, --quiet Suppress verbose output
# Specified version download
docker pull mysql:5.72.4 Delete Mirror
#delete mirror
docker rmi [OPTIONS] IMAGE[:TAG] [IMAGE...]
Options:
-f, --force Force Delete Mirror
--no-prune Do not delete untagged parents
#Delete the image of the specified version with the specified name
docker rmi mysql:5.7
#Force deletion of a single image with a unique mirror name
docker rmi -f Mirror Name[:TAG]
#Delete the mirror for a single specified id
docker rmi image ID[:TAG]
#Delete mirrors for multiple specified IDS
docker rmi image ID[:TAG] image ID[:TAG] image ID[:TAG]
#Iteratively delete all mirrors
docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq)
3.Container commands
3.1 Run Mirror
#Create a new container and start it (if the mirror is not available locally, it will automatically go to Hub to pull it)
docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
Options:
--name="Container New Name" Specify a name for the container and if not, it will be randomly assigned by default
-d Run the container in the background and return to the container ID,That is, start a daemon container
-i Run containers in interactive mode, usually with-t Use simultaneously
-t Reassign a pseudo input terminal to a container, usually with-i Use simultaneously
-P Random Port Mapping
-p Specify port mappings in the following four formats:
ip:hostPort:containerPort
ip::containerPort
hostPort:containerPort
containerPort
# Run Instance
#-Lowercase p host port: docker container port
#-Uppercase P randomly assigned port
docker run --name=tomcat1 -d -p 8080:8080 tomcat (Run in the background)
docker run --name=tomcat1 -it -P tomcat (Foreground running)
# Delete when used up
docker run -it --rm tomcat
# Specify environment variables (instances)
docker run -d --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" -e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms64m -Xmx512m" elasticsearch:7.6.2
"Parameter Description"
- "--name="Name": Container names such as tomacat01, tomacat02 are used to distinguish containers"
- "-e: Specify environment variables"
- "-d: Background daemon running (start daemon container)"
- "-it: Run interactively, enter the container to view content (launch the interactive container)"
- "-p: Port of the specified container - p 8080:8080"
- "-p: host port: container port"
- "-p: container port"
- "-P: randomly assigned port"
- "-v: Specify data volume"
- "-v container file location: Host File Location"
- "--volumes-from: Specify volume sharing for containers (synchronize whose data you specify! Inherit!)"
- "--volumes-from: inherited from that container" (parent container deletion does not affect existing data)
- "--net:default bridge"
3.2 Enter container
# Run a centos and enter the container docker run -it centos /bin/bash # Exit Container exit
3.3 View Containers
docker ps [OPTIONS]
Options:
-a, --all List all currently running containers+Historically run
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print containers using a Go template
-n, --last int Show Recent n Containers created by
-l, --latest Show recently created containers
--no-trunc Do not truncate output
-q, --quiet Silent mode, display only container number
-s, --size Display total file sizes
# View running containers
docker ps
# View all containers
docker ps -a3.4 Exit Container
# Direct container stops and exits exit # Container does not stop exiting Ctrl + P + Q
3.5 Delete Container
# Delete closed specified container docker rm bde00bc086cf # Force removal of running containers docker rm -f bde00bc086cf # Iteratively delete all containers docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq)
Start and Stop of 3.6 Container
# Start Container docker start container ID Or container name # Restart Container docker restart container ID Or container name # Stop Container docker stop container ID Or container name # Force Kill Container docker kill container ID Or container name
3.7 Enter a running container and interact with the command line
# Enter the specified container for modification to open a new terminal (opens a new terminal in the container, does not start a new process) docker exec -it container ID [/bin/bash] # Enter the executing terminal (directly into the terminal of the container start command, no new process will be started) docker attach container ID #The following are the advantages of exec #Return results directly without entering the specified container (do not write/bin/bash and use commands) docker exec -it container ID ls #Enter the specified container before operation docker exec -it container ID [/bin/bash] ls
3.8 Copy files from container to host
docker cp container ID:Path to Files in Container Host Path #Example docker cp 0cd4d9d94de2:/Test.java /Test.java
3.9 Other Common Commands
"View Log Command"
docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Options:
--details Show extra details provided to logs
-f, --follow Follow the latest log printing
--since string Show logs since timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37Z) or
relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
-n, --tail string Number of rows displayed from the end of the log(Default is " all"),That is, how many last bars are displayed
-t, --timestamps presentation time stamp
--until string Show logs before a timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37Z) or
relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
# View logs generated by container operation
docker logs -ft --tail 10 container ID "Parameter resolution:"
- "f: Formatted Log"
- "t: Carry Log Timestamp"
"View Progress"
# View information such as cpu (view processes running inside containers) docker top container ID
"View Container Meta Information"
# View container meta information (see container internal details) docker inspect container ID
2. Visualization Panel
1. Installation
# Install the visualization panel portainer (data volume path cannot be changed) docker search portainer docker pull portainer/portainer #Single-machine startup docker run -d -p 9000:9000 --restart=always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --privileged=true portainer/portainer
3. The submission container is a mirror
1. Submit Container
# Submit a copy of the container to become a new image (package the container) docker commit [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [REPOSITORY[:TAG]] Options: -a, --author string author(e.g., "John Hannibal Smith <hannibal@a-team.com>") -c, --change list Apply Dockerfile instruction to the created image -m, --message string Descriptive information submitted -p, --pause Pause container during commit (default true) # Sample Code Submission docker commit -a="thq" -m="Deleted document page" 65a83de5805c guigu/mytomcat:1.0 Remarks: guigu Is Namespace
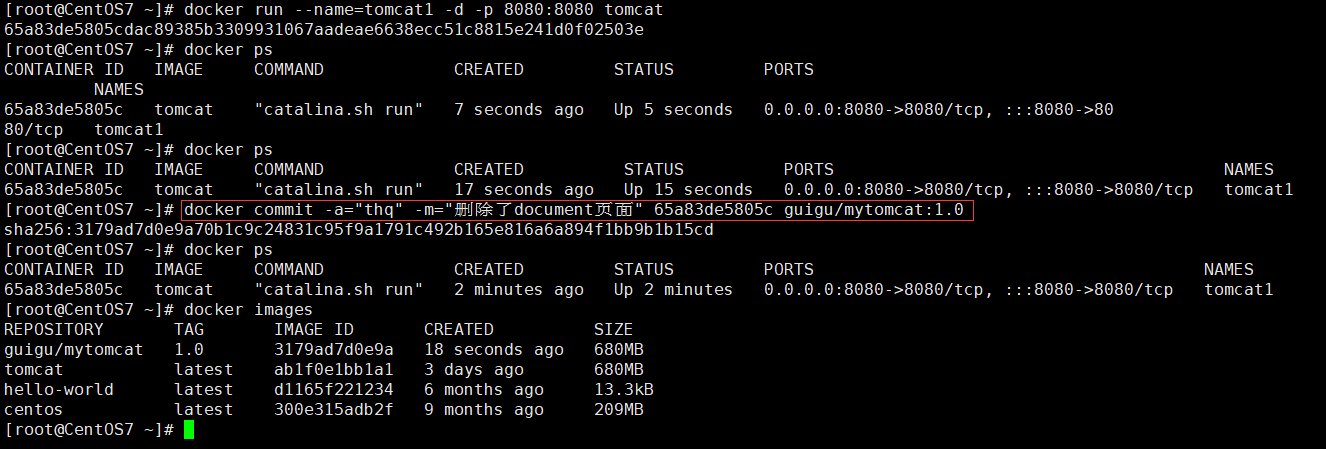 "Parameter Explanation:"
"Parameter Explanation:"
- "-a:author"
- "-m: Remarks"
- "-c: Apply the Dockerfile directive to the created image"
- "-p: Suspend container during submission (default is true)"
- "REPOSITORY: Target Mirror Name to Create"
4. Docker data volume usage
1. Basic use of data volumes
#Add directly named # Associated Data Volume docker run [Optional parameters] -v /Host Path/:/Container Path/ Mirror Name //View Binding Status docker inspect container ID # Instance commands for associating data volumes docker run it -v /Host absolute path directory:/Name of directory image in container or docker run it -v /Host absolute path directory:/Container contents:ro Mirror Name(Container read-only permissions added) or docker run -d -p 8080:8080 --name mytomcat -v /home/tomcat/webapps/:/usr/local/tomcat/webapps tomcat #Add as Dockerfile stay Dockerfile Use VOLUME Reserved word directives define container data volumes for data preservation and persistence
Remarks:
Docker mount Host Directory Docker access cannot open directory.: Permission denied
Solution: Add an additional--privileged=true parameter after mounting the directory
2.mysql Installation Actual
docker run -d -p 3366:3306 -v /home/mysql/conf:/etc/mysql/conf.d -v /home/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 --name mysql01 mysql:5.7
"Command Resolution:"
- "-d: daemon running"
- "-v: Add data volume (host and container location mapping)"
- "-p:heap mapping port out"
- "-e: Specify environment variables"
- "--name:container name"
5. Dockerfile
1.Build Mirror File
# Create a Dockerfile vim Dockerfile FROM centos VOLUME ["volume01","volume02"] CMD echo "-----end---" CMD /bin/bash :x # Building a docker image # Path to -f dockerfile # -t Generated Mirror Name # .Package in the context of the current path docker build -f /home/docker-volom/Dockerfile -t thq/centos:1.0 . # Build Basic Commands docker build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -
2.Dockerfile concepts
Dockerfile is a build file used to build a Docker image and is a script composed of a series of commands and parameters.
- Each reserved keyword (instruction) must be an uppercase letter
- Execution order from top to bottom
- #indicates a comment
- Each instruction creates and submits a new mirror layer!
3.A Brief Analysis of Dockerfile Grammar
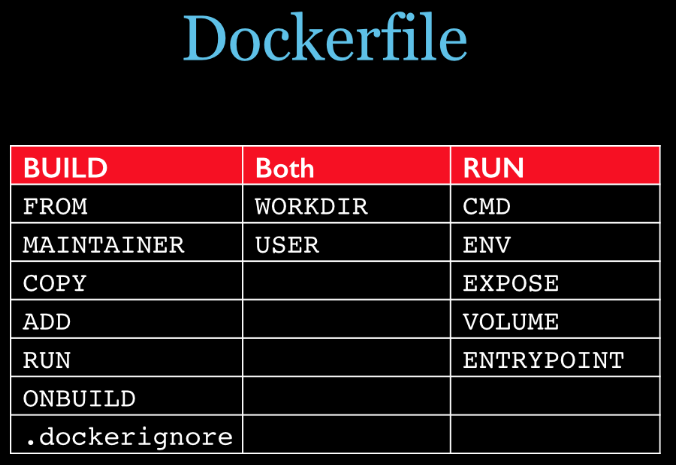
- "FROM: Basic Mirror, which mirror is the current new mirror based on. Everything is built from here."
- "MAINTAINER: Who wrote the mirror, name + mailbox"
- "RUN: Command to run when building a mirror"
- "ADD: Copies files from the host directory into the mirror and the ADD command automatically processes URL s and decompresses tar packages"
- "WORKDIR: Mirrored working directory, specifying the incoming working directory where the terminal logs in by default, a foothold, after the container is created."
- "VOLUME: Container data volume for data preservation and persistence work"
- "EXPOSE: Port Exposed by Current Container"
- "CMD: Specifies the command to run at startup of this container. Only the last CMD command will be valid. CMD will be replaced by parameters after docker run."
- "ENTRYPOINT: Specify the command to run when this container starts! Commands can be appended!"
- "ONBUILD: Run a command when building an inherited Dockerfile, the parent image is inherited by the child image and the onbuild of the parent image is triggered."
- "COPY: ADD-like, copy files and directories into the mirror"
- "ENV: Set environment variables when building"
# Build a centos with a complex command line vim Dockerfile # Mirror inherits from centos FROM centos # Author Information MAINTAINER thq<********@163.com> # Setting environment variables ENV MYPATH /usr/local # Set Working Directory WORKDIR $MYPATH # Execute command installation instructions RUN yum -y install vim RUN yum -y install net-tools # Expose Port EXPOSE 80 # Execute some instructions CMD echo "-------end------" CMD echo $MYPATH CMD /bin/bash :x # Build Mirror docker build -f /home/docker-volom/Dockerfile -t thq/mycentos:1.0 . Note: If not written-f /home/docker-volom/Dockerfile,Indicates that there will be one in the current directory Dockerfile Named files are executed so they can be omitted. #Custom Mirror Tomcat9 FROM centos MAINTAINER zzyy<zzyybs@126.com> #Copy c.txt of the host's current context to container/usr/local/path COPY c.txt /usr/local/cincontainer.txt #Add java and tomcat to the container ADD jdk-8u171-linux-x64.tar.gz /usr/local/ ADD apache-tomcat-9.0.8.tar.gz /usr/local/ #Install vim editor RUN yum -y install vim #Set WORKDIR path and login destination for work access ENV MYPATH /usr/local WORKDIR $MYPATH #Configuring java and tomcat environment variables ENV JAVA_HOME /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_171 ENV CLASSPATH $JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar ENV CATALINA_HOME /usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.8 ENV CATALINA_BASE /usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.8 ENV PATH $PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$CATALINA_HOME/lib:$CATALINA_HOME/bin #Port on which the container listens while it is running EXPOSE 8080 #Run tomcat at startup # ENTRYPOINT ["/usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.8/bin/startup.sh" ] # CMD ["/usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.8/bin/catalina.sh","run"] CMD /usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.8/bin/startup.sh && tail -F /usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.8/bin/logs/catalina.out #Build Mirror docker build -t zzyytomcat9 . #run docker run -d -p 9080:0880 --name myt9
#Real Dockerfile case for our project
FROM reg.ygops.com/os/alpine:openjdk8
LABEL maintainer sunkai
ADD http://res.ygops.com/sps/tools/simsun.ttf /usr/share/fonts/simsun/simsun.ttf
ADD ./target/blade-warehouse.jar /app.jar
RUN set -x \
&& apk add --no-cache ttf-dejavu fontconfig
EXPOSE 8101
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom", "-jar", "app.jar"]4.Summary of Dockerfile
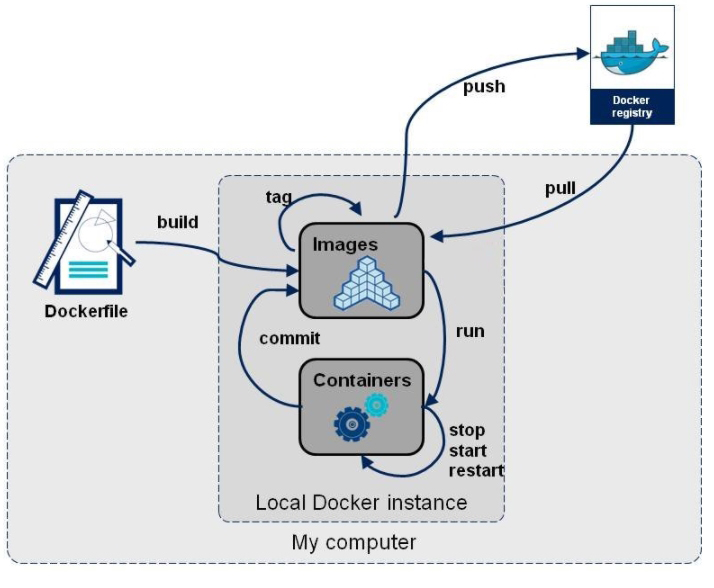
6. Custom Network
1.Network Mode Details
- "bridge: bridged network (default)"
- "Host: share with host"
- "none: no network configured"
- "Container: container network connectivity"
2.View all network modes
# View all network modes docker network ls
3.Create a custom network
# Create a network docker network create [OPTIONS] NETWORK # Create a mynet # create creation # Network mode used by driver # subnet Subnet Mask # Gateway gateway # mynety custom name docker netywork create --driver bridge --subnet 192.168.0.0/16 --gateway 192.168.0.1 mynety
4.Use a custom network
docker run -d --net mynety --name tom01 tomcat docker run -d --net mynety --name tom02 tomcat # Enter tom02 docker exec -it 7d75a637a90b865fe70259bd4e0b3f5c95133dc65693b05abaf078d31a362529 /bin/bash # Results are interoperable ping tom01
5.Container Network Interoperability
# Open Custom Networks and Containers Containers One Container Two IPS # Add containers that are not on the network to the current network docker network connect Custom Network Container
7. Packaging SpringBoot jar projects
1.Writing Dockerfile
FROM java:8 COPY *.jar /app.jar CMD ["--server.port=8080"] EXPOSE 8080 ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app.jar"]
2.Build Mirror
mkdir idea cd idea # Send Dockerfile and jar package to idea directory # Build Mirror docker build -t thqtest:1.0 . # Later run slightly
