Post slot
Mail slot is a one-way interprocess communication mechanism provided by Windows operating system, which can be used in single machine or multi machine distributed environment on network. For relatively short low-frequency messages, it is usually easier to use a mail slot than a named pipe or Unix domain socket.
Three simple messages can be read out:
- The data transmitted in the mail slot is unidirectional (client - > server)
- It can communicate between processes or between networks
- Small data per transmission (400B)
Name of mail slot:
- \\. \ \ mailslot\[path\]name – > native
- \\DomainName\[path\]name – > network domain name
- \\ComputerName\[path\]name – > network computer name
- \\*\mailslot\[path\]name -- > broadcast
In this case, mail slot will be used to realize communication between two processes, and the first name will be selected
Thinking analysis:
- The server creates a mail slot and waits for the data to arrive and read
- Client opens mail slot and writes data
The effect of the case is shown in the figure:
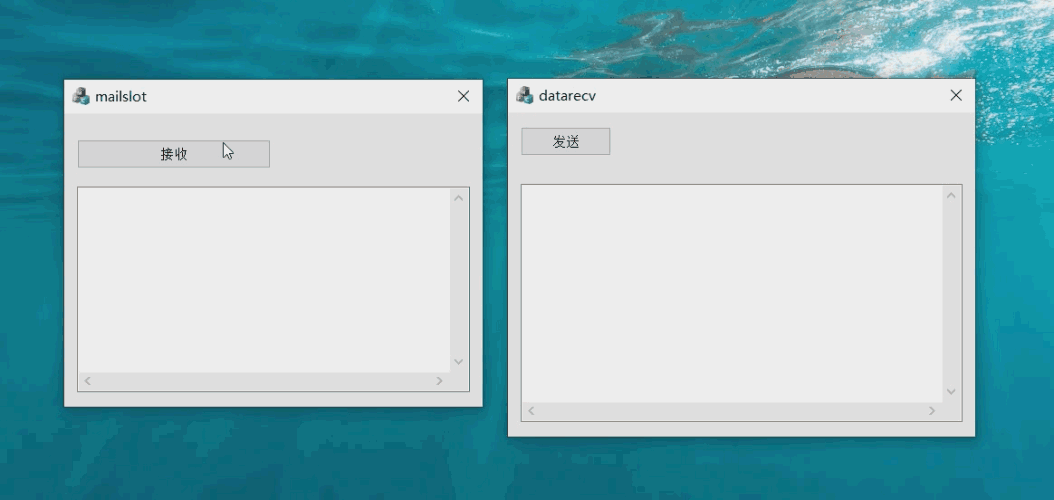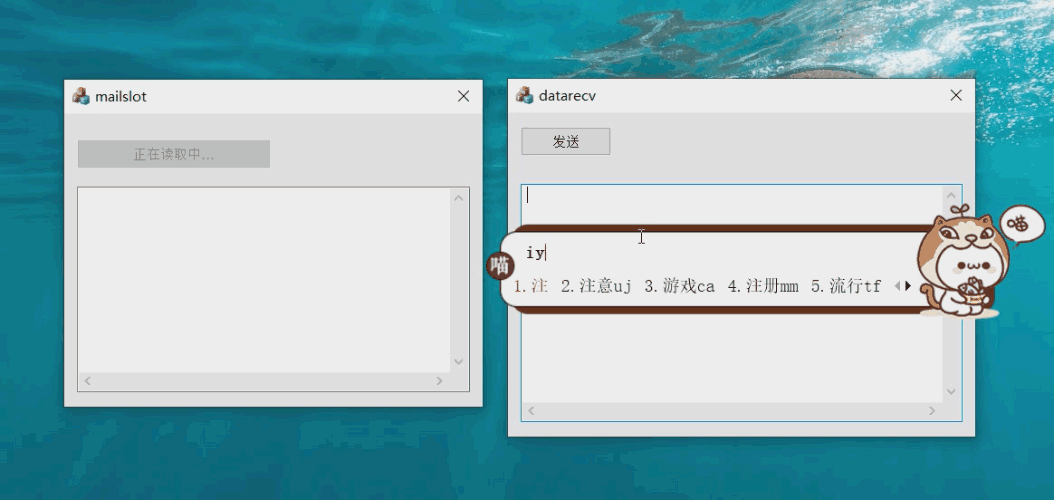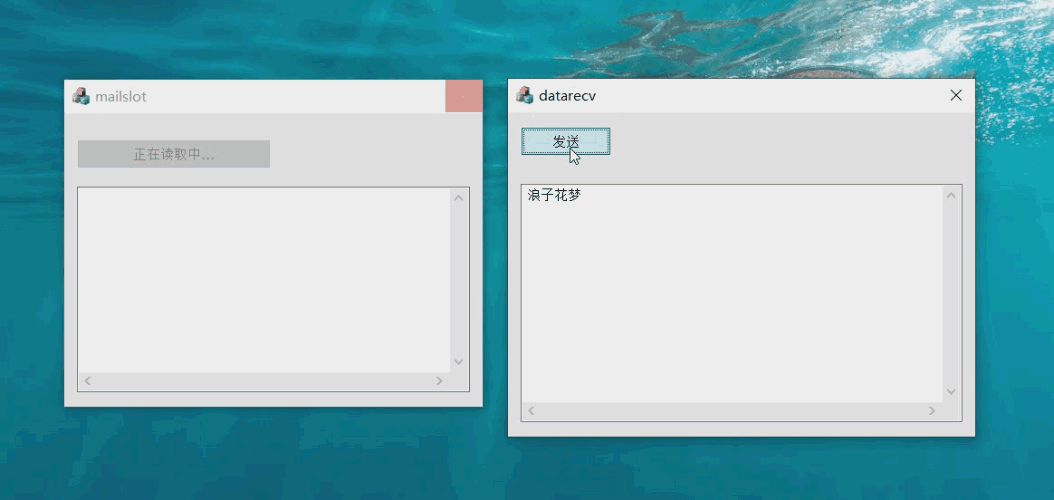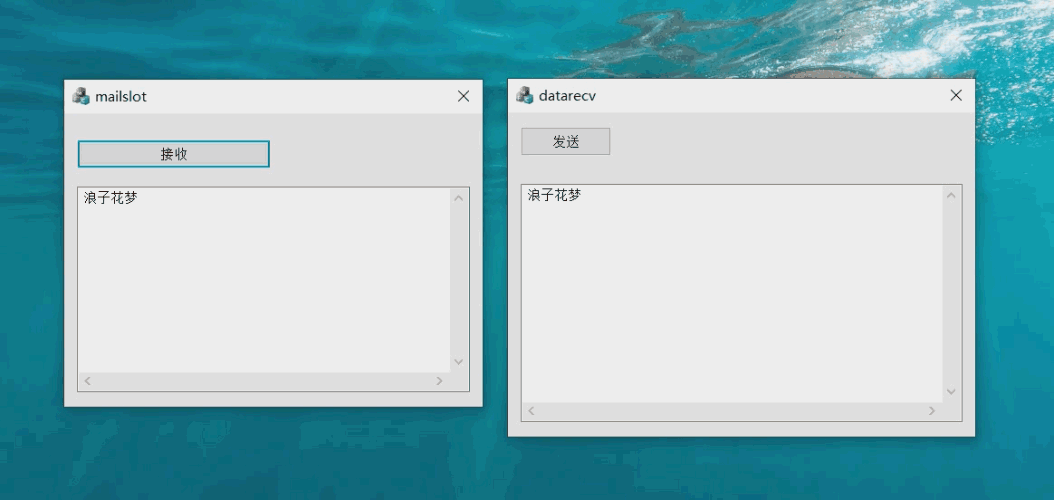
Server window and function realization steps:
- Window building and user-defined ID Name:
- Associate a variable for the button:

- Double click the receive button to realize the function of receiving data for the server:
m_b.EnableWindow(0); // Make the button unselectable m_b.SetWindowText(_T("Reading...")); // Set the contents of the button // Create slot / / = =/ HANDLE hmailslot = CreateMailslot(_T("\\\\.\\mailslot\\MyMailslot"), 0, MAILSLOT_WAIT_FOREVER, NULL); // Create a mail slot and wait for the data to arrive if(hmailslot == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) // Determine whether the mail slot is successfully created { m_b.EnableWindow(1); // Change the button back (can be selected) m_b.SetWindowText(_T("Receive")); // The content has changed back AfxMessageBox(_T("CreateMailslot error")); return; } TCHAR buf[400]; // It is used to receive the data obtained from the mail slot. The maximum can only be 400 ZeroMemory(buf, 400); // Qing 0 DWORD dwRead; // Number of data actually read // Read the contents of the mail slot in the same way as the file if(!ReadFile(hmailslot, buf, 400, &dwRead, NULL)) { m_b.EnablWindow(1); // If the reading fails, the button will be restored m_b.SetWindowText(_T("Receive")); AfxMessageBox(_T("ReadFile error")); CloseHandle(hmailslot); // Failed to read the file, close the handle of the mail slot return; } SetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT_DATA, buf); // Put the read into the edit box CloseHandle(hmailslot); m_b.EnableWindow(1); // Button restore m_b.SetWindowText(_T("Receive"));
Client window and function realization steps:
- Interface building and custom control ID:
- Double click the send button to send data to the client:
// Open the mail slot (the essence of the mail slot is a file) see the code below for the meaning of the parameters HANDLE hMailslot = CreateFile(_T("\\\\.\\mailslot\\MyMailslot"), GENERIC_WRITE, FILE_SHARE_READ, NULL, OPEN_EXISTING, FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NPRMAL, NULL); if(hMailslot == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) // Fail to open mail slot { AfxMessageBox(_T("Open mailslot failed.")); return 0; } TCHAR buf[400]; // Buffer for storing data, the maximum can only be 400 ZeroMemory(buf, 400); // Qing 0 GetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT_DATA, buf, 400); // Get data in control DWORD dwWrite; // Number of data actually written if(!WriteFile(hMailslot, buf, 400, &dwWrite, NULL)) { CloseHandle(hMailslot); // Failed to write data, closing handle AfxMessageBox(_T("Failed to send data!")); return; } CloseHandle(hMailslot); // Closing handle
The meaning of each parameter of CreateFile is shown in (2) Win32 process communication -- memory mapping file Mentioned in

