1. A brief introduction to class
A Class of Class represents a Class and interface in a running Java application. Enumeration is a kind, an annotation is an interface, and each array also belongs to a Class reflected as a Class object, which is shared by all arrays with the same element type and dimension. Primitive Java types (boolean, byte, char, short, int, long, float and double), and the keyword void are also represented as Class objects.
It is excerpted from jdk1.8 in Chinese. I may not understand it at first. Now I will explain it sentence by sentence.
First sentence: after a Class is loaded, the JVM will create a Class object corresponding to the Class in memory.
Second sentence: objects of the same type and arrays of the same dimension (regardless of length) share Class objects in the same memory.
The third sentence: the above primitive types will also have a Class object with the object in memory.
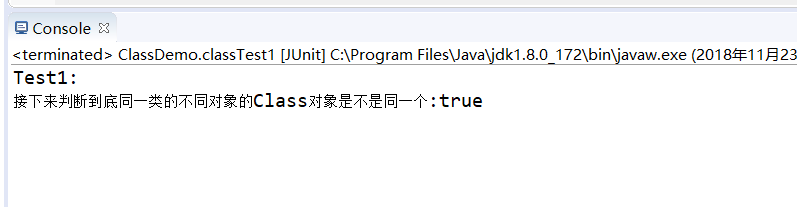
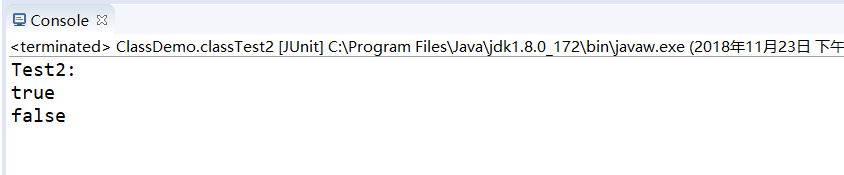
package com.dingyu; import org.junit.Test; /** * Class Easy to use * * @author 70241 * */ public class ClassDemo { @Test public void classTest1() { try { Class class1 = Class.forName("com.dingyu.User");// First acquisition Class Object method User user = new User(); Class class2 = user.getClass();// Second acquisition Class Object method Class class3=User.class;//Third access Class Object method System.out.println("Next, we will judge whether different objects of the same class Class Is the object the same:" + (class1.hashCode() == class2.hashCode()&&class1.hashCode() == class3.hashCode())); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void classTest2() { String[] s1 = new String[10]; String[] s2 = new String[30]; String[][] s3 = new String[3][30]; System.out.println(s1.getClass().hashCode()==s2.getClass().hashCode()); System.out.println(s1.getClass().hashCode()==s3.getClass().hashCode()); } }
2. Simple use of class to obtain class properties, constructors, methods and annotations
package com.dingyu; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.junit.Test; /** * Class Simple use of * * @author dingyu * */ public class ClassDemo02 { @Test public void usingClass() throws Exception { Class userClass = Class.forName("com.dingyu.User"); // Get class name System.out.println(userClass.getName());// Get full class name System.out.println(userClass.getSimpleName());// Get class name // Get attributes Field[] fields = userClass.getDeclaredFields();// Get all properties for (Field field : fields) { System.out.println(field.getName()); } System.out.println(userClass.getDeclaredField("id").getName());// Get the specified properties // Obtaining method Method[] methods = userClass.getDeclaredMethods();// Get all the ways for (Method method : methods) { System.out.println(method.getName()); } Method method = userClass.getDeclaredMethod("setId", int.class);// Gets the specified method, the name of the preceding method, and the parameters of the following method System.out.println(method.getName()); // Get constructor Constructor[] constructors = userClass.getDeclaredConstructors(); System.out.println(constructors.length); Constructor constructor = userClass.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class, int.class);// To get the specified constructor, you need to specify the parameters of the construction System.out.println(constructor.getName()); // Get annotations Annotation[] annotations = userClass.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : annotations) { System.out.println(annotation); } // Specify annotation name MyAnnotation annotation = (MyAnnotation)userClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println(annotation); } }
3.Class dynamic call constructor, method, modify attribute
package com.dingyu; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.junit.Test; /** * Use reflection to dynamically call constructors, methods, and modify properties * @author 70241 * */ public class ClassDemo03 { @Test @SuppressWarnings("all") public void usingClass() throws Exception { Class class1 = Class.forName("com.dingyu.User"); //Using reflection to call the constructor User user1 = (User) class1.newInstance();//Called parameterless Constructor constructor = class1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class,String.class,int.class);//Get a constructor with parameters User user2 = (User) constructor.newInstance(04,"dingyu",20);//Dynamically generate objects //Using reflection to call methods Method methodSetId = class1.getDeclaredMethod("setId",int.class); methodSetId.invoke(user1, 02);//implement user1 Medium setId,The parameters are given later System.out.println(user1.getId()); //Use reflection to modify the value of an attribute Field field = class1.getDeclaredField("age"); field.setAccessible(true);//because age It is private. Adding this sentence means that this property does not need to be checked for security field.set(user1, 20); System.out.println(field.get(user1)); System.out.println(user1.getAge()); } }
4. Reflect to get the generic type in the parameter with generic type or return value
package com.dingyu; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType; import java.lang.reflect.Type; import java.util.Map; /** * Reflection gets the type of a generic in a parameter with a generic or return value * @author dingyu * */ public class ClassDemo04 { public void test01(Map<Integer, String> map, String s) { } public Map<Integer, String> test02() { return null; } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //Parameter with generics Method method = ClassDemo04.class.getDeclaredMethod("test01", Map.class, String.class); Type[] types = method.getGenericParameterTypes();// Return to one Type An array of objects, Type Represents the formal parameter type of the executable represented by the object in declaration order // Print the type of these parameters for (Type type : types) { System.out.println(type.getTypeName()); if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {// If it's a generic parameter Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) type).getActualTypeArguments();// Get the type of the generic for (Type type2 : actualTypeArguments) { System.out.println(type2.getTypeName()); } } } //With generics in return value Method method02 = ClassDemo04.class.getDeclaredMethod("test02"); Type type = method02.getGenericReturnType();// Type returned // Print these return types System.out.println(type.getTypeName()); if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {// If it's a generic parameter Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) type).getActualTypeArguments();// Get the type of the generic for (Type type2 : actualTypeArguments) { System.out.println(type2.getTypeName()); } } } }