VBScript script language foundation
2.1 introduction of vbs script language
2.2 the first vbs scripting language - hello world
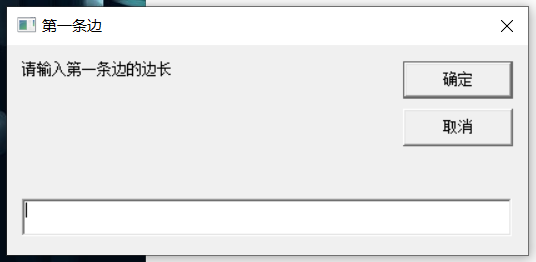
Open Notepad program, fill in the edit window, save the file extension as. vbs
dialog box:
-
Input box
inputbox("please input the length of the first edge", "the first edge")
2. Output box
msgbox("input error!")
Errors may be encountered:
1:
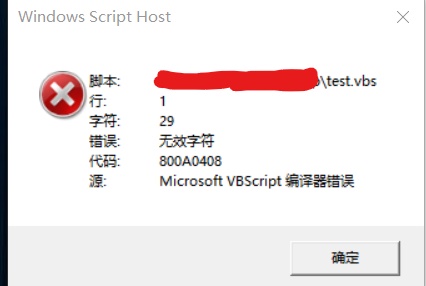
Solution: save vbs as ANSI code
2: You cannot use parentheses when calling procedure functions, i.e.: inputbox "please enter the length of the first edge", "The first edge" (because there is no assignment at this time, the function is directly used, and the function is a procedural function). However, if the function has only one parameter, you can also use parentheses when using the procedural function directly, such as: msgbox("Hello World!"); however, this will not work, such as: msgbox("Hello World!", "hh")
3: When you declare a variable, you cannot assign a value directly, but you can only assign it later, for example: dim a: a=msgbox("Hello World!", "title")
Output box - msgbox() function:
Msgbox syntax: msgbox "content of dialog box", "title of dialog box"
Parameter: if the third parameter is used, the second parameter cannot be omitted
The second parameter, numeric expression, indicates the number and type of buttons to be displayed and the icon style to be used. If omitted, the default value of buttons is 0.
msgbox "Hello World!"
msgbox"Hello World!"
msgbox c
msgbox("Hello World!")
msgbox ("Hello World!")
All of the above expressions are OK
Input box 1 inputbox() function:
Input box syntax format:
InputBox (dialog box content, dialog box title)
The return value of the inputbox() function is a string.
Variable:
-
VBScript language case insensitive
-
Variable naming rules:
The first character must be a letter.
Cannot contain an embedded period.
The length cannot exceed 255 characters.
-
There is only one basic data type Variant in VBScript
-
The data type of all variables is Variant
-
One way to declare variables is to use Dim
-
When you declare multiple variables, use commas to separate variables.
dim a,b,c
notes:
- Everything after a single quotation mark is interpreted as a comment
- What follows Rem is interpreted as a comment
Colons: separating statements
VBScript allows several statements in a line of code, but each statement is separated by a colon.
dim s,a,b a=2:b=3 s=a+b msgbox s
When VBScript is defined, there is only one variable type. In actual use, sometimes the system will automatically identify the type to be used and automatically convert it to the corresponding variable type.
2.3 arithmetic operation
Constant:
Reusing the same value can be set as a constant and declared as const
const pi=3.1415926
Arithmetic operation:
-
Add + subtract multiply * divide / quotient round / modulo (remainder) mod
-
Power operator: ^ 5 ^ 2 is the square of 5
-
Other functions:
int() takes an integer (not rounded), sqr() square root, abs() absolute value, hex() is converted to hexadecimal
cot() is converted to octal
Join operator:
& +
2.4 conditional statements and logical operations
Boolean type:
dim a,b a=true b=false ps:"true"It's a string, true Is a Boolean value
Logical operator:
- Equal to = not equal to < > greater than > less than < greater than > = less than or equal to<=
- Or or and not
if then conditional statement:
definition:
If (condition) then Execute statement end if
dim a
a=inputbox("Please enter a number greater than 100")
a=int(a)
if a>100 then
msgbox("correct")
end if
if a<100 then
msgbox("error")
end if
if then else conditional statement:
definition:
If (condition) then Execute statement 1 else Execute statement 2 end if
if a>100 then
msgbox("correct")
else
msgbox("error")
end if
Conditional statement combined with logical operation:
if a>10 and b>20 then ..... end if
Multiple conditional statements:
definition:
If (condition 1) then Execute statement 1 Else if (condition 2) then Execute statement 2 .... else Execute statement n end if end if
dim a
a=inputbox("Please enter a number greater than 100")
a=int(a)
if a>100 then .
msgbox("correct")
else if a=100 then
msgbox("boss,You're kidding me?") else
msgbox("error")
end if
end if
Error prone points:
dim a,b,c,d
a=inputbox()
b=inputbox()
c=inputbox()
d=a*2+b*2 'here d Is a numeric type, and c It is character type, so it has been c<>d
if c=d then
msgbox "f"
else
msgbox "d"
end if
select case multiple conditional statement: (without break)
dim a
a=inputbox("Enter a 1-3 Value of")
a=int(a)
select case a
case 1
msgbox "One"
case 2
msgbox "Two"
case 3
msgbox "Three"
case else
msgbox "Input error"
end select
other:
- Type conversion:
cbyte() is converted to byte type, cint() to integer type, and clng() to long integer type
cstr() to string
cdbl() is converted to double precision floating-point numbers, and csng() is converted to single precision floating-point numbers
- Time correlation function:
date(),time(), now()
year(), month(), day(), hour(), second() with parameters
- String correlation function:
len(),ucase(), lcase(), replace()
instr() finds the specified string, split() splits the string, and mid() intercepts the string
3.1 loop statement do loop
definition:
do Execute statement loop
dim sum
sum=0
do
sum=sum+int(inputbox("please enter the transaction amount"))
Loop 'is short of loop termination condition and is dead loop. You can only use ctrl+shift+esc to start the task manager to end the process
msgbox sum
In this case, you need to introduce exit do to terminate the loop
ex:
Password verification - exit do:
dim a
const pass="123456"
do
a=inputbox("Please input a password")
if a=pass then
msgbox("Password verification successful")
exit do
end if
loop
Password security verification (1) - do loop:
dim a,ctr
ctr=0
const pass="pass123_"
do
if ctr=3 then
msgbox("The certification limit has been reached.")
exit do
else
a=inputbox("Please input a password:")
if a=pass then
msgbox("Success, certification welcome!!")
exit do
else
ctr=ctr+1
msgbox("Authentication error, please check password.")
end if
end if
loop
Password security verification (2) - do while loop
dim a,ctr
ctr=0
const pass="pass123_"
do while ctr<3
a=inputbox("Please input a password:")
if a=pass then
msgbox("Successful certification, welcome!")
exit do
else
ctr=ctr+1
msgbox("Authentication error, please check password.")
end if
loop
Password security verification (2) -- do loop while
dim a,ctr
ctr=0
const pass="pass123_"
do
a=inputbox("Please input a password:")
if a=pass then
msgbox("Successful certification, welcome!")
exit do
else
ctr=ctr+1
msgbox("Authentication error, please check password.")
end if
loop while ctr<3
3.2 loop statement - while wend
definition:
While 'loop when condition is true Execute statement wend
dim countter
counter=0
while counter<5
msgbox counter
counter=counter+1
wend
Password security verification - while wend
dim a,ctr
ctr=0
const pass="pass123_"
while ctr<3
a=inputbox("Please input a password:")
if a=pass then
msgbox("Successful certification, welcome!")
ctr=3
else
ctr=ctr+1
msgbox("Authentication error, please check password.")
end if
wend
3.3 loop statement - for next
definition:
When you use a loop to increment (or decrement) one by one, you can use for next
for loop variable = initial value to final value step step step Circulatory body 1 exit for 'exit loop Circulatory body 2 next
dim counter
counter=0
for counter=0 to 5 step 1 'No write by default step Is 1
msgbox counter
next
Password security verification – for next:
dim a,ctr
ctr=0
const pass="pass123_"
for ctr=0 to 2
a=inputbox("Please input a password:")
if a=pass then
msgbox("Successful certification, welcome!")
exit for
else
msgbox ctr 'Add one at the end of a cycle
msgbox("Authentication error, please check password.")
end if
next
3.4 one dimensional array
definition:
Dim name (9) PS: starting from 0, the following table defines 10 array elements
dim a(9)
for i=0 to 9
a(i)=i
msgbox(a(i))
next
array function:
dim arr
arr=array("t1","t2","t3")
msgbox arr(0)
msgbox arr(1)
msgbox arr(2)
lbound function and ubound function:
The lbound function takes the minimum subscript, and the ubound function takes the maximum subscript
dim arr
arr=array("t1","t2","t3")
for i=0 to ubound(arr)-lbound(arr)
msgbox arr(i)
next
join function:
Change array to string
dim arr
arr=array("t1","t2","t3")
msgbox join(arr,",")
split function:
Changes a string to an array
dim arr,str str="t1,t2,t3" arr=split(str,",") msgbox arr(0) msgbox arr(1) msgbox arr(2)
ex:
One dimensional array - save Student Name:
dim name(5),str 'A total of 6 students, str Store the names of all students
for i=0 to 5
name(i)=inputbox("Please enter No"&i+1&"Names of students")
str=str&" "&name(i)
next
msgbox str
Three one dimensional arrays - store student information:
dim name(2),age(2),score(2),ctr,cname
for ctr=0 to 2
name(ctr)=inputbox("Please enter No"&ctr+1&"Names of students")
age(ctr)=inputbox("Please enter No"&ctr+1&"Age of students")
score(ctr)=inputbox("Please enter No"&ctr+1&"Results of students")
next
msgbox name(0)
msgbox age(1)
msgbox score(2)
Query all the information of the designated student:
cname=inputbox("Please enter the name you want to query:")
for ctr=0 to 2
if name(ctr)=cname then
exit for
end if
next
msgbox("full name:"&name(ctr)&" "&"Age:"&age(ctr)&" "&"Results:"&score(ctr))
3.5 loop statement - for each next
definition:
for each member in array or collection
Circulatory body
next
dim a(9),v
for i=0 to 9
a(i)=i
next
//Method 1:
for each v in a
msgbox v
next
//Method 2:
for i=0 to 9
msgbox a(i)
next
Multiplication formula - loop nesting:
dim i,j,str
for i=1 to 9
for j=1 to 9
str=str&i*j&" "
next
str=str&vbCrlf 'vbCrlf For carriage return and line feed
msgbox str
next
3.6 two dimensional array
definition:
dim a(3,2) ps: the subscript starts from 0 and defines 4 * 3 = 12 array elements
dim a(3,2),i,j,str
for i=0 to 3
for j=0 to 2
a(i,j)="x"&j
next
next
for i=0 to 3
for j=0 to 2
str=str&a(i,j)&" "
next
str=str&vbcrlf
msgbox str
next
ex:
Two dimensional array - store student information:
dim student(3,2),i,j,ctr,cname,opt
for i=0 to 3
for j=0 to 2
select case j
case 0
opt="name"
case 1
opt="age"
case 2
opt="score"
end select
student(i,j)=inputbox("Please enter No"&i+1&"Student's"&opt)
next
next
cname=inputbox("Please enter the name you want to query:")
for ctr=0 to 3
if student(ctr,0)=cname then
exit for
end if
next
msgbox("full name:"&student(ctr,0)&" "&"Age:"&student(ctr,1)&" "&"Results:"&student(ctr,2))
ps: use select ······· end select statement to express field name more clearly
3.7 functions
The defined functions and procedures can be placed before or after the call
definition:
Function function name (parameter list)
Function code
Function name = a value 'is used to return a value
end function
Definition of nonparametric function:
function func() msgbox "hello world!" end function
Function call:
call function name (parameter list)
call func
call func() 'is called directly and must be called with call statement
In principle, func tions cannot be used directly
func()
Definition of function with parameters:
dim name
function func(name)
msgbox "hello "&name
end function
Function call with parameters:
call func("Zhang San") "is used directly and must be called with a call statement
In principle, func tions cannot be used directly
func("Wangwu")
User defined function - sum of two numbers:
function add(num1,num2)
dim num
num=num1+num2
msgbox num
end function
call add(1,2)
add 1,2
ps: when you use call, you must take () but you can also leave ()
When call is not used, do not take (), but when there is no parameter or only one parameter, you can take ()
Function return value:
function add(num1,num2)
add=num1+numm2 'Used to return a value
end function
msgbox add(1,2)
3.8 process
Either a process or a function is called a process
Difference: procedure has no return value and cannot be placed in expression
Process definition:
sub procedure name (parameter list)
Process code
end sub
The definition of nonparametric process is as follows
sub func()
msgbox "hello world!"
end sub
Procedure call:
call procedure name (parameter list)
call func
call func()
func
func()
Definition of process with parameters:
dim name
sub func(name)
msgbox "helllo "&name
end sub
Call of procedure with parameters:
call func("Zhang San")
func "Li Si"
func("Wangwu")
Custom procedure - sum of two numbers:
sub add(num1,num2)
dim num
num=num1+num2
msgbox num
end sub
call add(1,2)
add 1,2 'Do not use parentheses at this time
ps: when using call, always bring ()
When call is not used, do not take (), but when there is no parameter or only one parameter, you can take ()
3.9 process and function
Summary:
-
Function has return value, procedure has no return value
Process:
sub total(x,y)
sum=x+y
msgbox "The sum of two numbers is "&sum
end sub
total 30,20
//Function:
```vbscript
dim a,b
function exp()
b=3
exp=b+1
end function
msgbox exp()+1
-
Functions can be placed in expressions, procedures cannot
msgbox exp*2+3 'is also correct
In this case, exp() can not be written () because there is no parameter
-
When the function return value is received, call cannot be used and must be accompanied by ()
str =call exp() 'syntax error
-
When you do not use call, do not take (). When there is no parameter or only one parameter, you can take ()
-
Function can only appear on the right side of an assignment statement or in an expression, and cannot be used directly. If you use a function directly, you must call it with a call statement and cancel the return value
3.10 VBS running external program
CreateObject
-
VBS also provides some internal functions and objects, but VBS does not provide any commands to access the components inside the Windows system.
-
It provides a very convenient and powerful command - CreateObject.
-
The CreateObject command can access all the com objects installed in windows system, and can call the commands stored in these components.
Common objects of Windows Script Host
WSH(Windows Scripting Host) is the host used to parse VBS. WSH can use script to realize the automation of computer work, but it also makes the system have security risks.
The WSH contains several common objects:
1, Scripting.FileSystemObject -- > provides a complete set of file system operation functions
2, Scripting.Dictionary -- > is used to return the dictionary object where the key value pair is stored
3, Wscript.Shell -> provides a set of functions to read system information, such as reading and writing the registry, finding the path of the specified file, reading DOS environment variables, and reading the settings in the link
4, Wscript.NetWork A - provides network connection and remote printer management
Function. (all Scripting objects are stored in the SCRRUN.DLL In the file, all Wscript objects are stored in the WSHOM.ocx File. )
CreateObject
Dim objShell
Set objShell = CreateObject("Wscript. Shell")
objShell.Run "notepad"
Set is a vbs instruction. If you assign a -- object reference to a variable, you need to use the set keyword.
The object of vbs has built-in functions and variables, and its reference method is to add "." after the variable, followed by the function to realize the function.
● objshell.run Call Wscript.shell Run is a function of running an external program in. notepad is the file name of notepad program. It can also be changed to calculator file name "calc", word file name winword
Both programs start at the same time
Dim objShell
Set objShell = CreateObject("Wscript. Shell")
objShell.Run "notepad"
objShell.Run "calc"
Two programs start in sequence
Dim objShell
Set objShell = CreateObject("Wscript.Shell")
objShell.Run "notepad", ,true
objShell.Run "calc"
'At this time, the calculator will not be opened until the Notepad is closed
The run function has three parameters:
- The first parameter is the path of the program you want to execute.
- The second parameter is the form of the window. 0 is running in the background; 1 is running normally; 2 is activating the program and displaying it as minimized; 3 is activating the program and displaying it as maximized. The default is 1
- The third parameter indicates whether the script will wait or continue to execute. If set to true, the script will wait for the calling program to exit and then execute backward. The default is false
- The run function has a return value. If the return value is 0, it means successful execution. If it is not 0, the return value is the error code. You can find the corresponding error through this code.
3.11 error handling
On Error Resume Next
- This line of statement tells VBS to skip the statement with an error at run time and execute the statement that follows it.
- When an error occurs, the statement will push the relevant error number, error description and related source code into the error stack.
- Although the On Error Resume Next statement prevents vbs scripts from stopping running when an error occurs, it does not actually handle errors.
err object
- vbscript provides an object, err object
- There are two ways: clear, raise
- Five attributes: description, helpcontext,helpfile,number,source
- The err object can be used directly without referring to instances
Example:
on error resume next
dim a,b,c
a=5
b=0
c=a/b
msgbox "hi!"
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
wscript.echo Similar to msgbox
3.12 file operation
vbs reading and writing operation of files
1. Open the file
-
Using the opentextfile method
set fs =createobject("scripting.filesystemobject") set ts=fs.opentextfile("d:\1.txt",1,true) -
Note that you need to fill in the full path of the file. The latter parameter is access mode. You can open the file in the current directory without entering the path
-
1 is forreading
-
2 is for writing
-
8 is appending
-
The third parameter specifies whether to create the specified file if it does not exist.
2. Read file
There are three ways to read a file:
read(x) read x characters
readline reads a line
readall read all
For example:
set fs =createobject("scripting.filesystemobject")
set ts=fs.opentextfile("d:\1.txt",1,true)
value=ts.read(20)
line=ts.readline
contents=ts.readall
The atendofstream property of the textstream object. This property returns true when it is at the end of the file. We can use a loop to detect that the end of the file is not reached. For example:
set fs =createobject("scripting.filesystemobject")
set t=fs.opentextfile("d:\3.txt",1,false)
do while t.atendofstream<>true
str=str&t.read(1)
loop
msgbox str
t.close
- skip(x) skip x characters
- Skip a line
3. Writing documents
It can be written in the form of forwriting and forappending
There are three ways to write:
- write(x), the output of this method does not newline. It needs to use chr(13) carriage return character, chr(10) line feed character, vbcrlf carriage return line feed character (when chr(13) and chr(10) are used separately, they are carriage return character and line feed character respectively; but if they are not used together, they are both carriage return and line feed character)
- writeline, which will wrap the line automatically (one line will be empty automatically)
- Write blank lines (n) write n blank lines
Example:
'Writing documents
data="hello, I like script programing"+vbcrlf
set fs =createobject("scripting.filesystemobject")
if (fs.fileexists("d:\4.txt")) then
set f =fs.opentextfile("d:\4.txt",8)
f.write data
f.writeline data
f.close
else
set f=fs.opentextfile("d:\4.txt",8, true)
f.writeblanklines 2
f.write data
f.close
end if
'Read write operation
'Write:
dim fs,f,t,str
set fs =createobject("scripting.filesystemobject")
set f=fs.createtextfile("d:\test.txt")
f.write("hello world!")
f.close
'Read:
set t=fs.opentextfile("d:\test.txt",1,false)
do while t.atendofstream<>true
str=str&t.read(1)
loop
t.close
msgbox str
3.13 shell operation
1. Open Notepad
The following vbscript code uses Notepad to open a copy of the currently running script.
set wshshell = wscript.createobject("wscript.shell")
wshshell.run "%windir%\notepad "
Here% windir%, or% systemroot%, represents the path C: windows
2. Execute the CMD command
The following vbscript code opens a command window, changes the path to c: \, and executes the dir command.
dim oshell
set oshell = wscript.createobject ("wscript.shell")
oshell.run "cmd /k "
Analog keyboard input:
3. Basic keyboard input
dim wshshell
set wshshell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
wshshell.run"notepad"
wscript.Sleep 3000 'Delay 3 seconds
wshshell.SendKeys " {Enter}" 'Analog input carriage return
wshshell.SendKeys "hello" 'Analog input hello
Input 4, special keyboard
For keys that need to be combined with shift, ctrl and alt, sendkeys uses special characters to indicate:
—shift +
—ctrl ^
—alt %
Press ctrl+E at the same time
—wshshell.sendkeys"^e"
Hold down the ctrl key while pressing the e and c keys
—wshshell.sendkeys"^(ec)"
Hold down the ctrl and e keys at the same time, then release the ctrl key, and press the c letter key alone
—wshshell.sendkeys"^ec"
5. Special control button
Special control keys, as long as the braces around these characters.
Send plus sign "+":
—wshshell.sendkeys"{+}"
Send enter key:
—wshshell.sendkeys"{enter}"
Send down arrow key:
—wshshell.sendkeys"{down}"
6. Repeat the letters:
The format is: {key number}
Send 10 letters "x"
—wshshell.sendkeys"{x 10}"
regular expression
4.1 introduction to regular expressions
What is a regular expression
Regular expression was first proposed by mathematician Stephen Kleene in 1956. Now the standard has been approved by ISO and recognized by Open Group
A regular expression uses a single string to describe and match a series of strings that conform to a certain syntactic rule.
Regular expressions consist of some common characters and some metacharacters with special meanings.
What do regular expressions do
Find / replace
Verify data format
Verify data validity
Data analysis
......
Application scenarios
It can quickly filter and replace some specific strings
– search text
- web crawler
- user input validation
- batch text processing
Three ways to search for characters:
- precise search, wildcard search, regular expression search
What do regular expressions do
· regular expression process
Take out the expression and compare the characters in the text at a time. If each character can match, the matching is successful, otherwise it fails.
Learning regular expressions is, in principle, learning various metacharacters.
It's not difficult to write regular expressions, but it's not very readable.
4.2 regular expression basis
Metacharacter
· wildcards
· qualifier
? locator
- metacharacters that represent the range and selection
- escape character
· non captured metacharacters
......
wildcard
| character | describe |
|---|---|
| . | Match any single character, match any character except newline |
| \d | Match any number |
| \w | Match characters that can form words, match letters, numbers, and underscores |
| \x | Matches any hexadecimal digit |
| \s | Match any white space character |
•. - matches any single character except "\ n". To match any character, including "|", use "(. |)". •\d - matches a numeric character. It is equivalent to [0-9]. •\w - matches any word characters that include underscores. Equivalent to "[A-Za-z0-9"_ ]”. •\s - matches any white space characters, including spaces, tabs, page breaks, and so on. It is equivalent to [\ f / N / R / T / v]. •\D - matches a non numeric character. Equivalent to [^ 0-9]. •\W - matches any non word characters. Equivalent to "[^ A-Za-z0-9"_ ]”. •\S - matches any non white space characters. It is equivalent to [^ / F / N / R / T / v].
qualifier
| character | describe |
|---|---|
| * | Matches the preceding subexpression zero or more times, equivalent to {0,} |
| + | Matches the previous subexpression one or more times, equivalent to {1,} |
| ? | Matches the previous subexpression zero or once, equivalent to {0,1} |
| {n} | Matching determined n times (n nonnegative integer) |
| {n,} | Match at least N times (n nonnegative integer) |
| {n,m} | Minimum matching n times and maximum matching m times (n, m non negative integer and N < = m) |
character repeat
•*
– zo * can match "z" and "zoo". *It is equivalent to {0,}.
•+
– "zo +" can match "zo" and "zo", but not "z". +It is equivalent to {1,}.
•?
- "do(es)?" can match "does" or "do" in "does". ? is equivalent to {0,1}.
•{n}
- "o{2}" cannot match "O" in "Bob", but can match two o's in "food".
•{n,}
- "o{2,}" cannot match "O" in "Bob", but can match all o in "fooood." o{1,} "is equivalent to" O + " o{0,} "is equivalent to" O * ".
•{n,m}
- "o{1,3}" will match the first three o's in "food." o{0,1} "is equivalent to" O? ". Note that you cannot have spaces between commas and two numbers.
Locator
| Metacharacter | describe |
|---|---|
| ^ | Match the beginning of the string, or exclude |
| $ | Matches the end of the string |
| \b | Matches the boundary of a string, matches the beginning or end of a word |
| \B | Non boundary of matching string |
The qualifier cannot be used for locators
Character escape
•\
Mark the next character as a special character, or an literal character, or a backward reference, or an octal escape character.
· "\ \ n" matches a newline character
· \ + means match+
· \ * match*
"\" matches "\"
· "\ (" matches "("
www.zjei.net And www.zjei.net
Scope, selection
| Metacharacter | describe |
|---|---|
| . | Match any single character |
| [] | Match any character in the bracket. If you don't match the character in bracket, add ^ after [to exclude |
| - | specified area |
| | | or |
Nonprinting characters
| character | describe |
|---|---|
| \cx | Matches the control character specified by x. For example, cM matches a Control-M or carriage return. The value of x must be one of A-Z or A-Z. Otherwise, c is treated as an original 'c' character. |
| \f | Match a page break. It is equivalent to ﹣ x0c and ﹣ cL |
| \n | Matches a newline character. It is equivalent to both the ﹣ x0a and the ﹣ cJ. |
| \r | Match a carriage return. It is equivalent to both the ﹣ x0d and the ﹣ cM. |
| \s | Matches any white space characters, including spaces, tabs, page breaks, and so on. It is equivalent to [\ f / N / R / T / v]. |
| \S | Matches any non white space characters. Equivalent to 1. |
| \t | Match a tab. It is equivalent to the two. |
| \v | Match a vertical tab. It is equivalent to both the ﹣ x0b and the ﹣ cK. |
How to construct regular expression
Regular expressions are constructed in the same way as mathematical expressions. That is to use a variety of metacharacters and operators to combine small expressions to create larger expressions. The components of a regular expression can be a single character, a set of characters, a range of characters, a selection between characters, or any combination of all of these components.
priority
| Priority (descending from top to bottom) | Metacharacter | describe |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \ | Escape character |
| 2 | (), (?😃, (?=), [] | Subexpressions and qualifications |
| 3 | *, +, ?, {n}, {n,}, {n,m} | qualifier |
| 4 | ^, $, \metacharacter | Location and sequence |
| 5 | | | or |
Examples
^[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*$ //Match positive integers
^((-\d+)|(0+))$ //Match non positive integers
^-?\d+$ //Match integer
^(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?$ //Matching floating point numbers
^[A-Za-z]+$ //Matches a string of 26 English letters
[\u4e00-\u9fa5] //Match Chinese characters
[a-zA-Z0-9_]+@[1-9a-z]+(\.[a-z]{2,5})+ //email
1[358][0-9]{9}Or 1[358]\d{9} //phone number
Priority of character class operators
They are arranged from the highest to the lowest as follows: 1 literal escape Group 2 [...] 3 range a-z 4 union [a-e][i-u] 5 intersection [A-Z & [aeiou]]
Examples
[abc] a, b or c [^ abc] any character except a, b, or c (negative) [a-zA-Z] a to Z or a to Z, including the letters at both ends [a-d[m-p]] a to d or m to P: [a-dm-p] (Union) [A-Z & & [def]] d, e, or f (intersection) [A-Z & [^ BC]] A to Z, except b and c: [ad-z] (minus) [A-Z & & [^ M-p]] A to Z, not m to p: [a-lq-z] (minus)
4.3 VBS regular expression
RegExp object
In VBS, RegExp objects are used to support the use of regular expressions.
The RegExp object provides three properties and three methods:
· attributes: Pattern, Global, IgnoreCase
Methods: Test, Replace and Execute
The creation of RegExp object
•set re = new regexp
•Set regex = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
Properties of RegExp object
•Pattern:
· this attribute is used to describe the matching pattern of a regular expression, such as "+" to match one or more previous expressions, and "." to match any single character other than the newline character.
•Global:
This property is used to set whether only the first or all matches are matched during the search process. When = True, all matches, if False, only one match.
•IgnoreCase:
· this property is used to set whether the matching string is case sensitive or not, = True is not sensitive, and = False is case sensitive.
Methods of RegExp object
•Test(string)
The method is used to perform a regular expression search on the specified string string and returns a Boolean value indicating whether a matching pattern has been found.
•Replace(string1,string2)
This method is used for string2 to replace the text found by performing regular expression in string1. The return value is the replaced string.
•Execute(string)
The method is used to perform a regular expression search on the specified string string, which returns a set of matches containing each match found in the specified string.
Dim re, str
Set re = New RegExp
'Equivalent to CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
re.Pattern = "[23456789]" 'Equivalent to"[2-9]"
str = "Spain received 3 millimeters of rain last week."
MsgBox re.Test(str)
MsgBox re.Replace(str, "many")
Dim re, str Set re = New RegExp re.Pattern = "\d" 'Change to"\d+"See what's different str = "a b c d e f 1 g 2 h ... 10 z" MsgBox re.Test(str) MsgBox re.Replace(str, "number")
Matches object
The Matches object is a collection that contains several independent Match objects.
· can only be created using the Execute method of the RegExp object.
The Matches object provides two properties:
Properties: Count, Item
Properties of the Matches object
•Count:
This property describes the total number of matching objects.
•Item(i):
This property is used to return the Match object i+1 in the Matches object.
Dim re, s, mtchs
Set re = New RegExp
re.Global = True
re.Pattern = "\w+"
s = "Apple:iphone_5s;NOKIA:Nokia_1020"
Set mtchs = re.Execute(s)
msgbox mtchs.count
For i=0 to mtchs.count-1
msgbox mtchs.item(i)
Next
Match object
When a regular expression is executed, zero or more Match objects may be generated.
Each Match object provides access to the string that matches the regular expression, the length of the string, and an index that identifies the location of the Match.
The Match object provides three properties:
Properties: FirstIndex, Length, Value
Properties of Match object
•FirstIndex :
Returns the matching position in the search string. Uses a zero based offset relative to the start of the search string.
•Length:
Returns the length of the match found in a string search.
•Value:
This property is used to return a matching value or text found in a search string.
Dim re, s, mtch
Set re = New RegExp
re.Global = True
re.Pattern = "\w+"
s = "Apple:iphone_5s;NOKIA:Nokia_1020"
Set colMatches = re.Execute(s)
msgbox colMatches.count
For each mtch in colMatches
msgbox mtch.value
msgbox mtch.firstindex
msgbox mtch.length
Next
4.4 advanced applications of regular expressions
Greedy and non greedy matching (1)
· first, match greedy and non greedy as much as possible
· Greed: matching as much as possible
| character string | expression | Matching results | explain |
|---|---|---|---|
| abcabca | (a)(\w+) | abcabca | Where (\ w +) matches all characters after a, that is, bcabca |
| abcabca | (a)(\w+)(a) | abcabca | Although (\ \ w +) can also match all characters after the first a, in order to make the following (a) match, (\ w +) will match all characters between the first a and the last a, namely bcabc, and give up the last a |
Dim re, str, mtch
Set re = New RegExp
re.Global = True
re.Pattern = "(a)(\w+)" 'try(a)(\w+)(a)
str = "abcabca" 'try abcabcabc
Set colMatches = re.Execute(str)
msgbox colMatches.count
For each mtch in colMatches
msgbox mtch.value
Next
Greedy and non greedy matching (2)
· non greedy: matching as little as possible
Add a '?' to the metacharacter that limits the number of matches
| character string | expression | Matching results | explain |
|---|---|---|---|
| abcabca | (a)(\w+?) | ab | Where (﹥ w +?) only matches b after a |
| abcabca | (a)(\w+?)(a) | abca | In order for the following (a) to match, (\ w +) will match bc after the first a |
Dim re, str, mtch
Set re = New RegExp
re.Global = True
re.Pattern = "(a)(\w+?)" 'try(a)(\w+?)(a)
str = "abcabca" 'try abaabaa
Set colMatches = re.Execute(str)
msgbox colMatches.count
For each mtch in colMatches
msgbox mtch.value
Next
Reverse reference
The matching result of the subexpression contained in parentheses () in the expression is recorded
· use the matching result that can refer to the previous nth subexpression
The ordinal number n of the subexpression is arranged in the order of the left bracket "("
The next value is the same as the first subexpression
String expression matching results
AAA, ාාාාාාාාාාාාාාාාාාා
Second matching bb
*Hello *, ාා##########|########|###) (. *?) (\ 1) first match * hello*
Second match ා world#
Dim re, str, mtch
Set re = New RegExp
re.Global = True
re.Pattern = "([ab])(\1)"
str = "aaa,#bbb#" 'try aba,#bab#
Set colMatches = re.Execute(str)
msgbox colMatches.count
For each mtch in colMatches
msgbox mtch.value
Next
Dim re, str, mtch
Set re = New RegExp
re.Global = True
re.Pattern = "(\*|#)(. *?) (- 1) "try to remove? And set greedy matching
str = "*hello*,#world#" 'try*hello*,#world*
Set colMatches = re.Execute(str)
msgbox colMatches.count
For each mtch in colMatches
msgbox mtch.value
Next
Non capture metacharacter
| character | describe |
|---|---|
| (?😃 | Do not cache the subexpression in which it is located |
| (?=) | The right side of the match must satisfy the pattern after? = |
| (?!) | The right side of the match must not satisfy the pattern after? = |
| (?<=) | The left side of the match must satisfy the pattern after? < = |
| (?<!) | The left side of the match must not satisfy the pattern after? < = |
Pre search
The pre search does not match and is a limiting condition
•(?:pattern)
- matches the pattern but does not get the matching result, that is, it is a non fetched match and is not stored for future use. This is useful when using the or character "(|)" to combine parts of a pattern.
For example, "industry (?: y|ies)" is a simpler expression than "industry|industries".
Forward pre search
•(?=pattern)
- forward positive prefetching to match the lookup string at the beginning of any string that matches a pattern. This is a non fetch match, that is, the match does not need to be retrieved for later use. For example, "Windows(?=95|98|NT|2000)" can match "windows" in "Windows2000", but not "windows" in "Windows3.1". Prefetching does not consume characters, that is, after a match occurs, the search for the next match begins immediately after the last match, rather than after the character that contains the prefetch.
•**(?!**pattern)
- forward negative prefetching, matching the lookup string at the beginning of any string that does not match the pattern. This is a non fetch match, that is, the match does not need to be retrieved for later use. For example, "Windows(?!95|98|NT|2000)" can match "windows" in "Windows3.1", but not "windows" in "Windows2000". Prefetching does not consume characters, that is, after a match occurs, the search for the next match begins immediately after the last match, rather than after the character that contains the prefetch.
· forward pre search:
The right side of – (? = xxx) must match the expression corresponding to xxx
- (?! xxx) right must not match the expression corresponding to xxx
| character string | expression | result |
|---|---|---|
| windows98 windowsNT windows2000 | Windows(?=NT|XP) | windows in windows NT |
Dim re, str, mtch
Set re = New RegExp
re.Global = True
re.IgnoreCase = True
re.Pattern = "Windows(?=NT|XP)" 'Change to Windows(?!NT|XP)
str = "windows98; windowsNT; windows2000"
Set colMatches = re.Execute(str)
msgbox colMatches.count
For each mtch in colMatches
msgbox mtch.value
Next
Reverse pre search
•**(?<=**pattern)
Reverse positive pre check is similar to positive pre check, but in the opposite direction. For example, (? < = 95| 98 | NT | 2000) Windows can match "Windows" in "2000 Windows", but not "Windows" in "3.1 Windows".
•(?pattern)
- reverse negative pretest is similar to positive negative pretest, but in the opposite direction. for example
"(? <! 95| 98| nt| 2000) windows" can match
"Windows" in "3.1 windows", but cannot match
Windows in 2000 windows.
· reverse pre search:
- (? < = xxxxx) the left side must match the expression corresponding to xxx
- (? <! Xxxxx) the left side must not match the expression corresponding to xxx
Examples:
–\b\w+(?=ing\b)
•The beginning of words ending with 'ing'
–(?<=\bre)\w+\b
•The end of words starting with 're'
- matches the second half of a word that starts with re (except for re), for example, when looking for reading a book, it matches ading.
Dim re, str, mtch
Set re = New RegExp
re.Global = True
re.IgnoreCase = True
re.Pattern = "\b\w+(?=ing\b)"
str = "The beginning of words ending with 'ing'."
Set colMatches = re.Execute(str)
msgbox colMatches.count
For each mtch in colMatches
msgbox mtch.value
Next
Exercises after class
1. Write a program to output your specialty. Input box () should have two parameters and output box msgbox() should have three parameters.
dim a
a=inputbox("Enter professional name","major")
msgbox a,0,"The major is:"
2. Write a program for three times input, respectively input your student number, name, class, and output three times.
dim a,b,c
a=inputbox("Student number:")
msgbox a
b=inputbox("full name:")
msgbox b
c=inputbox("Class:")
msgbox c
3. Make a program to get the remainder of 20 / 3.
dim a a=20 mod 3 msgbox a,,"a The remainder of is:"
4. Make a cuboid volume small program, respectively pop up three input boxes, input length, width, height, pop-up dialog box shows the volume.
dim a,b,c,v
a=int(inputbox("Length:"))
b=int(inputbox("Width:"))
c=int(inputbox("Height:"))
v=a*b*c
msgbox v,0,"The volume is:"
5. Given a number, greater than 10 and less than 20, output "correct", otherwise output "error".
dim a
a=inputbox("Enter a number:")
if a>10 and a<20 then
msgbox "correct"
else
msgbox "error"
end if
6. Input 12 or 15, output "correct", otherwise output "error".
dim a
a=inputbox("Enter a number:")
a=int(a)
if a=12 or a=15 then
msgbox "correct"
else
msgbox "error"
end if
7. A program is compiled to calculate the area of the circle. The radius is given by the user (using Inputbox), and PI value is 3.14159.
dim r,s
const pi=3.14159
r=inputbox("r=")
s=pi*r^2
msgbox(s)
1. Outputs all numbers from 1 to 100 that cannot be divisible by 3
dim i,s
for i=1 to 100
if i mod 3<>0 then
s=s&i&" "
end if
next
msgbox s
2. Find out whether 1-99 is a multiple of 7 or a digit number is 7 or a 10 digit number is 7, and output these numbers, and count how many
dim i,s,m
m=0
for i=1 to 99
if i mod 7=0 or i mod 10=7 or i \10=7 then
s=s&i&" "
m=m+1
end if
next
msgbox s,,"These figures are:"
msgbox m,,"The number is as follows:"
3. If a number is exactly equal to the sum of its factors, the number is called "perfect number". (factor: excluding the positive divisor of the number itself), for example, 6 = 1 + 2 + 3. Program to find all the completion within 1000.
dim i,j,s,m
for i=2 to 999
s=0
for j=1 to i-1
if i mod j=0 then
s=s+j
end if
next
if i=s then
m=m&i&" "
end if
next
msgbox m,,"1000 The number of completion within is:"
4. Narcissus number refers to an n-digit number (n ≥ 3). The sum of the n-th powers of the numbers on each digit is equal to itself. (for example: 1 ^ 3 + 5 ^ 3 + 3 ^ 3 = 153)
Tips:
153 digits are 3, 10 digits are 5, and 100 digits are 1
The number of 236 digits is 6, the number of tens is 3, and the number of 100 is 2
dim a,i,j,k,s
for a=100 to 999
i=a\100
j=(a mod 100)\10
k=a mod 10
if i^3+j^3+k^3=a then
s=s&a&" "
end if
next
msgbox s,,"100 From 999 to 999, the number of all daffodils is:"
5. In our country's classic mathematical work "nine chapters of arithmetic", there is such a question: 100 money for 100 chickens, 5 yuan for a rooster, 3 yuan for a hen and 1 yuan for 3 chickens) to find out how many ways to buy these chickens. If I can't understand it, I use colloquial language to say: someone wants to buy chickens, and with 100 yuan they just buy 100 chickens. The price is as follows: male: 5, female: 3, female: 3, small: 1 $3, Let's ask how many ways to sell (how to match the male and the female). Please solve this problem by circulation
Tips:
If the number of roosters is a, then the range of a is?
If the number of hens is b, then the range of b is?
dim gj,mj,xj,s
for gj=0 to 100
for mj=0 to 100
for xj=0 to 100
if(gj+mj+xj=100 and 5*gj+3*mj+xj/3=100) then
s=s&"cock:"&gj&" hen:"&mj&" chick:"&xj&vbCrlf
end if
next
next
next
msgbox s,,"All combinations:"
1. Define an array, including 5 elements, which are random integers (random input). They are required to be sorted from large to small and output.
dim a(4),m,s,t
for m=0 to 4
s= inputbox ("Please input 5 numbers in sequence,The first"&(m+1)&"individual:")
a(m)=int(s)
next
for i=0 to 3
for j=0 to 3-i
if a(j+1)>a(j) then
t=a(j)
a(j)=a(j+1)
a(j+1)=t
end if
next
next
msgbox join(a,",")
2. The existing string "10 / 12 / 34 / 23 / 45 / 35 / 45" is used to divide the characters according to the character "\" and calculate the sum of each character.
dim s,a,i,sum
sum=0
s="10\12\34\23\45\35\45"
a=split(s,"\")
for i=lbound(a) to ubound(a)
sum=sum+a(i)
next
msgbox sum,," The sum of the characters is:"
3. Read in 10 numbers, output even and their sum, and output odd and their average.
dim m,s,a(9),s1,s2,i,j,sum1,sum2,avr
sum1=0
sum2=0
j=0
for m=0 to 9
s= inputbox ("Please input 10 numbers in turn,The first"&(m+1)&"individual:")
a(m)=int(s)
next
for i=0 to 9
if a(i) mod 2=0 then
s1=s1&a(i)&" "
sum1=sum1+a(i)
else
s2=s2&a(i)&" "
sum2=sum2+a(i)
j=j+1
end if
next
msgbox s1,,"Even numbers are:"
msgbox sum1,,"The sum of even terms is:"
msgbox s2,,"The odd number is:"
msgbox sum2/j,,"The average number of odd items is as follows:"
4. Define an array and read in 10 numbers. Please use for each next to output their sum and average value.
dim v,m,s,a(9),sum,avr
sum=0
for m=0 to 9
s= inputbox ("Please input 10 numbers in turn,The first"&(m+1)&"individual:")
a(m)=int(s)
next
for each v in a
sum=sum+v
next
avr=sum/10
msgbox sum&","&avr,,"Their sum and average values were as follows:"
5. There are two two-dimensional arrays a(4,4) and b(4,4) (the element values are arbitrary), and exchange two arrays (the original values of all elements of a become b, and all the element values of b become a).
dim a(4,4),b(4,4),i,j,s1,s2
for m=0 to 4
for n=0 to 4
a(m,n)="a"&m&"-"&n
next
next
for m=0 to 4
for n=0 to 4
b(m,n)="b"&m&"-"&n
next
next
rem transformation:
for i=0 to 4
for j=0 to 4
t=a(i,j)
a(i,j)=b(i,j)
b(i,j)=t
next
next
rem Output:
for v1=0 to 4
for v2=0 to 4
str1=str1&a(v1,v2)&" "
next
str1=str1&vbcrlf
next
for v1=0 to 4
for v2=0 to 4
str2=str2&b(v1,v2)&" "
next
str2=str2&vbcrlf
next
msgbox str1,,"a Converted to:"
msgbox str2,,"b Converted to:"
1. Using the function, the user inputs two numbers and outputs the maximum value and the minimum value.
dim a,b
a=inputbox ("Please enter 2 numbers: the first one")
b=inputbox ("Please enter 2 numbers: the second")
function hh(a,b)
if a>b then
hh="The maximum value is:"&a&","&"The minimum value is:"&b
else if a<>b then
hh="The maximum value is:"&b&","&"The minimum value is:"&a
else
hh="The two numbers are equal and there is no maximum or minimum"
end if
end if
end function
msgbox hh(a,b)
2. Using the function, the user input the radius of the circle and output the area of the circle.
dim r
r=inputbox("Please enter the radius of the circle:")
const pi=3.14
function s(r)
s="The area of the circle is: "&pi*r^2
end function
msgbox s(r)
3. Using the process, the user inputs two numbers and outputs the maximum value and the minimum value.
dim a,b
a=inputbox ("Please enter 2 numbers: the first one")
b=inputbox ("Please enter 2 numbers: the second")
sub hh(a,b)
if a>b then
msgbox "The maximum value is:"&a&","&"The minimum value is:"&b
else if a<>b then
msgbox "The maximum value is:"&b&","&"The minimum value is:"&a
else
msgbox "The two numbers are equal and there is no maximum or minimum"
end if
end if
end sub
call hh(a,b)
4. Using the process, users input the radius of the circle and output the area of the circle.
dim r
const pi=3.1
r=inputbox("Please enter the radius of the circle:")
sub s(r)
msgbox "The area of the circle is: "&pi*r^2
end sub
call s(r)
5. Use function or procedure to judge whether the string length input by user is greater than 10.
dim s
s=inputbox("Please enter a string of any characters:")
sub str(s)
if len(s)>10 then
msgbox "String length greater than 10"
else
msgbox "String length less than 10"
end if
end sub
call str(s)
6. Use function or procedure to count the number of numbers in user input string.
dim s
s=inputbox("Please enter a string of any characters:")
sub str(s)
dim n,m,i
i=0
for n=1 to len(s)
m=mid(s,n,1) 'Returns the specified number of characters from a string, mid()function
if asc(m)>=48 and asc(m)<=57 then 'That corresponds to the first letter of a string ANSI Character code, asc()function
i=i+1
end if
next
msgbox "The number of numbers is:"&i
end sub
call str(s)
1. At the same time, open the CMD command, Notepad
on error resume next
dim a
set a=createobject("wscript.shell")
a.run"cmd"
a.run"notepad"
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
2. First turn off notepad and then turn on the calculator
on error resume next
dim a
set a=createobject("wscript.shell")
a.run"notepad",,true
a.run"calc"
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
3. Open Chrome browser
on error resume next
dim a
set a=createobject("wscript.shell")
a.run"chrome.exe"
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
4. Use VBS to create a text document D / 1.txt, which contains the following contents:
Beijing,
on error resume next
dim fs,t
set fs=createobject("scripting.filesystemobject")
set t=fs.createtextfile("d:/1.txt")
t.write("Beijing")
t.close
set t=nothing
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
5. Use VBS to pop up the input box, where you can input the name and create a text document D / 2.txt. The contents are as follows:
Welcome (name in input box)!
on error resume next
dim fs,t,h
set fs=createobject("scripting.filesystemobject")
set t=fs.createtextfile("d:/2.txt")
h=inputbox("Please enter name:")
t.write("welcome"&h&"!")
t.close
set t=nothing
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
6. Using VBS, merge the contents of the text documents of the previous two questions as follows:
Welcome to Beijing!
on error resume next
dim fs,t1,t2,str1,str2
set fs=createobject("scripting.filesystemobject")
set t1=fs.opentextfile("d:\1.txt",1)
set t2=fs.opentextfile("d:\2.txt",1)
str1=t1.readall
str2=t2.readall
msgbox(str1&","&str2)
t1.close
t2.close
set t1=nothing
set t2=nothing
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
7. Open notepad and input the following two lines through the analog keyboard:
This is the most wonderful day of my life
because I´m here with you now
on error resume next
dim a
set a=createobject("wscript.shell")
a.run"notepad"
wscript.sleep 3000
a.sendkeys"^ "
a.sendkeys"This is most wonderful day fo my life"
a.sendkeys"{enter}"
a.sendkeys"because I'm here with you now"
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
8. Use VBS to open the "CMD" command and create a folder named with your name in pinyin on disk C
on error resume next
dim a
set a=createobject("wscript.shell")
a.run"cmd"
wscript.sleep 3000
a.sendkeys"md d:\yanli"
a.sendkeys"{enter}"
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
9. Use VBS to open notepad and input your related information in it. The template is as follows:
Name: Zhang San
Student number: XXX
Current date: date()
Current time: time()
on error resume next
dim a
set a=createobject("wscript.shell")
a.run"notepad"
wscript.sleep 1000
a.sendkeys"^ "
a.sendkeys"name:bakabaka"
a.sendkeys"{enter}"
a.sendkeys"number:20200630"
a.sendkeys"{enter}"
a.sendkeys"date:"
a.sendkeys(date())
a.sendkeys"{enter}"bakabaka
a.sendkeys"time:"
a.sendkeys(time())
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
10. Open Chrome browser and enter http://www.baidu.com ,
Enter Baidu website and search for "VBScript" keyword
on error resume next
dim a
set a=createobject("wscript.shell")
a.run"""C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe"""
wscript.sleep 10000
a.sendkeys"^ "
a.sendkeys"http://www.baidu.com"
wscript.sleep 3000
a.sendkeys"{enter}"
wscript.sleep 3000
a.sendkeys"VBScript"
wscript.sleep 3000
a.sendkeys"{enter}"
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
1. Using VBS regular expression, search for and display each mobile phone number in the following string:
"NO1002028; Yanjing emor5;24; female; Zhejiang; civil servant; 13507593654;NO1002024; zhimunlov5; 40; female; Sichuan; worker; 13411652253;NO1002071; tongshuores; 27; female; Tianjin; medical staff; 13306512368"
dim str,matchs,reg
str="NO1002028;Yan Jing emor5;24;female;Zhejiang;civil servant;13507593654;NO1002024;The admiration of nlov5;40;female;Sichuan;worker;13411652253;NO1002071;Children's books ores;27;female;Tianjin;medical staff;13306512368"
set reg=new regexp
reg.pattern="1[358][0-9]{9}"
reg.global=true
set matchs=reg.execute(str)
for i=0 to matchs.count-1
msgbox matchs.item(i)
next
2. Using VBS regular expressions, search for and replace each person's age in the following string:
"NO1002028; Yanjing emor5;24; female; Zhejiang; civil servant; 13507593654;NO1002024; zhimunlov5; 40; female; Sichuan; worker; 13411652253;NO1002071; tongshuores; 27; female; Tianjin; medical staff; 13306512368"
dim str,matchs,reg str="NO1002028;Yan Jing emor5;24;female;Zhejiang;civil servant;13507593654;NO1002024;The admiration of nlov5;40;female;Sichuan;worker;13411652253;NO1002071;Children's books ores;27;female;Tianjin;medical staff;13306512368" set reg=new regexp reg.pattern="[0-9][0-9](?=;[\u4e00-\u9fa5];)" reg.global=true msgbox reg.replace(str,"age")
3. The VBS regular expression is used to verify whether the user's user name meets the format requirements of "can contain numbers, letters and underscores, and the first character is a letter, and the length is 6-20 digits".
dim str,matchs,reg
str=inputbox("Please enter user name:")
set reg=new regexp
reg.pattern="^[A-Za-z][\da-zA-Z_]{5,19}$"
msgbox reg.test(str)
4. The VBS regular expression is used to verify whether the password entered by the user meets the format requirements of "must contain upper case, lower case and number, and special characters (!, @, #,%, &), and greater than 6 digits".
dim str,matchs,reg
str=inputbox("Please input a password:")
set reg=new regexp
reg.pattern="^(?:(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[0-9])(?=.*[!@#%&])).{6,12}$"
msgbox reg.test(str)
5. Use VBS regular expression to verify whether the ID card number entered by the user conforms to the specification.
dim str,matchs,reg
str=inputbox("Please input ID card number:")
set reg=new regexp
reg.pattern="^[1-9][0-9]{14})|([1-9][0-9]{16}[0-9xX]$"
msgbox reg.test(str)
6. Use VBS regular expression to verify whether the format of the mailbox input by the user conforms to the specification.
dim str,matchs,reg
str=inputbox("Please enter email address:")
set reg=new regexp
reg.pattern="^[a-zA-Z0-9_]+@[1-9a-z]+(\.[a-z]{2,5})+$"
msgbox reg.test(str)
wscript.echo err.number&"–"&err.description&"–"&err.source
end if
10.open Chrome Browser, input http://www.baidu.com,
//Enter Baidu website and search for "VBScript" keyword
```vbscript
on error resume next
dim a
set a=createobject("wscript.shell")
a.run"""C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe"""
wscript.sleep 10000
a.sendkeys"^ "
a.sendkeys"http://www.baidu.com"
wscript.sleep 3000
a.sendkeys"{enter}"
wscript.sleep 3000
a.sendkeys"VBScript"
wscript.sleep 3000
a.sendkeys"{enter}"
if err.number<>0 then
wscript.echo err.number&"--"&err.description&"--"&err.source
end if
1. Using VBS regular expression, search for and display each mobile phone number in the following string:
"NO1002028; Yanjing emor5;24; female; Zhejiang; civil servant; 13507593654;NO1002024; zhimunlov5; 40; female; Sichuan; worker; 13411652253;NO1002071; tongshuores; 27; female; Tianjin; medical staff; 13306512368"
dim str,matchs,reg
str="NO1002028;Yan Jing emor5;24;female;Zhejiang;civil servant;13507593654;NO1002024;The admiration of nlov5;40;female;Sichuan;worker;13411652253;NO1002071;Children's books ores;27;female;Tianjin;medical staff;13306512368"
set reg=new regexp
reg.pattern="1[358][0-9]{9}"
reg.global=true
set matchs=reg.execute(str)
for i=0 to matchs.count-1
msgbox matchs.item(i)
next
2. Using VBS regular expressions, search for and replace each person's age in the following string:
"NO1002028; Yanjing emor5;24; female; Zhejiang; civil servant; 13507593654;NO1002024; zhimunlov5; 40; female; Sichuan; worker; 13411652253;NO1002071; tongshuores; 27; female; Tianjin; medical staff; 13306512368"
dim str,matchs,reg str="NO1002028;Yan Jing emor5;24;female;Zhejiang;civil servant;13507593654;NO1002024;The admiration of nlov5;40;female;Sichuan;worker;13411652253;NO1002071;Children's books ores;27;female;Tianjin;medical staff;13306512368" set reg=new regexp reg.pattern="[0-9][0-9](?=;[\u4e00-\u9fa5];)" reg.global=true msgbox reg.replace(str,"age")
3. The VBS regular expression is used to verify whether the user's user name meets the format requirements of "can contain numbers, letters and underscores, and the first character is a letter, and the length is 6-20 digits".
dim str,matchs,reg
str=inputbox("Please enter user name:")
set reg=new regexp
reg.pattern="^[A-Za-z][\da-zA-Z_]{5,19}$"
msgbox reg.test(str)
4. The VBS regular expression is used to verify whether the password entered by the user meets the format requirements of "must contain upper case, lower case and number, and special characters (!, @, #,%, &), and greater than 6 digits".
dim str,matchs,reg
str=inputbox("Please input a password:")
set reg=new regexp
reg.pattern="^(?:(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[0-9])(?=.*[!@#%&])).{6,12}$"
msgbox reg.test(str)
5. Use VBS regular expression to verify whether the ID card number entered by the user conforms to the specification.
dim str,matchs,reg
str=inputbox("Please input ID card number:")
set reg=new regexp
reg.pattern="^[1-9][0-9]{14})|([1-9][0-9]{16}[0-9xX]$"
msgbox reg.test(str)
6. Use VBS regular expression to verify whether the format of the mailbox input by the user conforms to the specification.
dim str,matchs,reg
str=inputbox("Please enter email address:")
set reg=new regexp
reg.pattern="^[a-zA-Z0-9_]+@[1-9a-z]+(\.[a-z]{2,5})+$"
msgbox reg.test(str)