Article directory
Reflection can not only instantiate objects, but also obtain the complete structure of a class. Three classes in java.lang.Class and java.lang.reflect package are used, as follows
Through the above classes, you can complete reflection operations, such as:
- Get all interfaces implemented by the class
- Get parent class
- Get all construction methods
- Get all methods
- Get all attributes
Define a Person class
package com.ReflectDemo; interface Information{ // Define Information interface public static final String NATIONAL = "China" ; // Define global constants public static final String AUTHOR = "Zhang San" ; // Define global constants public void sayChina() ; // No parameter, no method to return value public String sayHello(String name,int age) ; // Defines a method with two parameters and returns the contents } public class Person implements Information{ private String name ; private int age ; public Person(){ // Non parametric structure } public Person(String name){ this.name = name ; // Set name property } public Person(String name,int age){ this(name) ; this.age = age ; } public void sayChina(){ // Overwriting method System.out.println("Author:" + AUTHOR + ",Nationality:" + NATIONAL) ; } public String sayHello(String name,int age){ return "Hello, my name is" + name + ",This year:" + age + "Year old!" ; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name ; } public void setAge(int age){ this.age = age ; } public String getName(){ return this.name ; } public int getAge(){ return this.age ; } };
1, Get all interfaces implemented
Use the getInterfaces() method in the Class class, which is defined in the jdk document as follows:
package com.ReflectDemo; public class GetInterfaceDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Class<?> c1 = null; try { c1 = Class.forName("com.ReflectDemo.Person"); //Instanced object } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Class<?> c[] = c1.getInterfaces(); //Get all interfaces implemented for (Class<?> i : c) { System.out.println("Implemented interface name:" + i.getName()); //Output interface name } } }
Program running results:
2, Get parent
Use the getSuperclass() method in the Class class, which is defined in the jdk document as follows:
package com.ReflectDemo; public class GetSuperClassDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Class<?> c1 = null; try { c1 = Class.forName("com.ReflectDemo.Person"); //Instanced object } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Class<?> c2 = c1.getSuperclass(); //Get parent class System.out.println("Parent class name:" + c2.getName()); //Output the name of the parent class. The Person class does not explicitly inherit a class when it is written, so it inherits the Object class by default } }
Program running results:
3, Get all construction methods
Use the getConstructors() method in the Class,
Use the getName() method in the Class to get the method name
Use the getParameterTypes() method in the Constructor class to get all construction methods
Use the getModifiers() method in the Class to get the permission modifier, and the returned integer
Use the toString() method in the Modifier class to restore the integer of the permission Modifier to a string
package com.ReflectDemo; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Modifier; public class GetConstructorDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Class<?> c1 = null; try { c1 = Class.forName("com.ReflectDemo.Person"); //Instanced object } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Constructor<?> cons[] = c1.getConstructors(); //Get all construction methods for (Constructor<?> con : cons) { Class<?> params[] = con.getParameterTypes(); //Get parameter types in construction System.out.print("Construction method:"); int mo = con.getModifiers(); //Get permission modifier, get number System.out.print(Modifier.toString(mo) + " "); //Returns the modifier represented by a number to a string System.out.print(con.getName()); //Get construction method name System.out.print("("); for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) { System.out.print(params[i].getName() + " arg" + (i+1)); //Print parameter type, parameter name is arg if(i < params.length - 1){ System.out.print(","); //Comma between parameters } } System.out.println(") { }"); } } }
Program running results:
4, Get all methods
Use getMethods() method of Class to get all methods
Use the getReturnType() Method of the Method class to get the return type of the Method
Use getExceptionTypes() Method of Method class to get exception information
package com.ReflectDemo; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Modifier; public class GetMethodDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Class<?> c1 = null; try { c1 = Class.forName("com.ReflectDemo.Person"); //Instanced object } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Method method[] = c1.getMethods(); //Get all methods for (Method m : method) { Class<?> r = m.getReturnType(); //Get the return type of the method Class<?> p[] = m.getParameterTypes(); int mo = m.getModifiers(); System.out.print(Modifier.toString(mo) + " "); System.out.print(r.getName() + " "); System.out.print(m.getName()); System.out.print("("); for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) { System.out.print(p[i].getName() + " arg" + (i+1)); if(i < p.length - 1){ System.out.print(","); } } Class<?> ext[] = m.getExceptionTypes(); //Get exception information if(ext.length>0){ System.out.print(") throws "); }else{ System.out.print(") "); } for (int j = 0; j < ext.length; j++) { System.out.print(ext[j].getName()); if (j < ext.length - 1){ System.out.print(","); } } System.out.println(); //Line feed System.out.println(); //Line feed } } }
Program running results: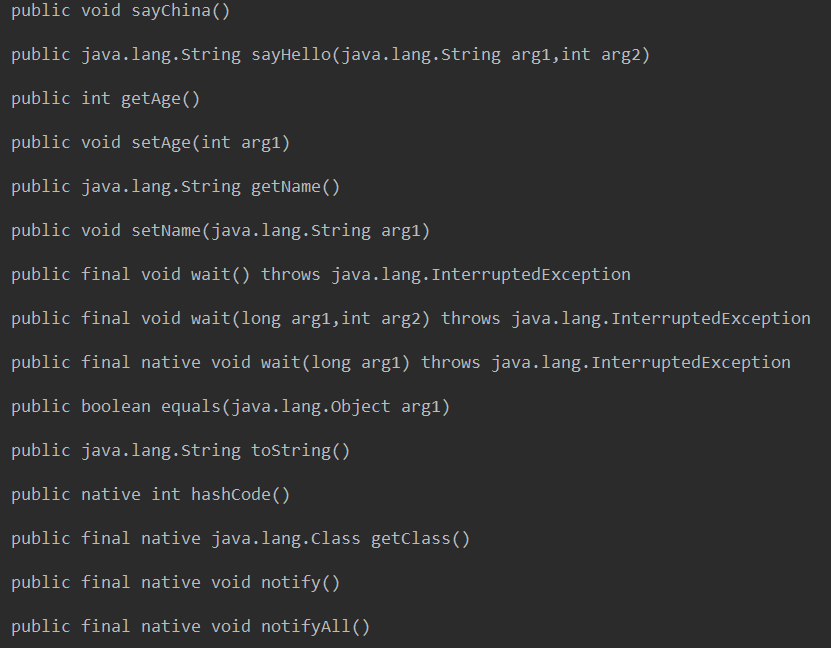
From the result of program running, it can be found that the program not only outputs the methods of Person class, but also the inherited methods of Object class
Prompt: the development tool code prompt for normal development is based on this reflection operation mode
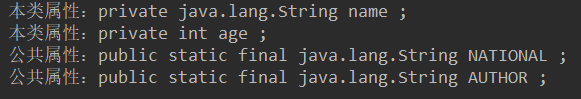
5, Get all attributes
Use the getDeclaredFields() method of Class to get the properties in this Class
Use the getFields() method of the Class to get the public properties in this Class
Use the getType() method of the Field class to get the type of the property
package com.ReflectDemo; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Modifier; public class GetFieldDemo{ public static void main(String args[]){ Class<?> c1 = null ; // Declare Class object try{ c1 = Class.forName("com.ReflectDemo.Person") ; // Instanced object }catch(ClassNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace() ; } { // Attributes of this class Field f[] = c1.getDeclaredFields() ; // Get properties in this class for(int i=0;i<f.length;i++){ Class<?> r = f[i].getType() ; // Get attribute type int mo = f[i].getModifiers() ; // Number to get modifier String priv = Modifier.toString(mo) ; // Restore modifier System.out.print("This type of attribute:") ; System.out.print(priv + " ") ; System.out.print(r.getName() + " ") ; // Get attribute type System.out.print(f[i].getName()) ; // Output attribute name System.out.println(" ;") ; } } { // Public attribute Field f[] = c1.getFields() ; // Get public properties in this class for(int i=0;i<f.length;i++){ Class<?> r = f[i].getType() ; // Get attribute type int mo = f[i].getModifiers() ; // Number to get modifier String priv = Modifier.toString(mo) ; // Restore modifier System.out.print("Public properties:") ; System.out.print(priv + " ") ; System.out.print(r.getName() + " ") ; // Get attribute type System.out.print(f[i].getName()) ; // Output attribute name System.out.println(" ;") ; } } } };
Program running results: