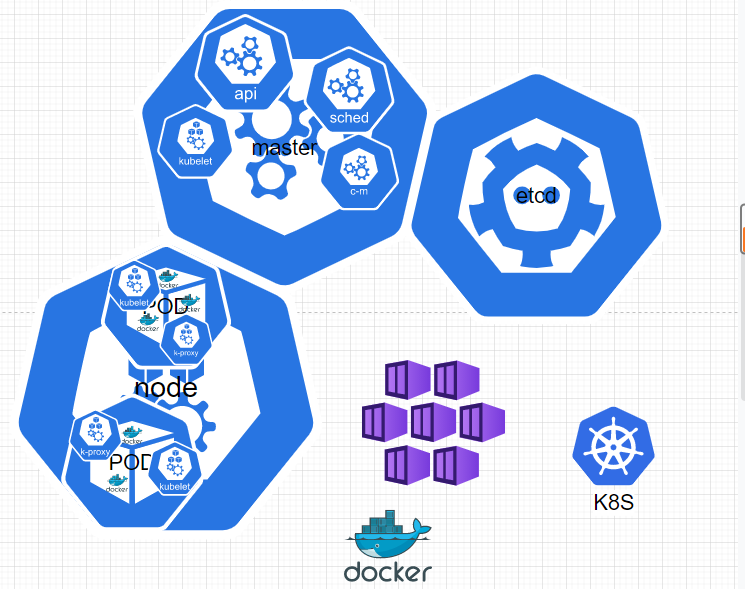
Write in front
- I see it in the book. Take it out and tidy it up separately. Generally, it is cluster deployment. Sometimes learning K8s is too heavy and I don't know how to start:
- Here I hope to have a preliminary understanding of K8S through my blog.
- The content of the blog includes:
- Setup of stand-alone version in K8s environment
- Tomcat+mysql a simple Java Web APP application practice
In the evening, you sit under the eaves and watch the sky slowly darken. You feel lonely and desolate and feel deprived of your life. I was a young man at that time, but I was afraid to live like this and grow old. In my opinion, this is more terrible than death-------- Wang Xiaobo
Setup of stand-alone version in K8s environment
1. Environmental preparation
| Environmental preparation |
|---|
| Turn off the firewall service (switching partitions) provided with CentoS |
| Install etcd and Kubernetes software (Docker software will be installed automatically): |
| Start all services in order: |
| View service status |
 |
# Turn off the firewall service of CentoS: systemctl disable firewalld --now sed -i '/swap/d' /etc/fstab # Install etcd and Kubernetes software (Docker software will be installed automatically): yum install -y etcd kubernetes #Start all services in order: systemctl start etcd systemctl start docker systemctl start kube-apiserver systemctl start kube-controller-manager systemctl start kube-scheduler systemctl start kubelet systemctl start kube-proxy # View service status systemctl status etcd docker kube-apiserver kube-controller-manager kube-scheduler kubelet kube-proxy
At this point, a stand-alone Kubernetes cluster environment is installed and started. Next, we can practice in this stand-alone Kubernetes cluster.
Image related address: https://hub.docker.com/u/kubeguide/.
A simple Java Web APP application practice
1. Start MySQL service
First, create an RC definition file for MySQL service: mysql-rc.yaml, the complete content and explanation of the file;
apiVersion: v1
kind: ReplicationController #Replica controller RC
metadata: # RC name, globally unique
name: mysql # Expected number of Pod copies
spec:
replicas: 1
selector: # Pod s that meet the target have this tag
app: mysql # Create a copy (instance) of the Pod based on this template
template:
metadata: #The tag owned by the Pod copy corresponds to the Selector of the RC
labels:
app: mysql
spec:
containers: # Definition part of Pod content container
- name: mysql # The name of the container and the Docker Image corresponding to the container
image: mysql
ports: #Port number of container application listening
- containerPort: 3306
env: #Environment variables injected into the container
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: "123456"

yaml definition file
| yaml definition file |
|---|
| The kind attribute is used to indicate the type of this resource object. For example, the value here is "ReplicationController", indicating that this is an RC: |
| The spec section contains the relevant attribute definitions of RC. For example, spec.selector is the Pod label selector of RC, that is, monitor and manage the Pod instances with these labels to ensure that there are always and only replicas Pod instances running in the current cluster. Here, we set replicas=1 to show that only one MySQL Pod instance can run. |
| When the number of pods running in the cluster is less than replicas, RC will generate a new Pod instance according to the Pod template defined in the spec.template section. spec.template.metadata.labels specifies the label of the Pod |
| It should be noted that the labels here must match the previous spec.selector, otherwise every time this RC creates a Pod that cannot match the Label, it will keep trying to create a new Pod. |
[root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl create -f mysql-rc.yaml replicationcontroller "mysql" created E:\docker>ssh root@39.97.241.18 Last login: Sun Aug 29 13:00:58 2021 from 121.56.4.34 Welcome to Alibaba Cloud Elastic Compute Service ! ^[[AHow would you spend your life?.I don t know, but I will cherish every minute to live. [root@liruilong ~]# kubectl get rc NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE mysql 1 1 1 1d [root@liruilong ~]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql-q7802 1/1 Running 0 1d [root@liruilong ~]#
Well, there was a problem at the beginning. The pod couldn't be created successfully. When I first started the container, the STATUS always showed CONTAINERCREATING. I used alicloud ESC single core 2G+40G cloud disk. At first, I thought there was a problem with the system audit, because other tutorials required dual cores, but later I found that it was not. I found a solution online, A meal is as fierce as a tiger. Later, I don't know how to do it.
- Some people say that the external network of the basic image cannot be pulled, and only the docker Hub can be used. Some people say that the problem of permissions and the problem of insufficient packages have been tried anyway. Here are some reliable solutions
- https://blog.csdn.net/gezilan/article/details/80011905
- https://www.freesion.com/article/8438814614/
K8s automatically creates a Pod according to the definition of mysqlde RC. Since it takes some time to schedule and create a Pod, for example, it takes some time to determine which node to schedule to, and it takes some time to download the image of the container in the Pod, at first we see that the status of the Pod will be displayed as Pending. When the Pod is successfully created, the status will eventually be updated to Running
We check the running containers through the docker ps instruction and find that the Pod container providing MySQL service has been created and is running normally. In addition, you will find that the container corresponding to MySQL Pod has also created a pause container from Google, which is the "root container" of Pod
We create a definition file mysql-sve.yaml of Kubernetes Service associated with it
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service # Indicates Kubernetes Service
metadata:
name: mysql # Globally unique name of the Service
spec:
ports:
- port: 3306 #Service provides the port number of the service
selector: #The Pod corresponding to the Service has the label defined here
app: mysql
We use the kubectl create command to create a Service object. Run the kubectl command:
[root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl create -f mysql-svc.yaml service "mysql" created [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl get svc NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE mysql 10.254.155.86 <none> 3306/TCP 1m [root@liruilong k8s]#
Note that the MySQL Service is assigned a Cluster IP address with a value of 10.254.155.86, which is a virtual address. Then, other newly created pods in the Kubernetes cluster can connect to and access it through the Cluster IP + port number 3306 of the Service.
In general, Cluster IP is automatically assigned by Kubernetes system after Service creation. Other pods cannot know the Cluster IP address of a Service in advance, so a Service discovery mechanism is needed to find the Service.
At first, Kubernetes cleverly used the Linux environment variable to solve this problem, and its mechanism will be described in detail later. Now we only need to know that according to the unique name of the Service, the container can obtain the Cluster IP address and port corresponding to the Service from the environment variable, so as to initiate a TCP/IP connection request.
2. Start Tomcat application
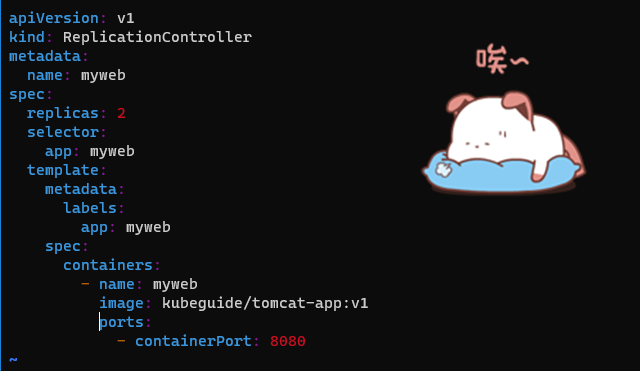
Create the corresponding RC file myweb-rc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ReplicationController
metadata:
name: myweb
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
app: myweb
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myweb
spec:
containers:
- name: myweb
image: kubeguide/tomcat-app:v1
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
replicas: 2: Here we use two tomcat(Pod) to provide services
[root@liruilong k8s]# vim myweb-rc.yaml [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl create -f myweb-rc.yaml replicationcontroller "myweb" created [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl get rc NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE mysql 1 1 1 1d myweb 2 2 0 20s [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql-q7802 1/1 Running 0 1d myweb-53r32 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 28s myweb-609w4 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 28s [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql-q7802 1/1 Running 0 1d myweb-53r32 1/1 Running 0 1m myweb-609w4 1/1 Running 0 1m [root@liruilong k8s]#
Finally, create the corresponding Service. The following is the complete yaml definition file myweb-svc.yaml:
Specified port mapping: 30001:8080
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myweb
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8080
nodePort: 30001
selector:
app: myweb

[root@liruilong k8s]# vim myweb-svc.yaml [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl create -f myweb-svc.yaml service "myweb" created [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl get services NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes 10.254.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 2d mysql 10.254.155.86 <none> 3306/TCP 5h myweb 10.254.122.63 <nodes> 8080:30001/TCP 54s [root@liruilong k8s]#
3. Access the web page through the browser
[root@liruilong k8s]# curl http://127.0.0.1:30001/demo/ <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>HPE University Docker&Kubernetes Learning</title> </head> <body align="center"> <h3> Error:com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.jdbc4.MySQLNonTransientConnectionException: Could not create connection to database server.</h3> </body> </html>
There is a problem with the database connection. Baidu found that there is a problem with the mysql driver version
[root@liruilong k8s]# docker logs a05d16ec69ff [root@liruilong k8s]# vim mysql-rc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ReplicationController #Replica controller RC
metadata: # RC name, globally unique
name: mysql # Expected number of Pod copies
spec:
replicas: 1
selector: # Pod s that meet the target have this tag
app: mysql # Create a copy (instance) of the Pod based on this template
template:
metadata: #The tag owned by the Pod copy corresponds to the Selector of the RC
labels:
app: mysql
spec:
containers: # Definition part of Pod content container
- name: mysql # The name of the container and the Docker Image corresponding to the container
image: mysql:5.7
ports: #Port number of container application listening
- containerPort: 3306
env: #Environment variables injected into the container
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: "123456"
[root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl delete -f mysql-rc.yaml replicationcontroller "mysql" deleted [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl create -f mysql-rc.yaml replicationcontroller "mysql" created [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl get rc NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE mysql 1 1 0 10s myweb 2 2 2 4h [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql-2cpt9 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 15s myweb-53r32 1/1 Running 0 4h myweb-609w4 1/1 Running 1 4h [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql-2cpt9 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 32s myweb-53r32 1/1 Running 0 4h myweb-609w4 1/1 Running 1 4h [root@liruilong k8s]#
We have defined two pod s of Tomcat in the SVC above, so two are shown here
Digest: sha256:7cf2e7d7ff876f93c8601406a5aa17484e6623875e64e7acc71432ad8e0a3d7e Status: Downloaded newer image for docker.io/mysql:5.7 [root@liruilong k8s]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql-2cpt9 1/1 Running 0 31m myweb-53r32 1/1 Running 0 5h myweb-609w4 1/1 Running 1 5h [root@liruilong k8s]# curl http://127.0.0.1:30001/demo/
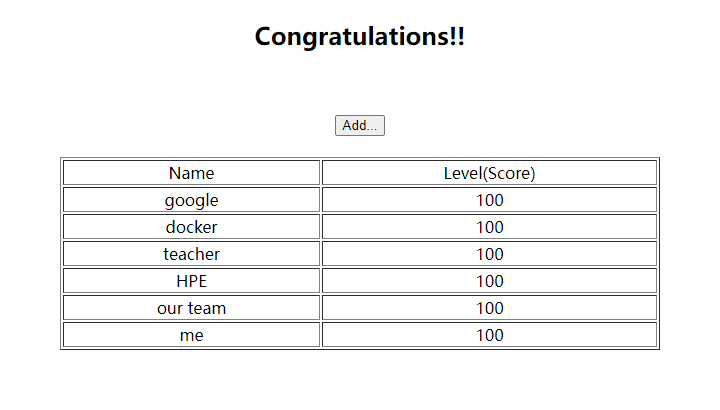
Test it
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>HPE University Docker&Kubernetes Learning</title>
</head>
<body align="center">
<h2>Congratulations!!</h2>
<br></br>
<input type="button" value="Add..." onclick="location.href='input.html'" >
<br></br>
<TABLE align="center" border="1" width="600px">
<TR>
<TD>Name</TD>
<TD>Level(Score)</TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD>google</TD>
<TD>100</TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD>docker</TD>
<TD>100</TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD>teacher</TD>
<TD>100</TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD>HPE</TD>
<TD>100</TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD>our team</TD>
<TD>100</TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD>me</TD>
<TD>100</TD>
</TR>
</TABLE>
</body>
</html>