Django Architecture
CentOS 7 system is compatible with Python 2 and Python 3. This project is based on Python 3 environment.
Install Django
CentOS 7 System Installation django
pip3 install djangoCreate the Django project dataPlatform under Windows and add the following code to set.py:
#In the MIDDLEWARE_CLASSES settings list,'django. contrib. sessions. middleware. Session Middleware', add the following:
#Make admin pages Chinese
'django.middleware.locale.LocaleMiddleware',#Add the last line
# Get admin static file
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'static')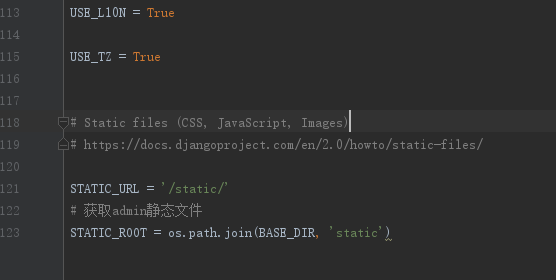
Then run under the CMD window
E:\dataPlatform>python manage.py collectstaticThis instruction generates static folders, mainly storing CSS, JS files, etc.
The final Django directory structure is as follows: 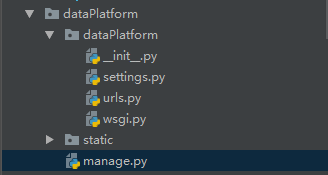
You can see that there are more folders static, and finally upload the project to the VirtualBox CentOS 7 system using FileZilla Client, as shown in the figure: 
uwsgi architecture
CentOS 7 System Installation uwsgi
pip3 install uwsgiTest whether uWSGi works properly:
uwsgi --http :8080 --chdir /dataPlatform -w dataPlatform.wsgi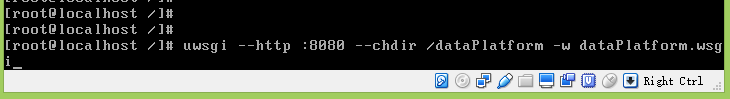
Operation results: 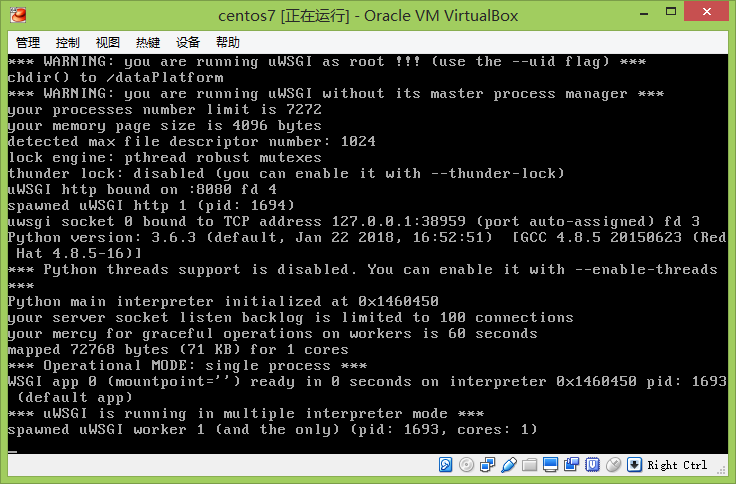
Enter the IP address and uWSGi port of CentOS7 on Windows browser
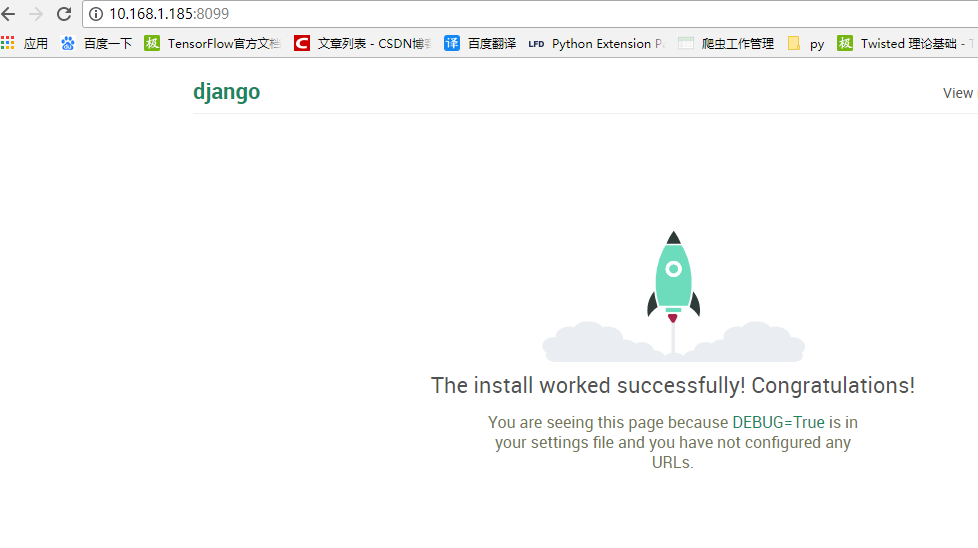
http://10.168.1.185:8080/Browsers can normally access the Django project of CentOS 7 system
UWSGi runs normally, then terminates by pressing Ctrl+z and enters instructions to view the process of uWSGi
lsof -iIf lsof is not installed on the system, it can be installed through yum install lsof
Then end the process of uWSGi: kill-9 1693 1693 is the process ID 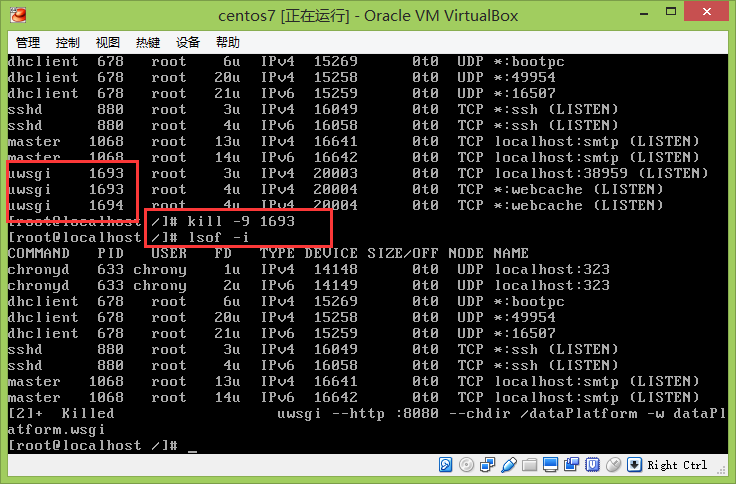
After the uWSGi test is completed, the configuration uWSGi file is written and the new file myweb_uwsgi.ini is created under the Django project. The file code is as follows.
# myweb_uwsgi.ini file
[uwsgi]
# Django-related settings
socket= :8080
# the base directory (full path)
chdir=/dataPlatform
# Django s wsgi file
module=dataPlatform.wsgi
# process-related settings
# master
master=true
# maximum number of worker processes
processes=4
# ... with appropriate permissions - may be needed
# chmod-socket = 664
# clear environment on exit
vacuum=truesocket specifies the port number for project execution.
chdir specifies the directory of the project.
module=dataPlatform.wsgi is for the myweb_uwsgi.ini file, which has a data Platform directory at its level, and a wsgi.py file under this directory.
The project catalogue is shown as follows: 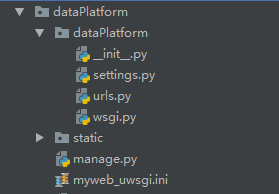
Run the uwsgi configuration file on CentOS 7, as shown in the figure: 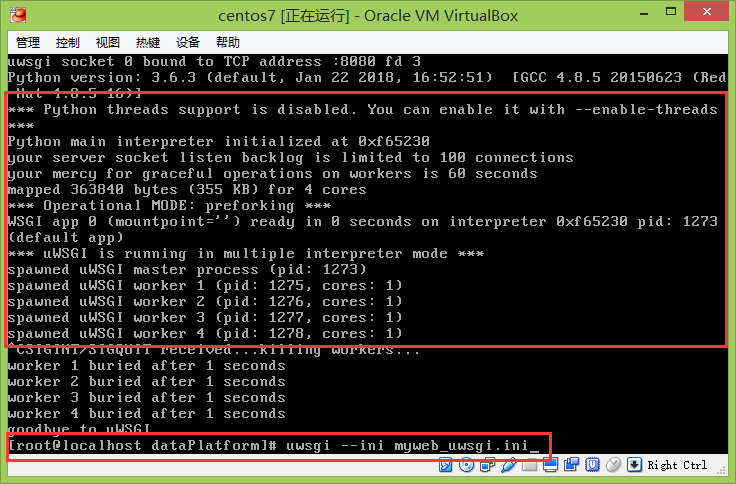
Input in Django path
uwsgi --ini myweb_uwsgi.iniThe results of the operation are shown in the figure above.
Install Nginx
Since the yum installation of CentOS 7 does not have Nginx, we add Nginx to yum
rpm -ivh http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-7-0.el7.ngx.noarch.rpmAfter adding, install nginx using yum
yum install nginxAfter installation, start nginx
service nginx startThen enter the IP address of CentOS 7 in windows browser 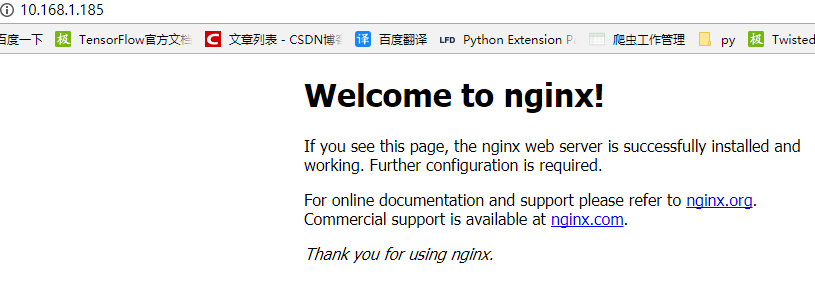
Modify the nginx.conf configuration file. Open the / etc/nginx/nginx.conf file and add the following:
………………
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
# Additional Contents
server {
listen 8099;
server_name 127.0.0.1
charset UTF-8;
access_log /var/log/nginx/myweb_access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/myweb_error.log;
client_max_body_size 75M;
location / {
include uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:8080;
uwsgi_read_timeout 2;
}
location /static {
expires 30d;
autoindex on;
add_header Cache-Control private;
alias /dataPlatform/static/;
}
}
}
The entire document reads as follows: 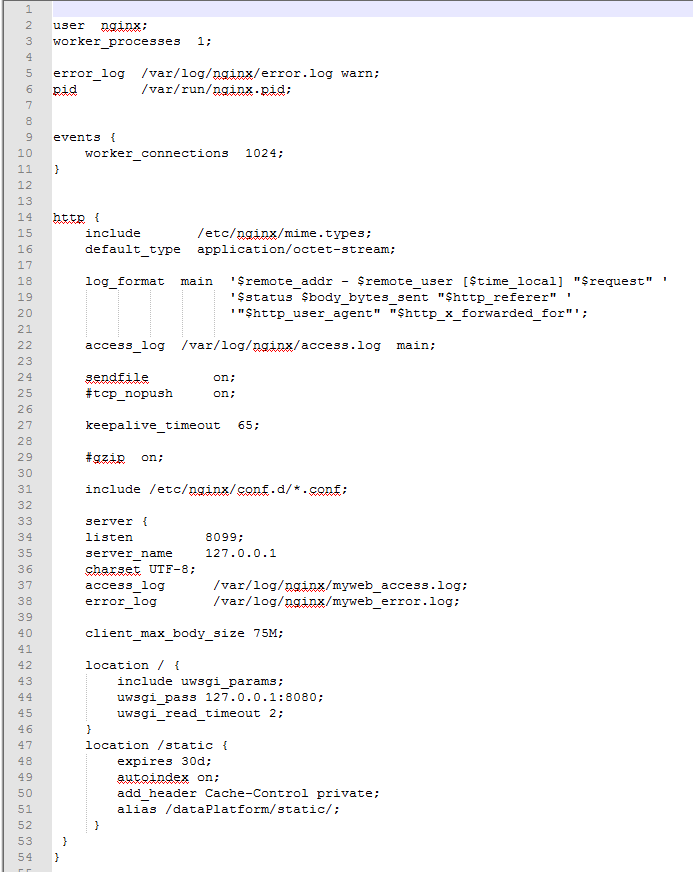
listen specifies the port number of the nginx agent uwsgi external.
Most of the information on server_name network is a web site (example, www.example.com), which takes IP address as an example.
How does nginx relate to uwsgi? Probably the most important is the configuration of these two lines.
include uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:8080;include must be specified as uwsgi_params; and uwsgi_pass refers to the port number of the native IP that must be consistent with the file in the myweb_uwsgi.ini configuration.
Finally, restart Nginx and run the following instructions on the Nginx path 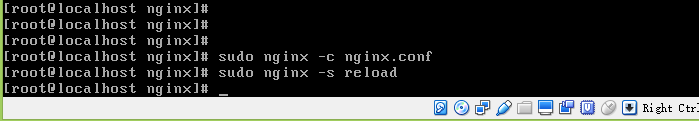
Then run the myweb_uwsgi.ini file (if the server restarts, start nginx first, then uwsgi) 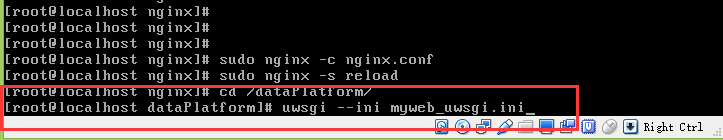
Access on browsers