In the object-oriented world, Class is the foundation of Java. java.lang.Class is actually inherited from java.lang.Object.
Class has a method called getName, which returns the class name of (class, interface, array class, primitive type, or void).
If you often debug the JVM, you will see the following strange things:
jcmd 1234 GC.class_histogram
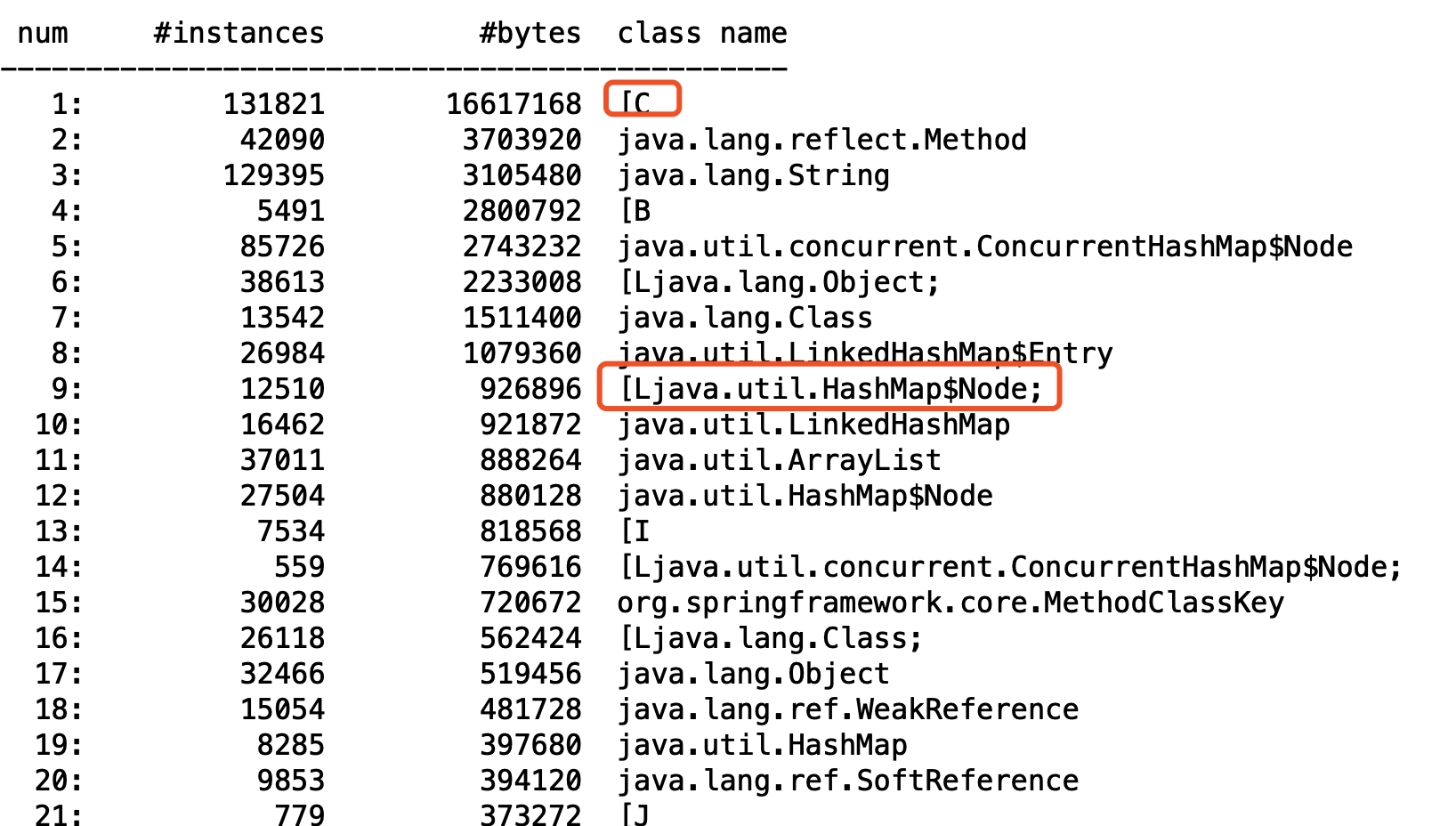
These strange contents are class name. Let's see what they mean.
class name is actually divided into three categories.
primitive type or void
If class objects are primitive or void, their class name is the corresponding keyword or void.
//primary class log.info(int.class.getName()); log.info(short.class.getName()); log.info(float.class.getName()); log.info(double.class.getName()); log.info(long.class.getName()); log.info(byte.class.getName()); log.info(char.class.getName()); log.info(boolean.class.getName()); //void log.info(void.class.getName());
Output results:
[main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - int [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - short [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - float [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - double [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - long [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - byte [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - char [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - boolean [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - void
reference type
If it is a reference type, the class name of the class will be returned:
//object class log.info(Object.class.getName());
Output results:
[main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - java.lang.Object
Array type
Array type is a bit complex. According to the hierarchical relationship of array, we will add [, and add as many [, as many levels as there are.
At the same time, the corresponding type will be converted to the corresponding code:
| Element type | Code |
|---|---|
| boolean | Z |
| byte | B |
| char | C |
| class or interface | Lclassname; |
| double | D |
| float | F |
| int | I |
| long | J |
| short | S |
Let's take an example:
//Array log.info(int[].class.getName()); log.info(short[].class.getName()); log.info(float[].class.getName()); log.info(double[].class.getName()); log.info(long[].class.getName()); log.info(byte[].class.getName()); log.info(char[].class.getName()); log.info(boolean[].class.getName()); log.info(Object[].class.getName()); //multiple arrays log.info(int[][][].class.getName());
Output results:
[main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - [I [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - [S [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - [F [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - [D [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - [J [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - [B [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - [C [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - [Z [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - [Ljava.lang.Object; [main] INFO com.flydean.classname.ClassNameUsage - [[[I
summary
OK, is the output of jcmd above understandable?
Examples of this article https://github.com/ddean2009/learn-java-base-9-to-20
Author of this article: the flydean program
Link to this article: http://www.flydean.com/java-class-name/
Source: flydean's blog
Welcome to my official account: the procedures, the more wonderful things waiting for you!