The book continues from the above. The previous article introduced the slightly simple synchronous fifo, and then began the more complex asynchronous fifo.
1. Difference between synchronous fifo and asynchronous fifo
When there is only one clock in the design, whether all registers use the same one, there will be no transmission speed mismatch; However, when there are multiple clock signals in the design and data is transmitted in these clock domains, data loss may occur due to clock signal mismatch. At this time, asynchronous fifo needs to cache data to ensure normal data transmission. Therefore, generally asynchronous fifo will include a dual port ram
2. Asynchronous fifo composition
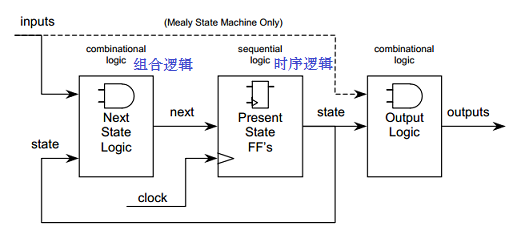
Figure 1. Asynchronous fifo
Module composition (6): top-level module, dual port RAM, 2 cross clock domain synchronous pointer modules, null judgment logic and full judgment logic.
3. Precautions
1) Avoid using binary counters to implement pointers, because if the current value is carried by one, all bits may change, and the error rate may increase. eg:0111 plus 1 will become 1000, and three of them will change, so the error rate will be increased.
2) To solve the above problems, it is recommended to directly use gray code counting.
3) Define more than one bit of the pointer's bit width. For example, suppose you want to design an asynchronous FIFO with a depth of 8. At this time, only 3 bits (2 ^ 3 = 8) are needed to define the read-write pointer. However, we design the pointer's bit width to 4 bits in the design. The function of the highest bit is to distinguish whether to read null or write full. Specific theory 1 As follows, when the highest bit is the same, the other bits are the same, it is considered to be read empty; When the highest bit is different and the other bits are the same, it is considered to be full
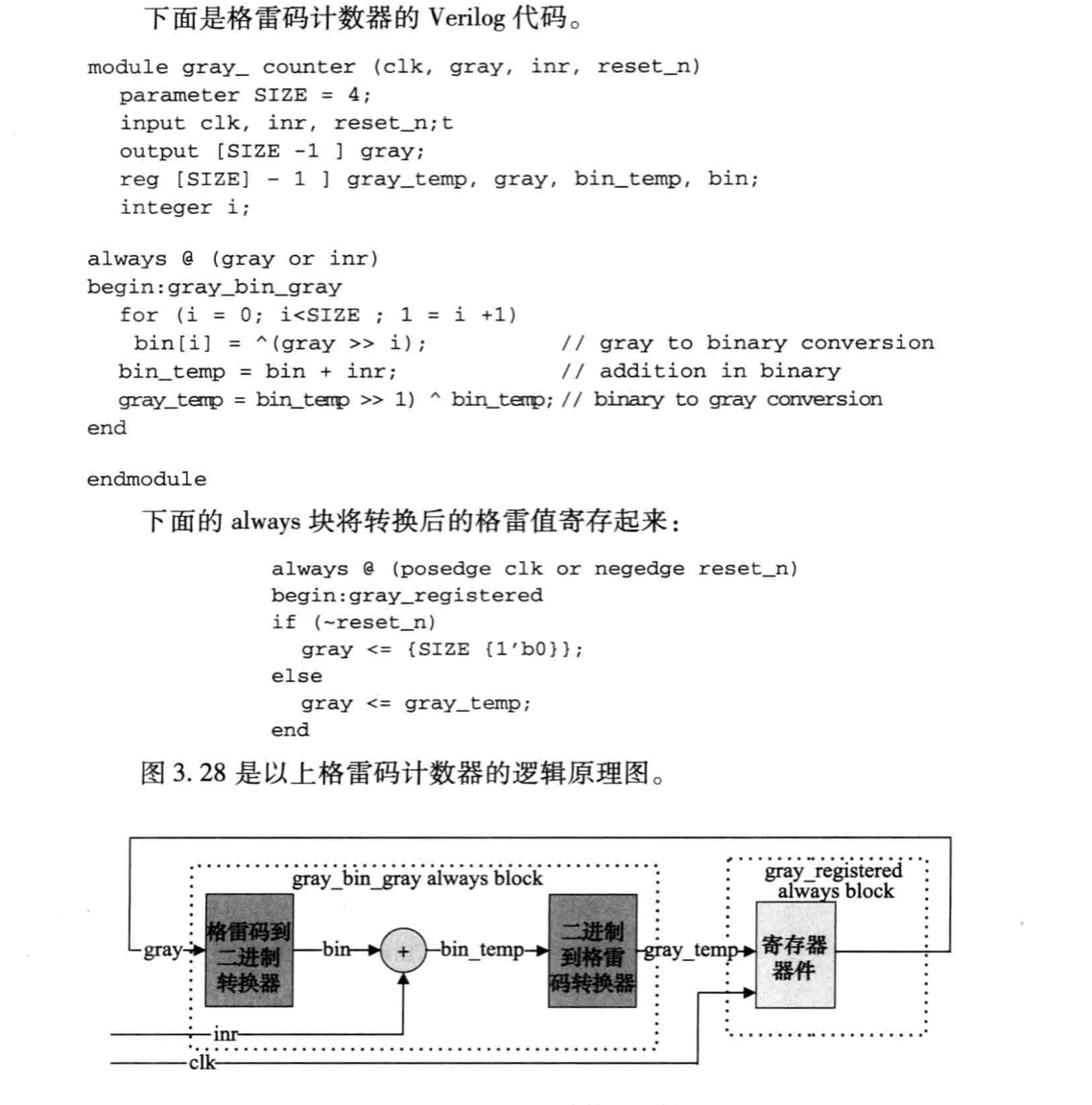
Design concept of gray code counter: Gray code to binary converter, adder, binary code to gray code converter, register for saving gray value
3. Corresponding module code segment
1) Top level module
//************Top level module************************* `timescale 1 ns/ 1 ps module asyn_fifo_top #( parameter DATA_WIDTH = 8, parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 4, parameter RAM_DEPTH = 16 ) ( input WCLK, input WRSTn, input RCLK, input RRSTn, input write, input read, input [ DATA_WIDTH - 1 : 0 ] wdata, output [ DATA_WIDTH - 1 : 0 ] rdata, output full, output empty ); wire [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] wpt; wire [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] rpt; wire [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] rp2_wpt; wire [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] wp2_rpt; wire [ ADDR_WIDTH - 1: 0 ] waddr; wire [ ADDR_WIDTH - 1: 0 ] raddr; double_ram#(.DATA_WIDTH(DATA_WIDTH), .ADDR_WIDTH(ADDR_WIDTH), .RAM_DEPTH(RAM_DEPTH)) ram_module (.WCLK(WCLK), .write(write), .waddr(waddr), .wdata(wdata), .raddr(raddr), .rdata(rdata)); r2w_sync #(.ADDR_WIDTH(ADDR_WIDTH)) r2w_module (.WCLK(WCLK), .WRSTn(WRSTn), .rpt(rpt), .rp2_wpt(rp2_wpt)); w2r_sync #(.ADDR_WIDTH(ADDR_WIDTH)) w2r_module (.RCLK(RCLK), .RRSTn(RRSTn), .wpt(wpt), .wp2_rpt(wp2_rpt)); full#(.ADDR_WIDTH(ADDR_WIDTH)) full_module(.WCLK(WCLK), .WRSTn(WRSTn), .write(write), .rp2_wpt(rp2_wpt), .wpt(wpt), .waddr(waddr), .full(full)); empty #(.ADDR_WIDTH(ADDR_WIDTH)) empty_module(.RCLK(RCLK), .RRSTn(RRSTn), .read(read), .wp2_rpt(wp2_rpt), .rpt(rpt), .raddr(raddr), .empty(empty)); endmodule
3.2 RAM module
//******************Dual interface RAM****************** module double_ram#( parameter DATA_WIDTH = 8, parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 4, parameter RAM_DEPTH = 16 ) ( input WCLK, //write clk input write, //write en input [ ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0 ] waddr, //write address from full.v input [ DATA_WIDTH - 1:0 ] wdata, //write data input [ ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0 ] raddr, //read address from empty.v output [ DATA_WIDTH - 1:0 ] rdata //read data ); reg [ DATA_WIDTH - 1:0 ] RAM [ RAM_DEPTH - 1:0 ]; //double Port ram always @ ( posedge WCLK ) begin if ( write == 1'b1 ) begin RAM [ waddr ] <= wdata; end else begin RAM [ waddr ] <= RAM [ waddr ]; end end assign rdata = RAM [ raddr ]; endmodule
3) Judge full logic module
//*****************Judge full logic****************
module full#(
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 4
)
(
input WRSTn,
input WCLK,
input write,
input [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] rp2_wpt,
output reg [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] wpt,
output [ ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0 ] waddr,
output reg full
);
reg [ ADDR_WIDTH :0 ] wbin;
wire [ ADDR_WIDTH :0 ] wbin_next;
wire [ ADDR_WIDTH :0 ] wgray_next;
wire full_reg;
always @ ( posedge WCLK or negedge WRSTn )
begin
if (!WRSTn)
begin
wpt <= 0;
wbin <= 0;
end
else
begin
wpt <= wgray_next;
wbin <= wbin_next;
end
end
assign wbin_next = ( !full ) ? ( wbin + write ) : wbin;
assign wgray_next = ( wbin_next >> 1 ) ^ wbin_next;
assign waddr = wbin [ ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0 ];
always @ ( posedge WCLK or negedge WRSTn )
begin
if (!WRSTn)
begin
full <= 0;
end
else
begin
full <= full_reg;
end
end
assign full_reg = ( wgray_next == { -rp2_wpt [ ADDR_WIDTH : ADDR_WIDTH - 1],rp2_wpt [ ADDR_WIDTH - 2:0]});
endmodule 4) Determine whether it is a null pointer
//********************Judge whether it is empty logic************ module empty#( parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 4 ) ( input RRSTn, input RCLK, input read, input [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] wp2_rpt, output reg [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] rpt, output reg [ ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0 ] raddr, output reg empty ); reg [ ADDR_WIDTH :0 ] rbin; wire [ ADDR_WIDTH :0 ] rbin_next; wire [ ADDR_WIDTH :0 ] rgray_next; wire empty_reg; always @ ( posedge RCLK or negedge RRSTn ) begin if (!RRSTn) begin rpt <= 0; rbin <= 0; end else begin rpt <= rgray_next; rbin <= rbin_next; end end assign rbin_next = ( !empty ) ? ( rbin + read ) : rbin; assign rgray_next = ( rbin_next >> 1 ) ^ rbin_next; //assign raddr = rbin [ ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0 ]; always @ ( posedge RCLK or negedge RRSTn ) begin if (read) begin raddr <= rbin [ ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0 ]; end end always @ ( posedge RCLK or negedge RRSTn ) begin if (!RRSTn) begin empty <= 0; end else begin empty <= empty_reg; end end assign empty_reg = ( rgray_next == wp2_rpt ); endmodule
5) Read write cross clock domain
//****************Read write cross clock domain****************
module r2w_sync#(
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 4
)
(
input WRSTn, //write RSTn
input WCLK, //write CLK
input [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] rpt, //output to write port gray
output reg [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] rp2_wpt //D trigger sync with two levels,second level
);
reg [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] rp1_wpt; //frist level
//reg [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] rp2_wpt;
always @ ( posedge WCLK or negedge WRSTn )
begin
if ( !WRSTn )
begin
{ rp2_wpt,rp1_wpt } <= 0;
end
else
begin
{ rp2_wpt,rp1_wpt } <= { rp1_wpt,rpt };
end
end
endmodule6) Write read cross clock domain
/**Write to Read Sync module**/
module w2r_sync#(
parameter ADDR_WIDTH = 4
)
(
input RRSTn, //read RSTn
input RCLK, //reaf CLK
input [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] wpt, //output to read port gray
output reg [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] wp2_rpt //D trigger sync with two levels,second level
);
reg [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] wp1_rpt; //frist level
//reg [ ADDR_WIDTH : 0 ] wp2_rpt;
always @ ( posedge RCLK or negedge RRSTn )
begin
if ( !RRSTn )
begin
{ wp2_rpt,wp1_rpt } <= 0;
end
else
begin
{ wp2_rpt,wp1_rpt } <= { wp1_rpt,wpt};
end
end
endmodule
4.tb
`timescale 1 ns/ 1 ps
module asyn_fifo_tb();
parameter DATA_WIDTH = 8;
reg WCLK;
reg WRSTn;
reg RCLK;
reg RRSTn;
reg write;
reg read;
reg [ DATA_WIDTH - 1 : 0 ] wdata;
wire [ DATA_WIDTH - 1 : 0 ] rdata;
wire full;
wire empty;
//integer i = 0;
asyn_fifo_top asyn_fifo(.WCLK(WCLK),
.WRSTn(WRSTn),
.RCLK(RCLK),
.RRSTn(RRSTn),
.write(write),
.read(read),
.wdata(wdata),
.rdata(rdata),
.full(full),
.empty(empty));
initial
begin
WCLK <= 0;
forever #100 WCLK = ~WCLK;
end
initial
begin
RCLK <= 0;
forever #200 RCLK = ~RCLK;
end
initial
begin
WRSTn = 0;
wdata = 0;
#100 WRSTn = 1;
end
initial
begin
RRSTn = 0;
#100 RRSTn = 1;
#10000;
$finish();
end
always @ ( posedge WCLK or negedge WRSTn )
begin
wdata <= wdata + 1'b1;
end
//always @(posedge WCLK or negedge WRSTn)
//begin
// if(WRSTn==1'b0)
// begin
// i <= 0;
// end
// else if(!full)
// begin
// i = i+1;
// end
// else begin
// i <= i;
// end
//end
//always @ (*)
//begin
// if (!full)
// wdata = i;
// else
// wdata = 0;
//end
always @ ( full or WRSTn )
begin
if (!WRSTn)
begin
write <= 0;
end
else if (!full)
begin
write <= 1;
end
else
begin
write <= 0;
end
end
always @ ( empty or RRSTn )
begin
if (!RRSTn)
begin
read <= 0;
end
else if (!empty)
begin
read <= 1;
end
else
begin
read <= 0;
end
end
initial begin
$fsdbDumpfile("jacky");
$fsdbDumpvars;
$vcdpluson;
end
endmodule
2, Another design idea (from csdn:FPGA)
//asyn_fifo code
module asyn_fifo #(
parameter data_width = 16;
parameter data_depth = 8;
parameter ram_depth = 256;
)
(
input rst_n,
input wr_clk, //Write clock domain signal
input wr_en,
input [data_width-1:0] data_in,
output full,
input rd_clk, //Clock reading domain signal
input rd_en,
input [data_width-1:0] data_out,
output empty,
)
reg [data_depth-1:0] wr_adr; //Defines the address of the read-write pointer
reg [data_depth-1:0] rd_adr;
reg [data_depth:0] wr_adr_ptr ; //Defines the pointer used for comparison
reg [data_depth:0] rd_adr_ptr ;
wire [data_depth:0] wr_adr_gray; //Convert the pointer used for comparison to gray code
reg [data_depth:0] wr_adr_gray1 ; //Used in two shots
reg [data_depth:0] wr_adr_gray2 ;
wire [data_depth:0] rd_adr_gray; //Convert the pointer used for comparison to gray code
reg [data_depth:0] rd_adr_gray1 ; //Used in two shots
reg [data_depth:0] rd_adr_gray2 ;
//*********************Data read / write module defined in dual port ram******************
assign wr_adr = wr_adr_ptr[data_depth-1:0] //Defines the relationship between the comparison pointer and the read / write pointer
assign rd_adr = rd_adr_ptr[data_depth-1:0]
integer i; //Instantiate a RAM
reg [data_width-1:0] ram_fifo [data_depth-1:0] ;
//Write in ram
always @ (posedge wr_clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(!rst_n)
begin //Set all ram to zero
for(i;i<ram_depth;i=i+1)
ram_fifo[i] <= 'd0;
end
else if (wr_en && ~full)
ram_fifo[wr_adr] <= data_in;
else
ram_fifo[wr_adr] <= ram_fifo[wr_adr];
end
//Reading data in ram
always @ (posedge rd_clk or rst_n)
begin
if (!rst_n)
data_out <= 'd0;
else if (rd_en && ~empty)
data_out <= ram_fifo [rd_adr];
else
data_out <= 'd0;
end
//**********After reading and writing, add 1 to the comparison pointer************
always @ (posedge wr_clk or !rst_n)
begin
if (!rst_n)
wr_adr_ptr <='b0;
else if (wr_en && ~full)
wr_adr_ptr <= wr_adr_ptr + 1'b1;
else
wr_adr_ptr <= wr_adr_ptr
end
always @ (posedge rd_clk or !rst_n)
begin
if (!rst_n)
rd_adr_ptr <= 'b0;
else if (rd_en && ~empty)
rd_adr_ptr <= rd_adr_ptr + 1'b0;
else
rd_adr_ptr <= rd_adr_ptr
end
//**********************Convert comparison pointer to gray code*******************
assign wr_adr_gray = (wr_adr_ptr >> 1)^ wr_adr_ptr;
assign rd_adr_gray = (rd_adr_ptr >> 1) ^ rd_adr_ptr;
//*************************Compare the size of gray code************
//When judging whether it is empty, judge whether the converted gray codes are equal in the time reading clock field
//When judging whether it is full, compare the highest bits of gray code and the remaining bits in the write clock field
//Make two beats of the comparison gray code under the corresponding clock to synchronize the clock domain
always @ (posedge wr_clk or !rst_n)
begin
if (!rst_n)
begin
rd_adr_gray1 <= 'b0;
rd_adr_gray2 <= 'b0;
end
else begin
rd_adr_gray1 <= rd_adr_gray;
rd_adr_gray2 <= rd_adr_gray1;
end
end
always @ (posedge rd_clk or !rst_n)
begin
if (!rst_n)
begin
wr_adr_gray1 <= 'b0;
wr_adr_gray2 <= 'b0;
end
else begin
wr_adr_gray1 <= wr_adr_gray;
wr_adr_gray2 <= wr_adr_gray1;
end
end
//Judge empty and full
assign empty = (rd_adr_gray2 == wr_adr_gray2) ? 1'b:1'b0;
assign full = (rd_adr_gray2[data_depth : data_depth-1] != wr_adr_gray2[data_depth:data_depth-1]) && (wr_adr_gray2[data_depth-2:0] == rd_adr_gray2[data_depth-2:0])
endmoduletb
//testbench for asynchronous fifo
`timescale 1ns/1ps
module asyn_fifo_tb;
reg rst_n;
reg wr_clk;
reg wr_en;
reg [15:0] data_in;
wire full;
reg rd_clk;
reg rd_en;
reg [15:0] data_out;
wire empty;
asyn_fifo asyn_fifo_inst
(
.rst_n (rst_n),
.wr_clk (wr_clk),
.wr_en (wr_en),
.data_in (data_in),
.full (full),
.rd_clk (rd_clk),
.rd_en (rd_en),
.data_out (data_out),
.empty (empty)
)
//Define clock
initial begin
wr_clk = 0;
forever #10 wr_clk = ~wr_clk;
end
initial begin
rd_clk = 0 ;
forever #30 rd_clk = ~rd_clk;
end
// Define input data_in
always @ (posedge wr_clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if (!rst_n)
data_in <= 'd0;
else if (wr_en)
data_in <= data_in + 1'b1;
else
data_in <= data_in;
end
//Define other input signals
initial begin
rst_n = 0;
wr_en =0;
rd_en = 0;
#200
rst_n = 1;
wr_en = 1;
#20000
wr_en = 0;
rd_en = 1;
#20000
rd_en = 0;
$stop
end
endmodule