Basic knowledge
In terms of types, it can be divided into two categories: orderly broadcasting and standard broadcasting
It can be divided into static registered broadcast and dynamic registered broadcast
In Android, broadcast is cross process, so when data is transferred between processes, security information may be leaked. The system also provides a local broadcast receiver for broadcast security management
Use
- Define broadcast receiver: inherit BroadcastReceiver and override onReceive
class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
// No time-consuming operation, more than 10s ANR
// do your job
}
}- Register broadcast recipients
Static registration
<receiver android:name=".MyReceiver ">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.test.receiver.LAUNCH"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>Dynamic registration
IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter()
intentFilter.addAction("com.test.receiver.LAUNCH");
registerReceiver(new MyReceiver,intentFilter);Working process of BroadcastReceiver
The working process of Android broadcast includes registration, sending and receiving
When the application is installed, the system automatically registers the static registered broadcast, and the PackageManagerService completes the whole registration process.
All four components of Android are parsed and registered by PMS during application installation.
The process of dynamic broadcasting (stealing picture)
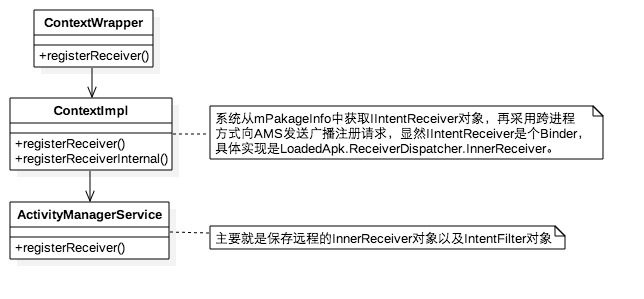
AMS's registerReceiver eventually stores the remote InnerReceiver object as well as the IntentFilter object. This completes the registration process
code snippet
public Intent registerReceiver(IApplicationThread caller, String callerPackage,
18581 IIntentReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter, String permission, int userId,
18582 int flags) {
......
18695 mRegisteredReceivers.put(receiver.asBinder(), rl);
......
18712 BroadcastFilter bf = new BroadcastFilter(filter, rl, callerPackage,
18713 permission, callingUid, userId, instantApp, visibleToInstantApps);
18714 rl.add(bf);
18715 if (!bf.debugCheck()) {
18716 Slog.w(TAG, "==> For Dynamic broadcast");
18717 }
18718 mReceiverResolver.addFilter(bf);
18719
......
18737
18738 return sticky;
18739 }
18740 }Sending and receiving process (stealing)
The whole process is contextimpl - > AMS - > applicationthread - > activitythread handler - > callback the onReceive of the receiver
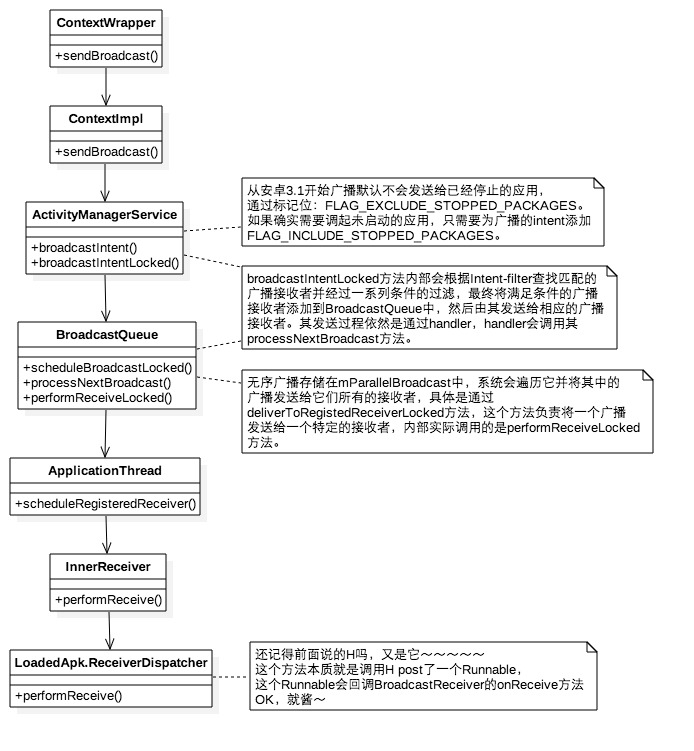
After Android 3.1, the default broadcast will not be sent to the stopped apps
The scheduleRegisteredReceiver method of ApplicationThread will eventually callback the onReceive method of the receiver
Code chip
ApplicationThread Of
989 // This function exists to make sure all receiver dispatching is
990 // correctly ordered, since these are one-way calls and the binder driver
991 // applies transaction ordering per object for such calls.
992 public void scheduleRegisteredReceiver(IIntentReceiver receiver, Intent intent,
993 int resultCode, String dataStr, Bundle extras, boolean ordered,
994 boolean sticky, int sendingUser, int processState) throws RemoteException {
995 updateProcessState(processState, false);
996 receiver.performReceive(intent, resultCode, dataStr, extras, ordered,
997 sticky, sendingUser);
998 }
LoadedApk.java in ReceiverDispatcher Of performReceive
public void performReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode, String data,
1372 Bundle extras, boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int sendingUser) {
1373 final Args args = new Args(intent, resultCode, data, extras, ordered,
1374 sticky, sendingUser);
1375 if (intent == null) {
1376 Log.wtf(TAG, "Null intent received");
1377 } else {
1378 if (ActivityThread.DEBUG_BROADCAST) {
1379 int seq = intent.getIntExtra("seq", -1);
1380 Slog.i(ActivityThread.TAG, "Enqueueing broadcast " + intent.getAction()
1381 + " seq=" + seq + " to " + mReceiver);
1382 }
1383 }
// Mpactivitythread is the handler in ActivityThread, and there is a callback onReceive in args run method
1384 if (intent == null || !mActivityThread.post(args.getRunnable())) {
1385 if (mRegistered && ordered) {
1386 IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
1387 if (ActivityThread.DEBUG_BROADCAST) Slog.i(ActivityThread.TAG,
1388 "Finishing sync broadcast to " + mReceiver);
1389 args.sendFinished(mgr);
1390 }
1391 }
1392 }Reference
Image reproduced from: http://blog.csdn.net/a296777513/article/details/54729325