7 Internet
Internet access
urllib
urllib is a Python module for opening URL s.
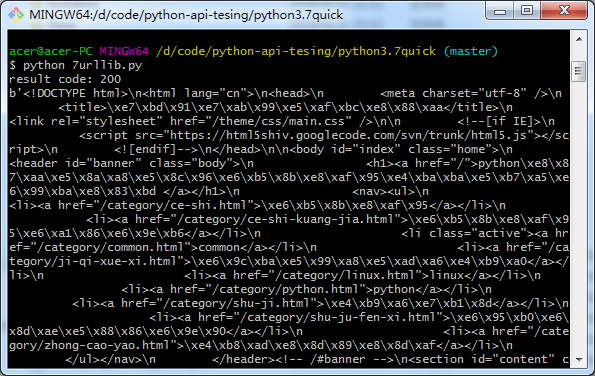
import urllib.request # open a connection to a URL using urllib webUrl = urllib.request.urlopen('https://china-testing.github.io/address.html') #get the result code and print it print ("result code: " + str(webUrl.getcode())) # read the data from the URL and print it data = webUrl.read() print (data)
json
json is a lightweight data exchange format inspired by JavaScript object literal syntax. It is the most popular data exchange format on the Internet.
json exposes API s familiar to users of the standard library Marshall and pickle modules.
>>> import json >>> json.dumps(['foo', {'bar': ('baz', None, 1.0, 2)}]) '["foo", {"bar": ["baz", null, 1.0, 2]}]' >>> print(json.dumps("\"foo\bar")) "\"foo\bar" >>> print(json.dumps('\u1234')) "\u1234" >>> print(json.dumps('\\')) "\\" >>> print(json.dumps({"c": 0, "b": 0, "a": 0}, sort_keys=True)) {"a": 0, "b": 0, "c": 0} >>> from io import StringIO >>> io = StringIO() >>> json.dump(['streaming API'], io) >>> io.getvalue() '["streaming API"]'
Reference material
- Discussion on qq group 144081101 591302926 567351477 nail free group 21745728
- Address of the latest version of this article
- python test development library involved in this article Thanks a lot!
XML
XML is the extensible markup language. It aims to store and transmit small amount of data, and is widely used to share structured information.
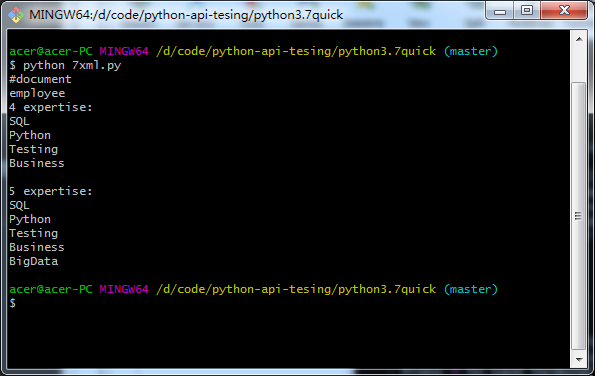
import xml.dom.minidom doc = xml.dom.minidom.parse("test.xml"); # print out the document node and the name of the first child tag print (doc.nodeName) print (doc.firstChild.tagName) # get a list of XML tags from the document and print each one expertise = doc.getElementsByTagName("expertise") print ("{} expertise:".format(expertise.length)) for skill in expertise: print(skill.getAttribute("name")) # create a new XML tag and add it into the document newexpertise = doc.createElement("expertise") newexpertise.setAttribute("name", "BigData") doc.firstChild.appendChild(newexpertise) print (" ") expertise = doc.getElementsByTagName("expertise") print ("{} expertise:".format(expertise.length)) for skill in expertise: print (skill.getAttribute("name"))
ElementTree is an easy way to work with XML files.
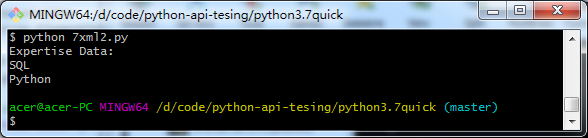
import xml.dom.minidom import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET tree = ET.parse('items.xml') root = tree.getroot() # all items data print('Expertise Data:') for elem in root: for subelem in elem: print(subelem.text)