catalogue
2, Neural network initialization
3, Turn on the camera and read the image by frame
5, Obtain neural network output
3. Get output layer image (content)
The image is divided into 3 images:
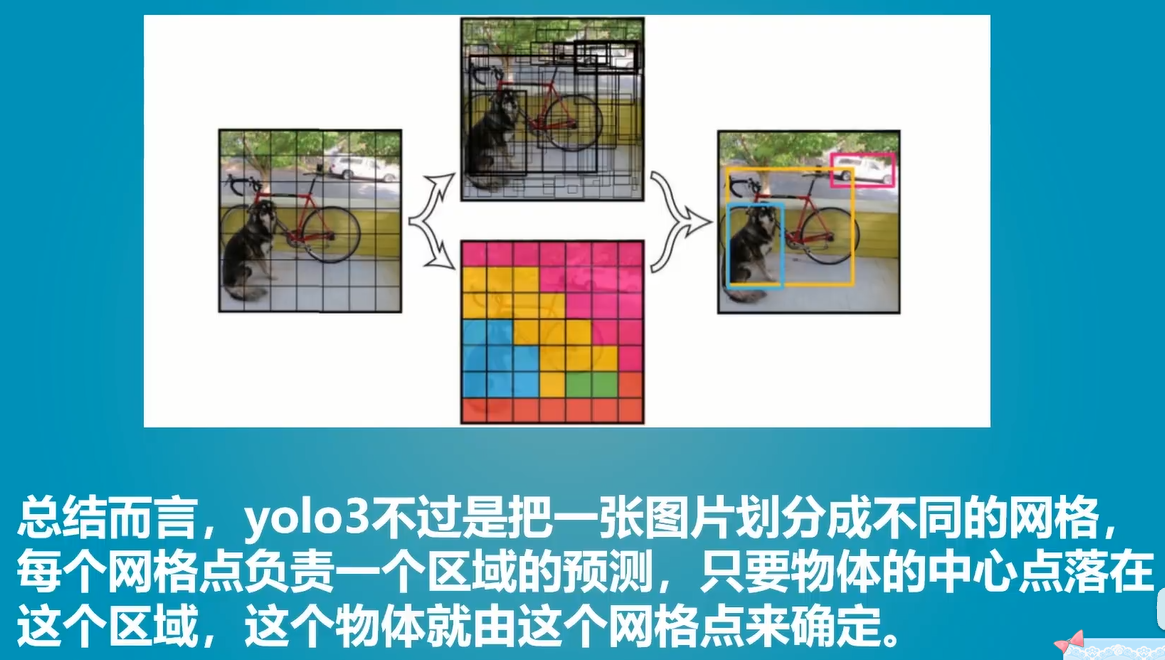
After multiple convolution compression, small objects are easy to disappear, so we use 52 * 52, 26 * 26 and 13 * 13 grids to detect small objects, medium objects and large objects respectively.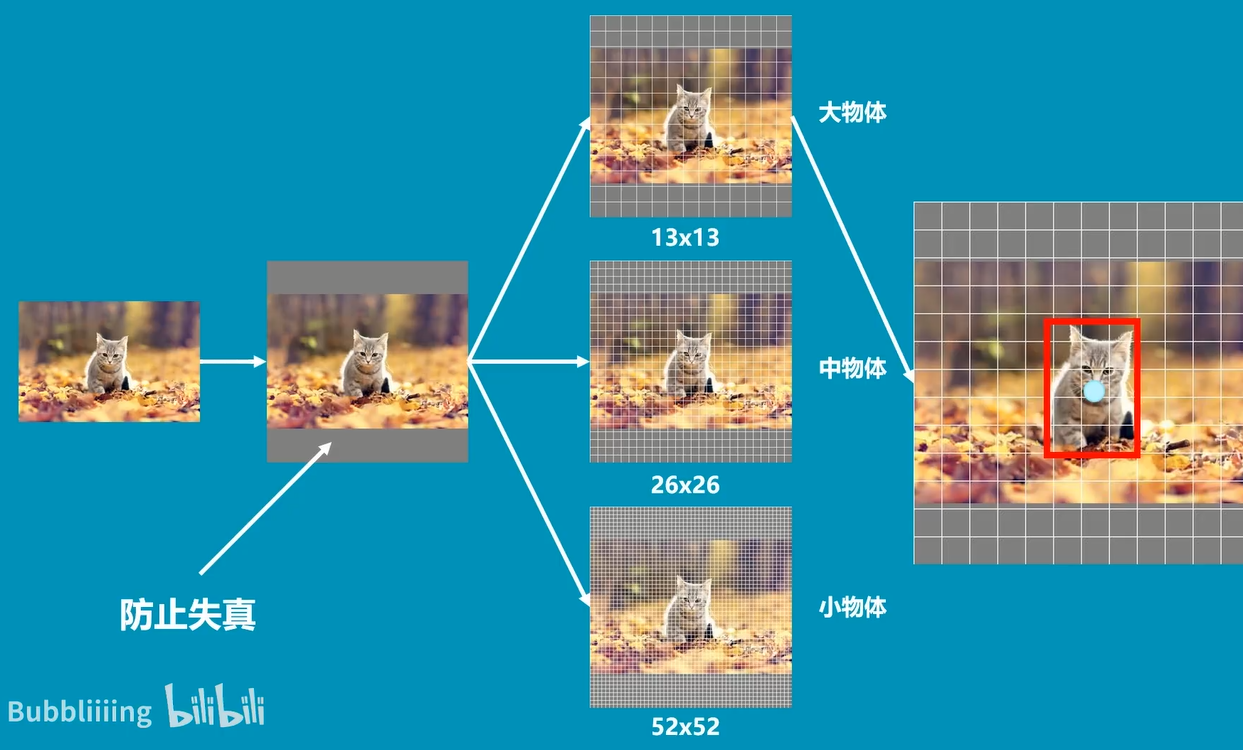

(the cat is a big object, so it is detected with a 13 * 13 grid)
Output layer output:

1, Read file
Three files are required:
coco.names,yolov3.cfg,yolov3.weights.
Download address:
https://download.csdn.net/download/great_yzl/34365174
(you can also download it from yolo's official website, but I don't know if the coco.names file is available)
yolov3.cfg and yolov3.weights are officially given models (those that have been set and trained can be used directly).
# read file
def ReadFile():
global name_list
name_list = []
# read file
with open('coco.names') as f:
name_list = f.read().split('\n')
print(name_list)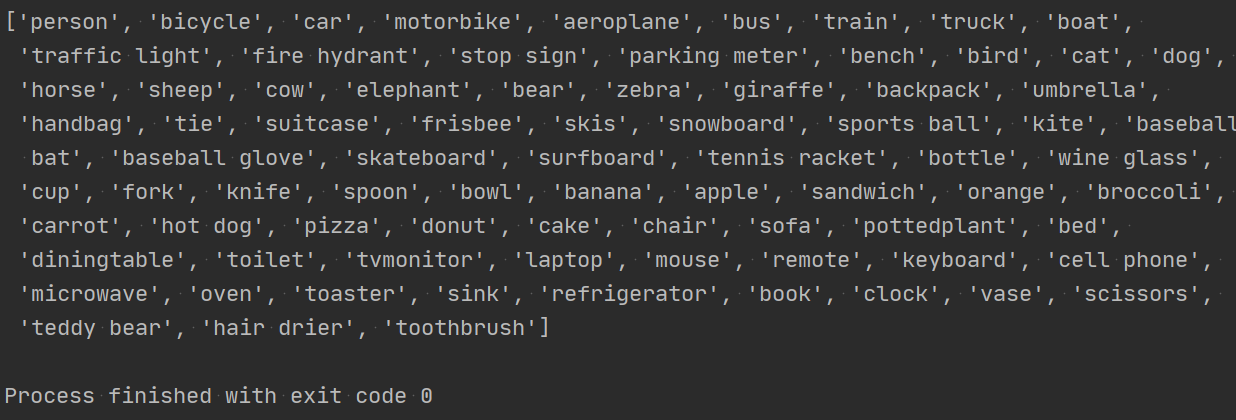
2, Neural network initialization
1. Build neural network
According to yolov3 official settings and weights
global network
model_configuration = 'yolov3.cfg' # Configuration model
model_weights = 'yolov3.weights' # weight
# 1. Creating neural networks
network = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet(model_configuration, model_weights)
# Configure model weights2. GPU acceleration
# 2. GPU acceleration
network.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV) # Set opencv as the backend
network.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CPU)3, Turn on the camera and read the image by frame
def Capture_Init():
global capture, w, h
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
w, h = 320, 320 while True:
global img
success, img = capture.read()
# img = cv2.imread("Resource/test4.jpg")
cv2.imshow('img', img)
# Set the interval time per frame (q key to exit)
cv2.waitKey(1)
# if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0XFF == ord("q"):
# break
4, Input to neural network
# Input to neural network
Input_to_Network(img)Transform the img data and input it into the image as a blob.
# Input to neural network
def Input_to_Network(image):
# Convert image to blob data type (a series of data type conversion such as normalization) (the network can understand this method)
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image, 1 / 255, (w, h), [0, 0, 0], 1, crop=False)
# Image normalized width and height clipping results
# Set neural network input
network.setInput(blob)
print(blob)
5, Obtain neural network output
1. Get the name of each layer
# Name of each layer of neural network
layersNames = network.getLayerNames()
print(layersNames)
2. Get output layer name
# 2. Get the name of neural network output layer
outputNames = [(layersNames[i[0] - 1]) for i in network.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
print(outputNames)
3. Get output layer image (content)
# 3. Get output layer image (content)
# outputs: three characteristic diagrams: small, medium and large. (13*13,26*26,52*52)
# Each feature map outputs 85 categories
outputs = network.forward(outputNames)
# print(outputs[0].shape)
# print(outputs[1].shape)
# print(outputs[2].shape)
# print(outputs[0][0])
return outputs# Obtain neural network output
def Network_Output():
# Name of each layer of neural network
layersNames = network.getLayerNames()
# Name of neural network output layer
outputNames = [(layersNames[i[0] - 1]) for i in network.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
# outputs: three characteristic diagrams: small, medium and large. (13*13,26*26,52*52)
# Each feature map outputs 85 categories
outputs = network.forward(outputNames)
# print(outputs[0].shape)
# print(outputs[1].shape)
# print(outputs[2].shape)
# print(outputs[0][0])
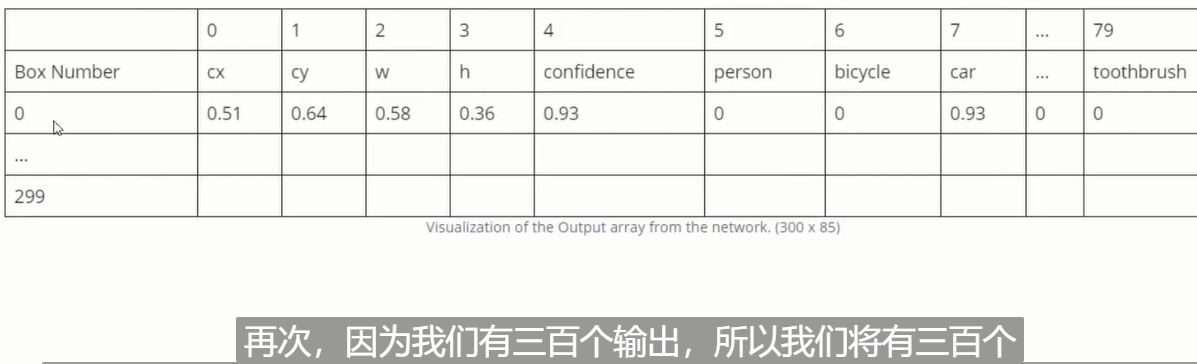
return outputsA series of results in the figure are obtained:
Prediction frame coordinates, length and width, confidence, and prediction scores of each category.
[5.9418369e-02 7.4009120e-02 5.7651168e-01 1.6734526e-01 6.5560471e-07
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00
0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00 0.0000000e+00]
6, Frame object
# Frame object
def GetObject(outputs, image):
# Create parameter list
h_p, w_p, c_p = image.shape # Height, width and number of channels of the image
bboxes = [] # Prediction frame
classIds = [] # Classification index
confidences = [] # Confidence1. Get all forecast boxes
Feature graph output
# Feature graph output
for output in outputs:Frame by frame output
# Frame by frame output
for one_class in output:Single prediction box results
# Calculate the prediction of each box
# First get its 85 classification, the score of each classification, then get the subscript of the maximum score as the index, and finally get its confidence
scores = one_class[5:] # Get all scores
classId = np.argmax(scores) # Get classification index
confidence = scores[classId] # Gain confidenceWhen the confidence is over half, the possible prediction results considered by the prediction box are stored in the list
# Add predicted objects (objects considered possible)
if confidence > 0.5:
# Obtain the width, height and coordinates of the prediction frame
w_b, h_b = int(one_class[2] * w_p), int(one_class[3] * h_p)
x, y = int((one_class[0] * w_p) - w_b / 2), int((one_class[1] * h_p) - h_b / 2)
# (x, y coordinates of center point)
bbox = [x, y, w_b, h_b]
# Add parameters to the list (prediction box parameters, classification index, confidence)
bboxes.append(bbox) # Prediction frame parameters
classIds.append(classId) # Classification index
confidences.append(float(confidence)) # Confidence
print(confidences)2. Keep a prediction box
Non maximum suppression was performed according to confidence and NMS. (the confidence has been filtered once before, and the confidence threshold can no longer be set this time).
# Keep a prediction box (set from confidence threshold and NMS threshold)
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(bboxes, confidences, 0.5, 0.1)
# Prediction frame confidence threshold NMS threshold (non maximum suppression)3. Draw the prediction box
# Output prediction box
for i in indices:
i = i[0]
box = bboxes[i]
x, y, w, h = box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]
# print(x,y,w,h)
cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(image, f'{name_list[classIds[i]].upper()} {int(confidences[i] * 100)}%',
(x, y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imshow('image', image) 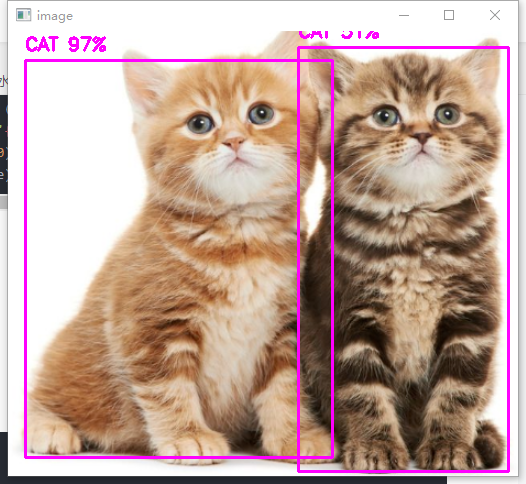
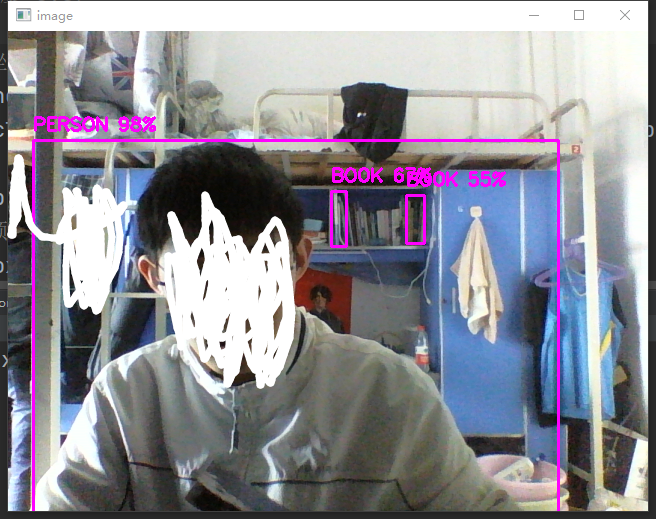
The biggest problem with forecasting is that it is relatively slow. In tiny's words, it is fast enough, but it is not accurate. There is still a lot of room for improvement.
Total code
import cv2
import numpy as np
# read file
def ReadFile():
global name_list
name_list = []
# read file
with open('yolo/coco.names') as f:
name_list = f.read().split('\n')
# print(name_list)
# Build neural network
def Network_Init():
global network
model_configuration = 'yolo/yolov3.cfg' # Configuration model
model_weights = 'yolo/yolov3.weights' # weight
# 1. Creating neural networks
network = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet(model_configuration, model_weights)
# Configure model weights
# 2. GPU acceleration
network.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV) # Set opencv as the backend
network.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CPU)
# print(network)
# Turn on the camera
def Capture_Init():
global capture, w, h
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
w, h = 320, 320
# Input to neural network
def Input_to_Network(image):
# Convert image to blob data type (a series of data type conversion such as normalization) (the network can understand this method)
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image, 1 / 255, (w, h), [0, 0, 0], 1, crop=False)
# Image normalized width and height clipping results
# Set neural network input
network.setInput(blob)
# print(blob)
# Obtain neural network output
def Network_Output():
# 1. Obtain the name of each layer of neural network
layersNames = network.getLayerNames()
# 2. Get the name of neural network output layer
outputNames = [(layersNames[i[0] - 1]) for i in network.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
# print(outputNames)
# 3. Get output layer image (content)
# outputs: three characteristic diagrams: small, medium and large. (13*13,26*26,52*52)
# Each feature map outputs 85 categories
outputs = network.forward(outputNames)
# print(outputs[0].shape)
# print(outputs[1].shape)
# print(outputs[2].shape)
# print(outputs[0][0])
return outputs
# Frame object
def GetObject(outputs, image):
# Create parameter list
h_p, w_p, c_p = image.shape # Height, width and number of channels of the image
bboxes = [] # Prediction frame
classIds = [] # Classification index
confidences = [] # Confidence
# 1. Get the status of all forecast boxes
# outputs: small, medium and large characteristic diagrams
# output: small, medium and large single characteristic diagram
# oneclass: small, medium and large
# Feature graph output
for output in outputs:
# Frame by frame output
for one_class in output:
# Calculate the prediction result of each box
# First get its 85 classification, the score of each classification, then get the subscript of the maximum score as the index, and finally get its confidence
scores = one_class[5:] # Get all scores
classId = np.argmax(scores) # Get classification index
confidence = scores[classId] # Gain confidence
# Add predicted objects (objects considered possible)
if confidence > 0.5:
# Obtain the width, height and coordinates of the prediction frame
w_b, h_b = int(one_class[2] * w_p), int(one_class[3] * h_p)
x, y = int((one_class[0] * w_p) - w_b / 2), int((one_class[1] * h_p) - h_b / 2)
# (x, y coordinates of center point)
bbox = [x, y, w_b, h_b]
# Add parameters to the list (prediction box parameters, classification index, confidence)
bboxes.append(bbox) # Prediction frame parameters
classIds.append(classId) # Classification index
confidences.append(float(confidence)) # Confidence
print(confidences)
# Keep a prediction box (set from confidence threshold and NMS threshold)
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(bboxes, confidences, 0.5, 0.1)
# Prediction frame confidence threshold NMS threshold (non maximum suppression)
# Output prediction box
for i in indices:
i = i[0]
box = bboxes[i]
x, y, w, h = box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]
# print(x,y,w,h)
cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(image, f'{name_list[classIds[i]].upper()} {int(confidences[i] * 100)}%',
(x, y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imshow('image', image)
if __name__ == '__main__':
ReadFile() #read file
Network_Init() #Neural network initialization
Capture_Init() #Camera initialization
while True:
global img
# success, img = capture.read()
img = cv2.imread("Resource/test4.jpg")
# Input to neural network
Input_to_Network(img)
# Obtain neural network output
outputs = Network_Output()
# Frame object
GetObject(outputs, img)
# Set the interval time per frame (q key to exit)
cv2.waitKey(1)
# if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0XFF == ord("q"):
# break
cv2.waitKey(0)