Xiaosheng blog: http://xsboke.blog.51cto.com
If in doubt, please Click here The author will reply in time (or comment directly in the current article).
-------Thank you for your reference. If you have any questions, welcome to exchange
I. detailed explanation of the principle (click and zoom in the picture)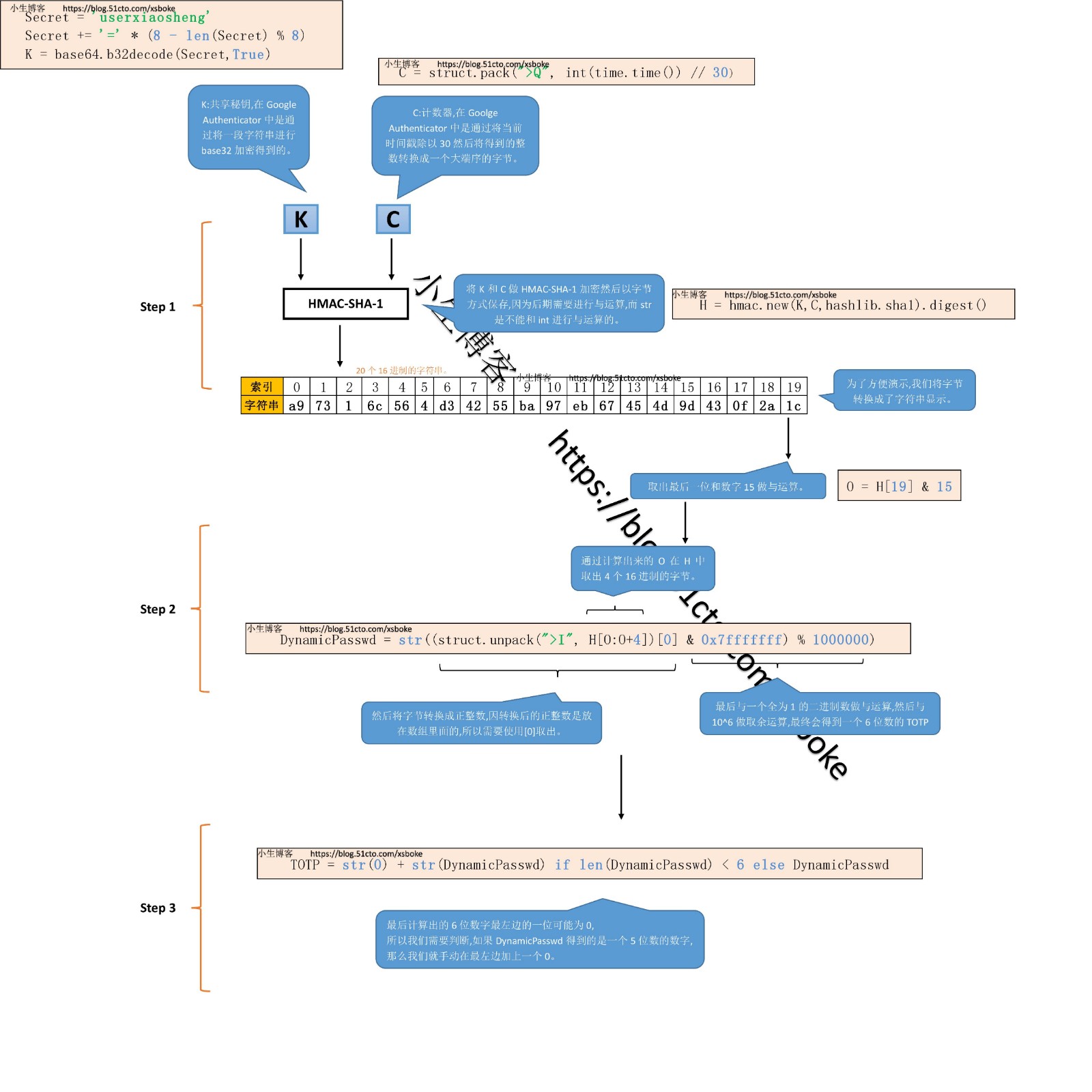
II. Verification
1. Download Google authentication.
2. The QR code is generated by the qrcode and pyotp modules of Python.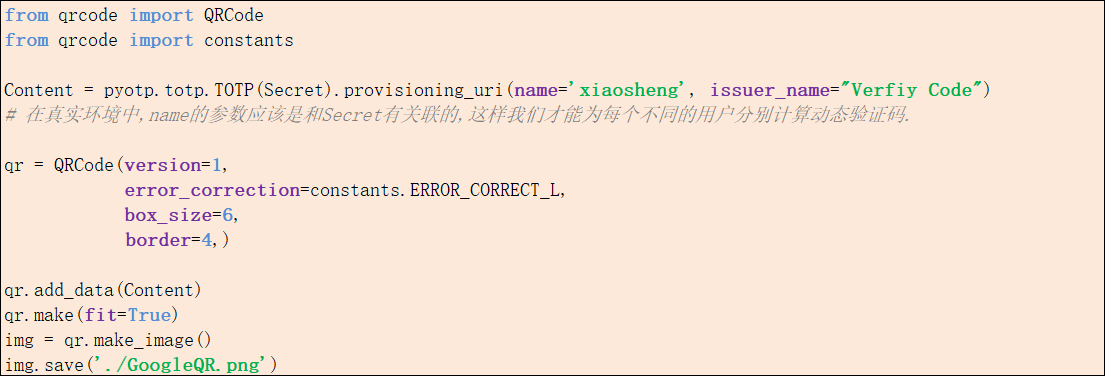
3. Then scan the generated QR code with the downloaded Google authenticator
If there is no Google service, select to enter the Secret key, fill in the name parameter in the account window, and fill in the Secret in the Secret key.
4. Compare the 6-digit dynamic code displayed by Google verifier on the mobile phone, and you will find that it is consistent with the 6-digit dynamic code in the code calculation in [principle details]
Source code
1. Calculate Google Authenticator 6-bit dynamic code
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# How Google Authenticator works TOTP (time based one time password)
import hmac
import hashlib
import base64
import struct
import time
import pyotp
# setup 1 : base32 secret
Secret = 'userxiaosheng'
Secret += '=' * (8-len(Secret)%8) # The base64 module in py3 requires that the string must be a multiple of 8, and the insufficient part uses = complement
K = base64.b32decode(Secret,True)
# setup 2 : get current timestamp
# Int (time. Time()) / / how many 30 seconds have passed since 30
C = struct.pack(">Q", int(time.time()) // 30) bytes with big endian interval and long integer
# setup 3 : start hmac-sha1
# hmac = SHA1(secret + SHA1(secret + input))
H = hmac.new(K,C,hashlib.sha1).digest() # Use hmac sha1 encryption, and fetch = b'\x0f\x1a\xaeL\x0c\x8e\x19g\x8dv}\xde7\xbc\x95\xeal\xa3\xc1\xee' in bytes
O = H[19] & 15 # bin(15)=00001111=0b1111
DynamicPasswd = str((struct.unpack(">I", H[O:O+4])[0] & 0x7fffffff) % 1000000)
# Struct. Unpack ('> I', H [O: O + 4]) [0] -- a number (integer) converted to big endian and not negative, because the conversion is an array, similar to "(2828101188,)", so it needs to be taken out by [0]
# h[o:o+4] - if four bytes are taken, o=10, then the index is 10, 11, 12, 13 bytes respectively
# &0x7fffffff = 11111111 -- do and operate with the number of byte conversion
# %1000000 -- divide the resulting number by 1000000 and then take the remainder
TOTP = str(0) + str(DynamicPasswd) if len(DynamicPasswd) < 6 else DynamicPasswd
# passwd = passwd if len(passwd) < 6 else str(0) + str(passwd)
# If the final 6 digits, the first 0, may only output 5 digits, so here we make a judgment, if it is 5 digits, then add the first 0
print(TOTP)2. Generate QR code
from qrcode import QRCode
from qrcode import constants
Content = pyotp.totp.TOTP(Secret).provisioning_uri(name='xiaosheng', issuer_name="Verfiy Code")
# In the real environment, the name parameter should be associated with Secret, so that we can calculate the dynamic verification code for each different user
qr = QRCode(version=1,
error_correction=constants.ERROR_CORRECT_L,
box_size=6,
border=4,)
qr.add_data(Content)
qr.make(fit=True)
img = qr.make_image()
img.save('./GoogleQR.png')