Arrays in java and source code for the Arrays class
The java.util.Arrays class is a tool class provided by JDK to handle various methods of arrays, and each method is essentially a static method that can be called directly by the class name Arrays.
Class Definition
public final
class Array {
private Array() {}
public static Object newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int length)
throws NegativeArraySizeException {
return newArray(componentType, length);
}
public static Object newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int... dimensions)
throws IllegalArgumentException, NegativeArraySizeException {
return multiNewArray(componentType, dimensions);
}
public static native int getLength(Object array)
throws IllegalArgumentException;
public static native Object get(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native boolean getBoolean(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native byte getByte(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native char getChar(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native short getShort(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native int getInt(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native long getLong(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native float getFloat(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native double getDouble(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void set(Object array, int index, Object value)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setBoolean(Object array, int index, boolean z)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setByte(Object array, int index, byte b)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setChar(Object array, int index, char c)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setShort(Object array, int index, short s)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setInt(Object array, int index, int i)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setLong(Object array, int index, long l)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setFloat(Object array, int index, float f)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setDouble(Object array, int index, double d)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
private static native Object newArray(Class<?> componentType, int length)
throws NegativeArraySizeException;
private static native Object multiNewArray(Class<?> componentType,
int[] dimensions)
throws IllegalArgumentException, NegativeArraySizeException;
}The java.lang.reflect.Array.setChar(Object array, int index, double value) method sets the value of the index component of the specified array object to the specified double value.
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] array = new double[]{1.0,2.0,3.0};
Array.setDouble(array, 0, 2.0);
Array.setDouble(array, 1, 3.0);
Array.setDouble(array, 2, 4.0);
System.out.println("array[0] = " + Array.getDouble(array, 0));
System.out.println("array[1] = " + Array.getDouble(array, 1));
System.out.println("array[2] = " + Array.getDouble(array, 2));
}
}Compiling and running the above program will produce the following results-
array[0] = 2.0 array[1] = 3.0 array[2] = 4.0
Definition of the Arrays class
public class Arrays {
private static final int MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN = 1 << 13;
// Suppresses default constructor, ensuring non-instantiability.
private Arrays() {}
static final class NaturalOrder implements Comparator<Object> {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public int compare(Object first, Object second) {
return ((Comparable<Object>)first).compareTo(second);
}
static final NaturalOrder INSTANCE = new NaturalOrder();
}
private static void rangeCheck(int arrayLength, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"fromIndex(" + fromIndex + ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
}
if (fromIndex < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(fromIndex);
}
if (toIndex > arrayLength) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(toIndex);
}
}
public static void sort(int[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(long[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(short[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(char[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(byte[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
public static void sort(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1);
}
public static void sort(float[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(double[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void parallelSort(byte[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJByte.Sorter
(null, a, new byte[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJByte.Sorter
(null, a, new byte[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(char[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJChar.Sorter
(null, a, new char[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJChar.Sorter
(null, a, new char[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(short[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJShort.Sorter
(null, a, new short[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJShort.Sorter
(null, a, new short[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(int[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJInt.Sorter
(null, a, new int[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJInt.Sorter
(null, a, new int[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(long[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJLong.Sorter
(null, a, new long[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJLong.Sorter
(null, a, new long[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(float[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJFloat.Sorter
(null, a, new float[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJFloat.Sorter
(null, a, new float[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(double[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJDouble.Sorter
(null, a, new double[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJDouble.Sorter
(null, a, new double[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void parallelSort(T[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, 0, n, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
0, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>>
void parallelSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
fromIndex, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> void parallelSort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> cmp) {
if (cmp == null)
cmp = NaturalOrder.INSTANCE;
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, 0, n, cmp, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
0, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, cmp).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> void parallelSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> cmp) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (cmp == null)
cmp = NaturalOrder.INSTANCE;
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, cmp, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
fromIndex, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, cmp).invoke();
}
static final class LegacyMergeSort {
private static final boolean userRequested =
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new sun.security.action.GetBooleanAction(
"java.util.Arrays.useLegacyMergeSort")).booleanValue();
}
public static void sort(Object[] a) {
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a);
else
ComparableTimSort.sort(a, 0, a.length, null, 0, 0);
}
/** To be removed in a future release. */
private static void legacyMergeSort(Object[] a) {
Object[] aux = a.clone();
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0);
}
public static void sort(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
else
ComparableTimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, null, 0, 0);
}
/** To be removed in a future release. */
private static void legacyMergeSort(Object[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
Object[] aux = copyOfRange(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex);
}
private static final int INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD = 7;
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
private static void mergeSort(Object[] src,
Object[] dest,
int low,
int high,
int off) {
int length = high - low;
// Insertion sort on smallest arrays
if (length < INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD) {
for (int i=low; i<high; i++)
for (int j=i; j>low &&
((Comparable) dest[j-1]).compareTo(dest[j])>0; j--)
swap(dest, j, j-1);
return;
}
// Recursively sort halves of dest into src
int destLow = low;
int destHigh = high;
low += off;
high += off;
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
mergeSort(dest, src, low, mid, -off);
mergeSort(dest, src, mid, high, -off);
// If list is already sorted, just copy from src to dest. This is an
// optimization that results in faster sorts for nearly ordered lists.
if (((Comparable)src[mid-1]).compareTo(src[mid]) <= 0) {
System.arraycopy(src, low, dest, destLow, length);
return;
}
// Merge sorted halves (now in src) into dest
for(int i = destLow, p = low, q = mid; i < destHigh; i++) {
if (q >= high || p < mid && ((Comparable)src[p]).compareTo(src[q])<=0)
dest[i] = src[p++];
else
dest[i] = src[q++];
}
}
private static void swap(Object[] x, int a, int b) {
Object t = x[a];
x[a] = x[b];
x[b] = t;
}
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
sort(a);
} else {
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, c);
else
TimSort.sort(a, 0, a.length, c, null, 0, 0);
}
}
/** To be removed in a future release. */
private static <T> void legacyMergeSort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c) {
T[] aux = a.clone();
if (c==null)
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0);
else
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0, c);
}
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
} else {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c);
else
TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c, null, 0, 0);
}
}
/** To be removed in a future release. */
private static <T> void legacyMergeSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> c) {
T[] aux = copyOfRange(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (c==null)
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex);
else
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex, c);
}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
private static void mergeSort(Object[] src,
Object[] dest,
int low, int high, int off,
Comparator c) {
int length = high - low;
// Insertion sort on smallest arrays
if (length < INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD) {
for (int i=low; i<high; i++)
for (int j=i; j>low && c.compare(dest[j-1], dest[j])>0; j--)
swap(dest, j, j-1);
return;
}
// Recursively sort halves of dest into src
int destLow = low;
int destHigh = high;
low += off;
high += off;
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
mergeSort(dest, src, low, mid, -off, c);
mergeSort(dest, src, mid, high, -off, c);
// If list is already sorted, just copy from src to dest. This is an
// optimization that results in faster sorts for nearly ordered lists.
if (c.compare(src[mid-1], src[mid]) <= 0) {
System.arraycopy(src, low, dest, destLow, length);
return;
}
// Merge sorted halves (now in src) into dest
for(int i = destLow, p = low, q = mid; i < destHigh; i++) {
if (q >= high || p < mid && c.compare(src[p], src[q]) <= 0)
dest[i] = src[p++];
else
dest[i] = src[q++];
}
}This method is used for sorting arrays. There is a series of overloaded methods for this method in the Arrays class, which can sort seven basic data types including byte,char,double,float,int,long,short, etc. There are also Object types (which implement the Comparable interface) and Comparator

sort() in the Arrays class uses an optimized fast sorting algorithm;
For arrays of basic data types, such as int[],double[],char[], the Arrays class only provides the default ascending sort, but does not provide the corresponding descending sort method.
Array sorting function prototype:
static void sort (int[] a) Sorts the specified array of ints in ascending numerical order
static void sort (int[] a,int fromIndex,int toIndex) sorts the specified range of the specified int array in ascending numerical order
The idea of quick sorting is to first select a benchmark, which can be either the first number or any number, then point to the position 0 and the position length-1 of the array you want to sort with two pointers, left and right, respectively. With left<right guaranteed, first iterate forward to find the first one less than thatThe number of the benchmark is then exchanged with the number at the left position, and then the first number greater than the benchmark is searched backward and forward, and then exchanged with the number at the position that right points to, and so on, we will see a number on the left side of the benchmark that is less than the benchmark, at the baseQuasi-right are numbers larger than the datum.Quick sorting normally has O (n*logn) time complexity, but when we enter a set of completely or basically ordered arrays, the quick sorting algorithm will be replaced by a bubble sorting algorithm, which will make the time complexity O (n^2) bad. This can also be changed when we select a benchmark.In this case, we can use the three-way selection, that is, the middle value among arr[left], arr[(left+right)/2], and arr[right], to avoid degrading the performance of our fast sorting algorithm in the worst case.
Arrays of basic types
Here we take int[] as an example:
int[] num = {1,3,8,5,2,4,6,7};
Arrays.sort(num);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));//[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]Sort the original arrays in ascending order by calling the sort(int[] a) method.
The DualPivotQuicksort.sort method is called inside the Arrays.sort method, which has a long source code and is used to divide the length of the array into different algorithms, including quick sorting, insert sorting, and bubble sorting.
(2) Array of object types
This type of array sorting implements the Comparable interface, overriding the compareTo method for sorting.
String[] str = {"a","f","c","d"};
Arrays.sort(str);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str));//[a, c, d, f]The String type implements the Comparable interface, and the internal compareTo method compares by dictionary code.
(3) If the Comparable interface is not implemented, the sorting can be achieved by Comparator.
Person[] p = new Person[]{new Person("zhangsan",22),new Person("wangwu",11),new Person("lisi",33)};
Arrays.sort(p,new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
if(o1 == null || o2 == null){
return 0;
}
return o1.getPage()-o2.getPage();
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(p));4. Sort in descending order, you can do so
Arrays.sort(a,Collections.reverseOrder());
However, it is important to note that the basic type (int,double, char) cannot be used. If the int type needs to be changed to Integer, float to Float, for example;
Integer[] a = new Integer[10];
Float[] a = new Float[10];
//The example above can be changed to
Integer[] a = {9, 8, 7, 2, 3, 4, 1, 0, 6, 5}; comparetor can be used to sort arrays directly in descending order
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class ArraysDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int wrapper class object array, assignment
Integer[] arr = {12,15,32,16,20,25};
//Incoming reference type object arr, implementing Comparator interface with anonymous class, i1 in ascending and descending order
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer i1, Integer i2) {
int num = i2 - i1;
return num;
}
});
//Print Array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
Now that the Comparator Comparator object is used here, let's talk about the two Comparators in Java, Comparable and Compparator
Differences: (1) Comparable is under the java.lang package and Comparator is under the java.util package;
(2) Implementing the Comparable interface overrides the ComparetTo() method, and implementing the Comparator interface requires overriding the compare() method;
(3) The Comparable interface embeds the comparison code into its own code of the class to be compared, and the Comparator interface implements the comparison in a separate class;
(4) If the previous class design did not take into account the comparison of classes and did not implement the Comparable interface, the latter can use the Comparator interface to sort the algorithms;
Comparable interface forces natural sort, Comparator interface does not force natural sort, you can specify sort
public static int binarySearch(long[] a, long key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
long key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
long key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
long midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
int midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(short[] a, short key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
short key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
short key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
short midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(char[] a, char key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
char key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
char key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
char midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(byte[] a, byte key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
byte key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
byte key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
byte midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(double[] a, double key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
double key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
double key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
double midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is smaller
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is larger
else {
long midBits = Double.doubleToLongBits(midVal);
long keyBits = Double.doubleToLongBits(key);
if (midBits == keyBits) // Values are equal
return mid; // Key found
else if (midBits < keyBits) // (-0.0, 0.0) or (!NaN, NaN)
low = mid + 1;
else // (0.0, -0.0) or (NaN, !NaN)
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(float[] a, float key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
float key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
float key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
float midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is smaller
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is larger
else {
int midBits = Float.floatToIntBits(midVal);
int keyBits = Float.floatToIntBits(key);
if (midBits == keyBits) // Values are equal
return mid; // Key found
else if (midBits < keyBits) // (-0.0, 0.0) or (!NaN, NaN)
low = mid + 1;
else // (0.0, -0.0) or (NaN, !NaN)
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(Object[] a, Object key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Object key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Object key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Comparable midVal = (Comparable)a[mid];
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
int cmp = midVal.compareTo(key);
if (cmp < 0)
low = mid + 1;
else if (cmp > 0)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static <T> int binarySearch(T[] a, T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key, c);
}
public static <T> int binarySearch(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key, c);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static <T> int binarySearch0(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
T midVal = a[mid];
int cmp = c.compare(midVal, key);
if (cmp < 0)
low = mid + 1;
else if (cmp > 0)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
Find an element in the array by dichotomy.This method, like the sort method, is suitable for a variety of basic data types and objects.
Note that dichotomy is the search for and ordered arrays (such as sorting with Arrays.sort() and then calling this method).Found element returns subscript, not -1
Examples:
int[] num = {1,3,8,5,2,4,6,7};
Arrays.sort(num);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));//[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(num, 2));//Returns the subscript 1 of an element public static boolean equals(long[] a, long[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(int[] a, int[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(short[] a, short a2[]) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(char[] a, char[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(byte[] a, byte[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(boolean[] a, boolean[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(double[] a, double[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (Double.doubleToLongBits(a[i])!=Double.doubleToLongBits(a2[i]))
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(float[] a, float[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (Float.floatToIntBits(a[i])!=Float.floatToIntBits(a2[i]))
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(Object[] a, Object[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++) {
Object o1 = a[i];
Object o2 = a2[i];
if (!(o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2)))
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static boolean deepEquals(Object[] a1, Object[] a2) {
if (a1 == a2)
return true;
if (a1 == null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a1.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Object e1 = a1[i];
Object e2 = a2[i];
if (e1 == e2)
continue;
if (e1 == null)
return false;
// Figure out whether the two elements are equal
boolean eq = deepEquals0(e1, e2);
if (!eq)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static boolean deepEquals0(Object e1, Object e2) {
assert e1 != null;
boolean eq;
if (e1 instanceof Object[] && e2 instanceof Object[])
eq = deepEquals ((Object[]) e1, (Object[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof byte[] && e2 instanceof byte[])
eq = equals((byte[]) e1, (byte[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof short[] && e2 instanceof short[])
eq = equals((short[]) e1, (short[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof int[] && e2 instanceof int[])
eq = equals((int[]) e1, (int[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof long[] && e2 instanceof long[])
eq = equals((long[]) e1, (long[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof char[] && e2 instanceof char[])
eq = equals((char[]) e1, (char[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof float[] && e2 instanceof float[])
eq = equals((float[]) e1, (float[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof double[] && e2 instanceof double[])
eq = equals((double[]) e1, (double[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof boolean[] && e2 instanceof boolean[])
eq = equals((boolean[]) e1, (boolean[]) e2);
else
eq = e1.equals(e2);
return eq;
}①,equals
equals is used to compare whether each element of the corresponding position in two arrays is equal.

②,deepEquals
Is also used to compare whether the elements of two arrays are equal, but deepEquals can compare multidimensional arrays and are nested arrays at any level.
String[][] name1 = {{ "G","a","o" },{ "H","u","a","n"},{ "j","i","e"}};
String[][] name2 = {{ "G","a","o" },{ "H","u","a","n"},{ "j","i","e"}};
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(name1,name2));// false
System.out.println(Arrays.deepEquals(name1,name2));// true public static void fill(long[] a, long val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, long val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(int[] a, int val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, int val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(short[] a, short val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, short val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(char[] a, char val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, char val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(byte[] a, byte val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, byte val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(boolean[] a, boolean val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(boolean[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
boolean val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(double[] a, double val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,double val){
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(float[] a, float val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, float val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(Object[] a, Object val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, Object val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
// Cloning
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {
return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static byte[] copyOf(byte[] original, int newLength) {
byte[] copy = new byte[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static short[] copyOf(short[] original, int newLength) {
short[] copy = new short[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static int[] copyOf(int[] original, int newLength) {
int[] copy = new int[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static long[] copyOf(long[] original, int newLength) {
long[] copy = new long[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static char[] copyOf(char[] original, int newLength) {
char[] copy = new char[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static float[] copyOf(float[] original, int newLength) {
float[] copy = new float[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static double[] copyOf(double[] original, int newLength) {
double[] copy = new double[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static boolean[] copyOf(boolean[] original, int newLength) {
boolean[] copy = new boolean[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOfRange(T[] original, int from, int to) {
return copyOfRange(original, from, to, (Class<? extends T[]>) original.getClass());
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOfRange(U[] original, int from, int to, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static byte[] copyOfRange(byte[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
byte[] copy = new byte[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static short[] copyOfRange(short[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
short[] copy = new short[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static int[] copyOfRange(int[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
int[] copy = new int[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static long[] copyOfRange(long[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
long[] copy = new long[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static char[] copyOfRange(char[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
char[] copy = new char[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static float[] copyOfRange(float[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
float[] copy = new float[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static double[] copyOfRange(double[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
double[] copy = new double[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static boolean[] copyOfRange(boolean[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
boolean[] copy = new boolean[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}fill
These methods are used to assign values to arrays and can specify a range.
copyOf
Copy array elements.The underlying implementation is System.arraycopy(), which is a native method.
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);src: Source Array
srcPos: The starting position of the source array to be copied
dest: Destination Array
destPos: Starting position of destination array placement
Length: the length of the copy
Note: Both src and dest must be arrays of the same type or convertible type.
int[] num1 = {1,2,3};
int[] num2 = new int[3];
System.arraycopy(num1, 0, num2, 0, num1.length);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num2));//[1, 2, 3] @SafeVarargs
@SuppressWarnings("varargs")
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
return new ArrayList<>(a);
}
/**
* @serial include
*/
private static class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements RandomAccess, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2764017481108945198L;
private final E[] a;
ArrayList(E[] array) {
a = Objects.requireNonNull(array);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return a.length;
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
return a.clone();
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
int size = size();
if (a.length < size)
return Arrays.copyOf(this.a, size,
(Class<? extends T[]>) a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(this.a, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
@Override
public E get(int index) {
return a[index];
}
@Override
public E set(int index, E element) {
E oldValue = a[index];
a[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
@Override
public int indexOf(Object o) {
E[] a = this.a;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
if (a[i] == null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
if (o.equals(a[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(a, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (E e : a) {
action.accept(e);
}
}
@Override
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
E[] a = this.a;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = operator.apply(a[i]);
}
}
@Override
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
Arrays.sort(a, c);
}
}The purpose is to return a fixed-size list supported by the specified array.
Note: The ArrayList returned by this method is not our common collection class java.util.ArrayList.Here, the ArrayList is an internal class of Arrays, java.util.Arrays.ArrayList.This internal class has the following properties and methods:

(1) The returned ArrayList array is a fixed-length list, and we can only view or modify it, but we cannot add or delete it
From the source code, we find that this class has no methods such as add() or remove(). If you add or remove it, the method corresponding to its parent AbstractList will be called, and the method tracing the parent will eventually throw an UnsupportedOperationException exception.The following:
String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
List<String> listStr = Arrays.asList(str);
listStr.set(1, "e");//Can be modified
System.out.println(listStr.toString());//[a, e, c]
listStr.add("a");//Adding elements will error java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException 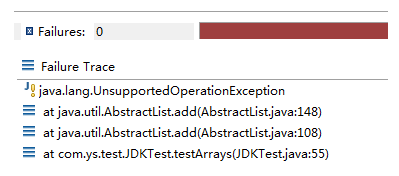
(2) Array differences between reference types and basic types
String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
List listStr = Arrays.asList(str);
System.out.println(listStr.size());//3
int[] i = {1,2,3};
List listI = Arrays.asList(i);
System.out.println(listI.size());//1The results above show that the first listStr.size()==3 and the second listI.size()==1.Why is that?
Looking at the source code, in Arrays.asList, the method is declared <T> List <T> asList (T... a).The method receives a variable parameter, and the variable parameter type is used as a generic parameter.We know that basic data types cannot be used as generic parameters, but arrays are reference types, so arrays can be generic, so int[] is the entire parameter type, not int as the parameter type.
The generic completion of the above method should therefore be:
String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
List<String> listStr = Arrays.asList(str);
System.out.println(listStr.size());//3
int[] i = {1,2,3};
List<int[]> listI = Arrays.asList(i);//Notice here that the List parameter is int[], not int
System.out.println(listI.size());//1
Integer[] in = {1,2,3};
List<Integer> listIn = Arrays.asList(in);//The wrapper class Integer with the parameter int here, so the collection length is 3
System.out.println(listIn.size());//3(3) The elements in the returned list ArrayList are references, not separate objects
String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
List<String> listStr = Arrays.asList(str);
//Before performing update operation
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str));//[a, b, c]
listStr.set(0, "d");//Change the first element a to d
//After performing the update operation
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str));//[d, b, c]Let's look at modifying the contents of the collection, and the contents of the original array have changed, so what's passed in here is the reference type.
(4) With known array data, how to quickly get a List that can be added, deleted or modified?
String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
List<String> listStr = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(str));
listStr.add("d");
System.out.println(listStr.size());//4The ArrayList collection class here is explained in more detail later, and you only need to know this for now.
_, Arrays.asList() method usage scenarios
The Arrays tool class provides a method, asList, that converts a variable-length parameter or array into a List.However, the length of the generated List is fixed; modifications can be made (for example, elements in a location); operations that affect the length cannot be performed (such as add, remove, and so on), or an UnsupportedOperationException exception will be thrown.
Arrays.asList is therefore better suited for scenarios where you already have array data or some elements and need to quickly build a List that can only be used for read operations without adding or deleting operations.
public static int hashCode(long a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (long element : a) {
int elementHash = (int)(element ^ (element >>> 32));
result = 31 * result + elementHash;
}
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(int a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (int element : a)
result = 31 * result + element;
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(short a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (short element : a)
result = 31 * result + element;
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(char a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (char element : a)
result = 31 * result + element;
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(byte a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (byte element : a)
result = 31 * result + element;
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(boolean a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (boolean element : a)
result = 31 * result + (element ? 1231 : 1237);
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(float a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (float element : a)
result = 31 * result + Float.floatToIntBits(element);
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(double a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (double element : a) {
long bits = Double.doubleToLongBits(element);
result = 31 * result + (int)(bits ^ (bits >>> 32));
}
return result;
}
public static int hashCode(Object a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (Object element : a)
result = 31 * result + (element == null ? 0 : element.hashCode());
return result;
}
public static int deepHashCode(Object a[]) {
if (a == null)
return 0;
int result = 1;
for (Object element : a) {
int elementHash = 0;
if (element instanceof Object[])
elementHash = deepHashCode((Object[]) element);
else if (element instanceof byte[])
elementHash = hashCode((byte[]) element);
else if (element instanceof short[])
elementHash = hashCode((short[]) element);
else if (element instanceof int[])
elementHash = hashCode((int[]) element);
else if (element instanceof long[])
elementHash = hashCode((long[]) element);
else if (element instanceof char[])
elementHash = hashCode((char[]) element);
else if (element instanceof float[])
elementHash = hashCode((float[]) element);
else if (element instanceof double[])
elementHash = hashCode((double[]) element);
else if (element instanceof boolean[])
elementHash = hashCode((boolean[]) element);
else if (element != null)
elementHash = element.hashCode();
result = 31 * result + elementHash;
}
return result;
}
public static String toString(long[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(int[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(short[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(char[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(byte[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(boolean[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(float[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(double[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(a[i]);
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String toString(Object[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(String.valueOf(a[i]));
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(", ");
}
}
public static String deepToString(Object[] a) {
if (a == null)
return "null";
int bufLen = 20 * a.length;
if (a.length != 0 && bufLen <= 0)
bufLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(bufLen);
deepToString(a, buf, new HashSet<Object[]>());
return buf.toString();
}
private static void deepToString(Object[] a, StringBuilder buf,
Set<Object[]> dejaVu) {
if (a == null) {
buf.append("null");
return;
}
int iMax = a.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1) {
buf.append("[]");
return;
}
dejaVu.add(a);
buf.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
Object element = a[i];
if (element == null) {
buf.append("null");
} else {
Class<?> eClass = element.getClass();
if (eClass.isArray()) {
if (eClass == byte[].class)
buf.append(toString((byte[]) element));
else if (eClass == short[].class)
buf.append(toString((short[]) element));
else if (eClass == int[].class)
buf.append(toString((int[]) element));
else if (eClass == long[].class)
buf.append(toString((long[]) element));
else if (eClass == char[].class)
buf.append(toString((char[]) element));
else if (eClass == float[].class)
buf.append(toString((float[]) element));
else if (eClass == double[].class)
buf.append(toString((double[]) element));
else if (eClass == boolean[].class)
buf.append(toString((boolean[]) element));
else { // element is an array of object references
if (dejaVu.contains(element))
buf.append("[...]");
else
deepToString((Object[])element, buf, dejaVu);
}
} else { // element is non-null and not an array
buf.append(element.toString());
}
}
if (i == iMax)
break;
buf.append(", ");
}
buf.append(']');
dejaVu.remove(a);
}
toString prints elements of a one-dimensional array, while deepToString prints elements of a multi-level nested array.