Vue.js event handler
<template> <div id="app"> <button v-on:click="fn">click me</button> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ name:'cyy' } }, methods:{ fn(e){ console.log(this.name);//cyy if(e){ console.log(e.target.tagName);//BUTTON } } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
In addition to directly binding to a method, you can also use inline JavaScript statements:
<template> <div id="app"> <button v-on:click="fn('success')">click me</button> <button v-on:click="fn('fail')">click me</button> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ name:'cyy' } }, methods:{ fn(res){ console.log(res); } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
Vue.js provides event modifiers for v-on to handle DOM event details, such as: event.preventDefault() or event.stopPropagation().
Vue.js calls the modifier through an instruction suffix represented by a dot (.).
- .stop
- .prevent
- .capture
- .self
- .once
<! -- prevent click events from bubbling -- > <a v-on:click.stop="doThis"></a> <! -- submit event no longer reloads page -- > <form v-on:submit.prevent="onSubmit"></form> <! -- modifiers can be concatenated -- > <a v-on:click.stop.prevent="doThat"></a> <! -- modifier only -- > <form v-on:submit.prevent></form> <! -- use event capture mode when adding event listeners -- > <div v-on:click.capture="doThis">...</div> <! -- the callback is triggered only when the event is triggered on the element itself, not on a child element -- > <div v-on:click.self="doThat">...</div> <! -- click event can only be clicked once, new in version 2.1.4 -- > <a v-on:click.once="doThis"></a>
Vue allows you to add key modifiers for v-on when listening for keyboard events:
<!-- Only in keyCode Called at 13 vm.submit() --> <input v-on:keyup.13="submit">
Vue provides aliases for the most commonly used keys:
<!-- Ditto --> <input v-on:keyup.enter="submit"> <!-- Abbreviation syntax --> <input @keyup.enter="submit">
All key aliases:
- .enter
- .tab
- . delete (capture delete and backspace keys)
- .esc
- .space
- .up
- .down
- .left
- .right
- .ctrl
- .alt
- .shift
- .meta
<template> <div id="app"> <input v-on:keyup.enter="fn" v-on:keyup.tab="fn" v-on:keyup.delete="fn" v-on:keyup.esc="fn" v-on:keyup.space="fn" v-on:keyup.up="fn" v-on:keyup.down="fn" v-on:keyup.left="fn" v-on:keyup.right="fn" v-on:keyup.ctrl="fn" v-on:keyup.alt="fn" v-on:keyup.shift="fn" v-on:keyup.meta="fn" />enter </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ name:'cyy' } }, methods:{ fn(e){ console.log(e.keyCode); } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
When binding the v-on:click event, you want to pass in the parameter as well as the current element:
<template> <div id="app"> <!-- You have to use $event --> <p @click="fn('cyy',$event)">bind methods fn</p> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ name:'cyy' } }, methods:{ fn(name,e){ console.log(name); console.log(e.target); } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
v-model automatically selects the correct method to update the element according to the control type.
The example demonstrates the use of v-model in the input and textarea elements to realize bidirectional data binding:
<template> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model="text"> <p>{{text}}</p> <textarea cols="30" rows="3" v-model="textarea"></textarea> <p>{{textarea}}</p> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ text:'cyy', textarea:'this is a long text' } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
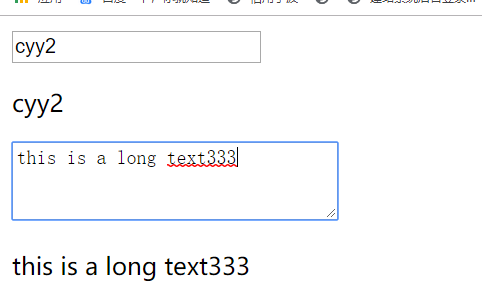
If one check box is a logical value, if more than one check box is bound to the same array:
<template> <div id="app"> <!-- Single check box --> <input type="checkbox" id="one" v-model="checked"> <label for="#one">{{checked}}</label> <br> <br> <!-- Multiple check boxes --> <input type="checkbox" name="more" id="item1" value="item1" v-model="moreChecked"> <label for="#item1">item1</label> <input type="checkbox" name="more" id="item2" value="item2" v-model="moreChecked"> <label for="#item2">item2</label> <input type="checkbox" name="more" id="item3" value="item3" v-model="moreChecked"> <label for="#item3">item3</label> <p>you checked:{{moreChecked}}</p> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ checked:true, moreChecked:[] } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
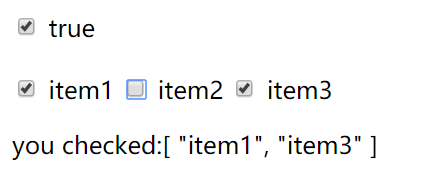
Two way data binding for radio buttons is demonstrated in the following example:
<template> <div id="app"> <!-- radio button --> <input type="radio" name="more" id="item1" value="item1" v-model="checked"> <label for="#item1">item1</label> <input type="radio" name="more" id="item2" value="item2" v-model="checked"> <label for="#item2">item2</label> <input type="radio" name="more" id="item3" value="item3" v-model="checked"> <label for="#item3">item3</label> <p>you checked:{{checked}}</p> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ checked:'item1', } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
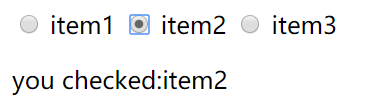
The two-way data binding of the drop-down list is demonstrated in the following example:
<template> <div id="app"> <select name="choose" id="choose" v-model="choose"> <option value="">Please select</option> <option value="item1">item1</option> <option value="item2">item2</option> </select> <p>you choose:{{choose}}</p> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ choose:'', } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
.lazy
By default, v-model synchronizes the value and data of the input box in the input event, but you can add a modifier lazy to change it to synchronize in the change event:
<template> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model="text"> <p>{{text}}</p> <!-- stay "change" instead of "input" Update in event --> <input type="text" v-model.lazy="text2"> <p>{{text2}}</p> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ text:'', text2:'' } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
If you want to automatically convert the user's input value to the number type (return the original value if the conversion result of the original value is NaN), you can add a modifier number to v-model to process the input value:
This is usually useful because the value entered in HTML also always returns a string type when type = number.
<template> <div id="app"> <input type="number" v-model.number="num"> <p>{{num}}</p> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ num:0 } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
If you want to automatically filter the first and last spaces of user input, you can add trim modifier to v-model to filter input:
<template> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model="text"> <p>{{text}}</p> <!-- Filter spaces --> <input type="text" v-model.trim="text2"> <p>{{text2}}</p> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ text:'', text2:'' } }, } </script> <style scoped> </style>
I didn't seem to succeed
Select all and deselect all:
<template> <div id="app"> <input type="checkbox" name="check" id="check" v-model="checked" @change="changeAll()">{{checked?'Deselect all':'All election'}} <br/> <input type="checkbox" name="mylist" value="item1" id="item1" v-model="checkedList"> <label for="#item1">item1</label> <input type="checkbox" name="mylist" value="item2" id="item2" v-model="checkedList"> <label for="#item2">item2</label> <input type="checkbox" name="mylist" value="item3" id="item3" v-model="checkedList"> <label for="#item3">item3</label> </div> </template> <script> var count=1; export default { name: 'App', data(){ return{ checked:false, checkedList:[], checkedArr:['item1','item2','item3'] } }, methods:{ changeAll(){ if(this.checked){ this.checkedList=this.checkedArr; }else{ this.checkedList=[]; } } }, watch:{ checkedList(){ if(this.checkedList.length===this.checkedArr.length){ this.checked=true; }else{ this.checked=false; } } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>