- Object oriented: objects, messages, classes, and inheritance,
- Language basis: variables, arrays, data types, operators, and control flow.
- Classes and objects
- statement
- Interface
- Number and character: number and String objects
- generic paradigm
- package
II. Language foundation:
- variables: basic data type, string, array, default, constant
- Operators: operators
- expressions,statements,blocks: expressions,statements,blocks
- control flow statements: control statement if for ect
Variables: basic data type, string, array, default, constant
Instance Variables: non static fields such as: Dog.sex
Class Variables: static field static fields such as: static int numGears = 6; sometimes you can add final to indicate constant.
Local Variables: local or local variable int count = 0; valid between braces.
Parameters: public static void main(String[] args)
This Agreement:

Variables are case sensitive
Data type:
long creditCardNumber = 1234_5678_9012_3456L; long socialSecurityNumber = 999_99_9999L; float pi = 3.14_15F; long hexBytes = 0xFF_EC_DE_5E; long hexWords = 0xCAFE_BABE; long maxLong = 0x7fff_ffff_ffff_ffffL; byte nybbles = 0b0010_0101; long bytes = 0b11010010_01101001_10010100_10010010; // Invalid: cannot put underscores // adjacent to a decimal point float pi1 = 3_.1415F; // Invalid: cannot put underscores // adjacent to a decimal point float pi2 = 3._1415F; // Invalid: cannot put underscores // prior to an L suffix long socialSecurityNumber1 = 999_99_9999_L; // OK (decimal literal) int x1 = 5_2; // Invalid: cannot put underscores // At the end of a literal int x2 = 52_; // OK (decimal literal) int x3 = 5_______2; // Invalid: cannot put underscores // in the 0x radix prefix int x4 = 0_x52; // Invalid: cannot put underscores // at the beginning of a number int x5 = 0x_52; // OK (hexadecimal literal) int x6 = 0x5_2; // Invalid: cannot put underscores // at the end of a number int x7 = 0x52_;
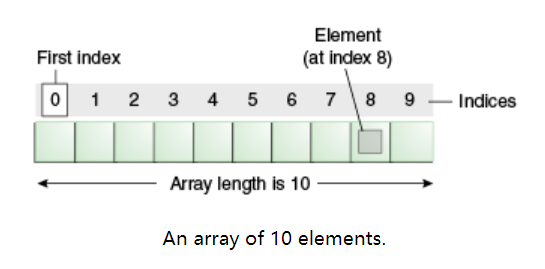
Array: container object, containing several elements
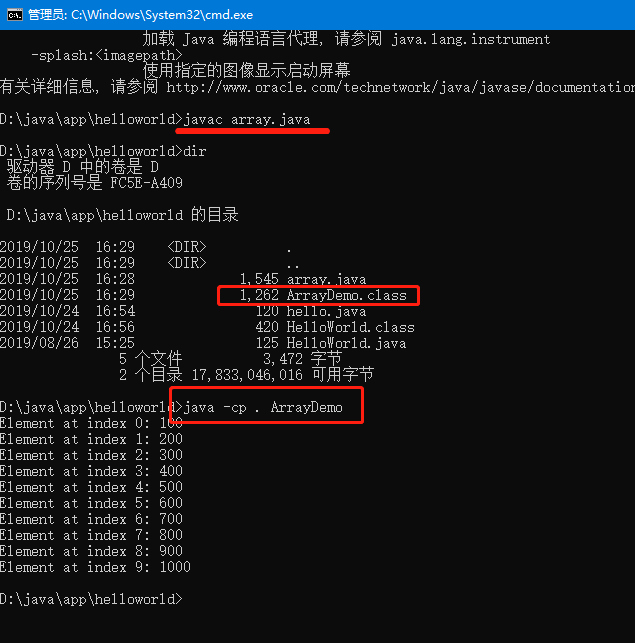
class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// declares an array of integers
int[] anArray;
// allocates memory for 10 integers
anArray = new int[10];
// initialize first element
anArray[0] = 100;
// initialize second element
anArray[1] = 200;
// and so forth
anArray[2] = 300;
anArray[3] = 400;
anArray[4] = 500;
anArray[5] = 600;
anArray[6] = 700;
anArray[7] = 800;
anArray[8] = 900;
anArray[9] = 1000;
System.out.println("Element at index 0: "
+ anArray[0]);
System.out.println("Element at index 1: "
+ anArray[1]);
System.out.println("Element at index 2: "
+ anArray[2]);
System.out.println("Element at index 3: "
+ anArray[3]);
System.out.println("Element at index 4: "
+ anArray[4]);
System.out.println("Element at index 5: "
+ anArray[5]);
System.out.println("Element at index 6: "
+ anArray[6]);
System.out.println("Element at index 7: "
+ anArray[7]);
System.out.println("Element at index 8: "
+ anArray[8]);
System.out.println("Element at index 9: "
+ anArray[9]);
}
} 
- The term "instance variable" is another name for non-static field.
- The term "class variable" is another name for static field.
- A local variable stores temporary state; it is declared inside a method.
- A variable declared within the opening and closing parenthesis of a method is called a parameter.
- What are the eight primitive data types supported by the Java programming language? byte, short, int, long, float, double, boolean, char
- Character strings are represented by the class java.lang.String.
- An array is a container object that holds a fixed number of values of a single type.
Operators: operators
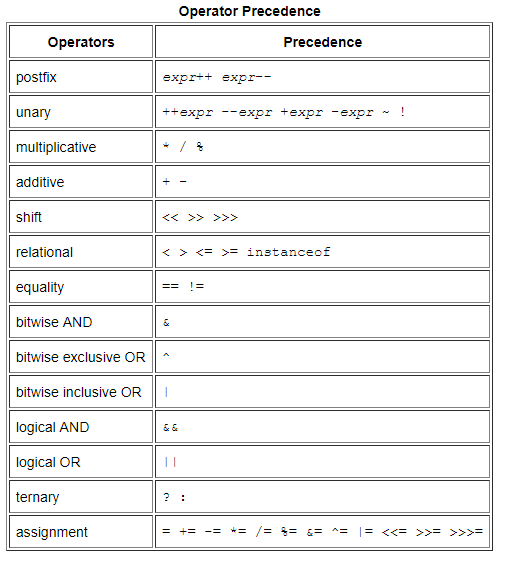
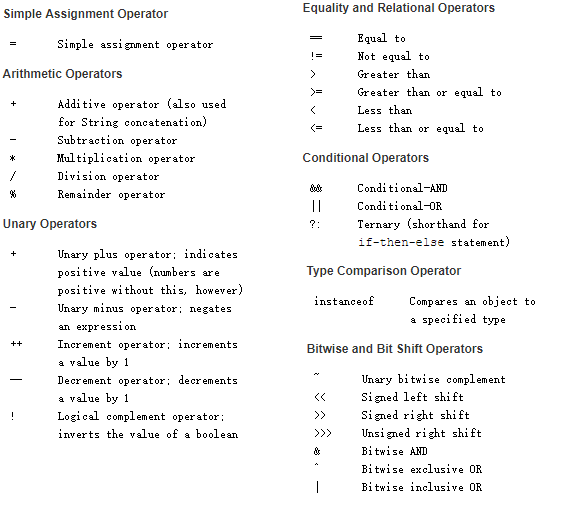
Let's not watch it one by one. Here's the section: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/op1.html
expressions,statements,blocks: expressions,statements,blocks
slightly
control flow statements: control statement if for ect
class IfElseDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testscore = 76;
char grade;
if (testscore >= 90) {
grade = 'A';
} else if (testscore >= 80) {
grade = 'B';
} else if (testscore >= 70) {
grade = 'C';
} else if (testscore >= 60) {
grade = 'D';
} else {
grade = 'F';
}
System.out.println("Grade = " + grade);
}
}public class SwitchDemoFallThrough {
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.ArrayList<String> futureMonths =
new java.util.ArrayList<String>();
int month = 8;
switch (month) {
case 1: futureMonths.add("January");
case 2: futureMonths.add("February");
case 3: futureMonths.add("March");
case 4: futureMonths.add("April");
case 5: futureMonths.add("May");
case 6: futureMonths.add("June");
case 7: futureMonths.add("July");
case 8: futureMonths.add("August"); //Here, if you don't use break, you will continue to execute the following statement
case 9: futureMonths.add("September");
case 10: futureMonths.add("October");
case 11: futureMonths.add("November");
case 12: futureMonths.add("December");
break;
default: break;
}
if (futureMonths.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Invalid month number");
} else {
for (String monthName : futureMonths) {
System.out.println(monthName);
}
}
}
}
Output:
August
September
October
November
December Note: This example checks if the expression in the switch statement is null. Ensure that the expression in any switch statement is not null to prevent a NullPointerException from being thrown.
Note: This example checks if the expression in the switch statement is null. Ensure that the expression in any switch statement is not null to prevent a NullPointerException from being thrown.
class WhileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
int count = 1;
while (count < 11) {
System.out.println("Count is: " + count);
count++;
}
}
}class DoWhileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
int count = 1;
do {
System.out.println("Count is: " + count);
count++;
} while (count < 11);
}
}class ForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=1; i<11; i++){
System.out.println("Count is: " + i);
}
}
}
class EnhancedForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] numbers =
{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
for (int item : numbers) {
System.out.println("Count is: " + item);
}
}
}
class BreakDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrayOfInts =
{ 32, 87, 3, 589,
12, 1076, 2000,
8, 622, 127 };
int searchfor = 12;
int i;
boolean foundIt = false;
for (i = 0; i < arrayOfInts.length; i++) {
if (arrayOfInts[i] == searchfor) {
foundIt = true;
break;
}
}
if (foundIt) {
System.out.println("Found " + searchfor + " at index " + i);
} else {
System.out.println(searchfor + " not in the array");
}
}
}
class BreakWithLabelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arrayOfInts = {
{ 32, 87, 3, 589 },
{ 12, 1076, 2000, 8 },
{ 622, 127, 77, 955 }
};
int searchfor = 12;
int i;
int j = 0;
boolean foundIt = false;
search:
for (i = 0; i < arrayOfInts.length; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < arrayOfInts[i].length;
j++) {
if (arrayOfInts[i][j] == searchfor) {
foundIt = true;
break search;
}
}
}
if (foundIt) {
System.out.println("Found " + searchfor + " at " + i + ", " + j);
} else {
System.out.println(searchfor + " not in the array");
}
}
}class ContinueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String searchMe = "peter piper picked a " + "peck of pickled peppers";
int max = searchMe.length();
int numPs = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
// interested only in p's
if (searchMe.charAt(i) != 'p')
continue;
// process p's
numPs++;
}
System.out.println("Found " + numPs + " p's in the string.");
}
}class ContinueWithLabelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String searchMe = "Look for a substring in me";
String substring = "sub";
boolean foundIt = false;
int max = searchMe.length() -
substring.length();
test:
for (int i = 0; i <= max; i++) {
int n = substring.length();
int j = i;
int k = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (searchMe.charAt(j++) != substring.charAt(k++)) {
continue test;
}
}
foundIt = true;
break test;
}
System.out.println(foundIt ? "Found it" : "Didn't find it");
}
}