1. BOM
JavaScript foundation is divided into three parts:
ECMAScript: the Syntax Standard for JavaScript. Including variables, expressions, operators, functions, if statements, for statements, etc.
DOM: document object model, API for manipulating elements on Web pages. For example, let the box move, change color, rotate the map, etc.
BOM: browser object model, API for operating some functions of browser. Let the browser scroll automatically, for example.
1.1 introduction to BOM
BOM: Browser Object Model, Browser Object Model.
Structure diagram of BOM:
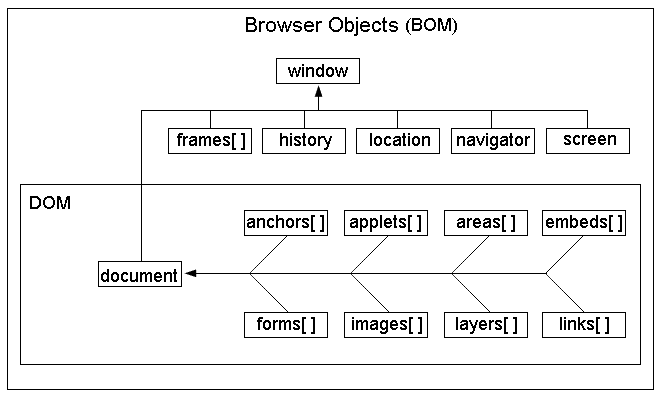
It can also be seen from the figure above:
Window object is the top (core) object of BOM, through which all objects are extended. It can also be called window sub object.
DOM is part of BOM.
window object:
window objects are top-level objects in JavaScript.
Global variables and custom functions are also properties and methods of window objects.
When the properties and methods under the window object are called, the window can be omitted.
Let's talk about the common built-in methods and objects of BOM.
1.2 pop up system dialog box
For example, alert(1) is a shorthand for window.alert(1), because it is a child of window.
There are three types of system dialog boxes:
alert(); //The appearance is different in different browsers confirm(); //Compatibility is not good. prompt(); //Not recommended
1.3 opening and closing windows
1.3.1 open window
window.open(url,target)
Parameter interpretation:
url: the address to open.
target: the location of the new window. It can be: "blank", "self", "parent" parent framework.
1.3.2 close window
close();
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<!--Interrow js Medium open() window Can not omit-->
<button onclick="window.open('https://I-beta. Cnblogs. Com ') "> programming friendly little ashes < / button >
<button>Open Baidu</button>
<button onclick="window.close()">Close</button>
<button>Close</button>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var oBtn = document.getElementsByTagName('button')[1];
var closeBtn = document.getElementsByTagName('button')[3];
oBtn.onclick = function(){
//open('https://www.baidu.com')
//Open a blank page
open('about:blank',"_self")
}
closeBtn.onclick = function(){
if(confirm("Close?")){
close();
}
}
</script>
</html>
1.4 location object
window.location can be abbreviated to location. Location is equivalent to the browser address bar, which can parse the url into independent fragments.
1.4.1 properties of location object
href: Jump
hash returns the content after ා in the url, including#
host hostname, including port
Hostname hostname
Path part in pathname url
Protocol protocol is generally http, https
search query string
Example of location.href attribute:
Example 1: click the box to jump.
<body>
<div>smyhvae</div>
<script>
var div = document.getElementsByTagName("div")[0];
div.onclick = function () {
location.href = "http://www.baidu.com"; //click div When, jump to the specified link
// window.open("http://www.baidu.com","_blank "); / / method 2
}
</script>
</body>
Example 2: automatically jump to Baidu after 5 seconds.
Sometimes, when we visit a non-existent web page, we will be prompted to automatically jump to the specified page after 5 seconds, and then location can be used. Give an example:
<script> setTimeout(function () { location.href = "http://www.baidu.com"; }, 5000); </script>
1.4.2 method of location object
location.reload(): reload
setTimeout(function(){ //3 Seconds to refresh the whole page window.location.reload(); },3000)
1.5 navigator object
Some properties of window.navigator can get some information of the client.
userAgent: system, browser)
platform: Browser supported system, win/mac/linux
Example:
console.log(navigator.userAgent);
console.log(navigator.platform);
1.6 history object
1. Backward:
history.back()
history.go(-1): 0 Refresh
2. Forward:
history.forward()
history.go(1)
Not much. Because the browser already has buttons for these functions.