/**Create table **/ /**Create table 1**/ CREATE TABLE `product` ( `id` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `amount` INT(10) UNSIGNED DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; /**Create table 2**/ CREATE TABLE `product_details` ( `id` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, `weight` INT(10) UNSIGNED DEFAULT NULL, `exist` INT(10) UNSIGNED DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; /**Insert data**/ INSERT INTO product(id,amount) VALUES (1,100),(2,200),(3,300),(4,400); INSERT INTO product_details(id,weight,exist) VALUES (2,22,0),(4,44,1),(5,55,0),(6,66,1); /**Query data**/ SELECT * FROM product; SELECT * FROM product_details;
I. left outer link query
/**Left connection query**/ SELECT * FROM product LEFT JOIN product_details ON (product.`id` = product_details.`id`);
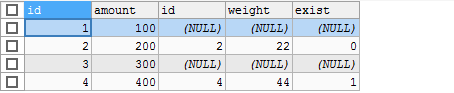 (51CTO water print low!)
(51CTO water print low!)
SELECT * FROM product LEFT JOIN product_details ON (product.id = product_details.id) AND product_details.id=2;
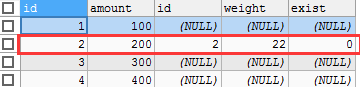
This query uses the ON condition to determine that all data rows that match are retrieved from the product details table of the LEFT JOIN.
SELECT * FROM product LEFT JOIN product_details ON (product.id = product_details.id) WHERE product_details.id=2;
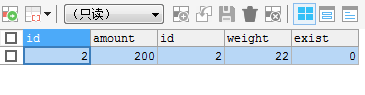
This query makes a LEFT JOIN, and then uses the WHERE clause to filter out the unqualified data rows from the LEFT JOIN data.
Another example:
SELECT * FROM product LEFT JOIN product_details ON product.id = product_details.id AND product.amount=100;
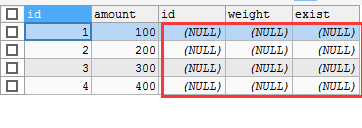
All data rows from the product table are retrieved, but no records are matched in the product details table
(the product.id = product_details.id AND product.amount=100 condition does not match any data)
SELECT * FROM product LEFT JOIN product_details ON (product.id = product_details.id) AND product.amount=200

All data rows from the product table have been retrieved, and one of the data matches.
It can be seen from the above: the WHERE condition occurs after the matching stage!