There is no road in the world, and when there are more people to walk, it becomes a road--Lu Xun

The topic of this discussion is the need to step out of a "road" between services, so that bug s have a "road" to follow.
Why use jaeger... this multi-language solution? Do you follow the opentracing specification? Is it ready-to-use? More?
As for why it's good to follow the opentracing standard.........................................................
Anyway, let sleeves dry first.
Know Jaeger
Understand before using:
Jaeger: open source, end-to-end distributed tracing
Jaeger: End-to-end tracing of open source, distributed systems
Monitor and troubleshoot transactions in complex distributed systems
Transaction processing for monitoring and problem checking between complex distributed systems.
The jaeger system and process are shown below.
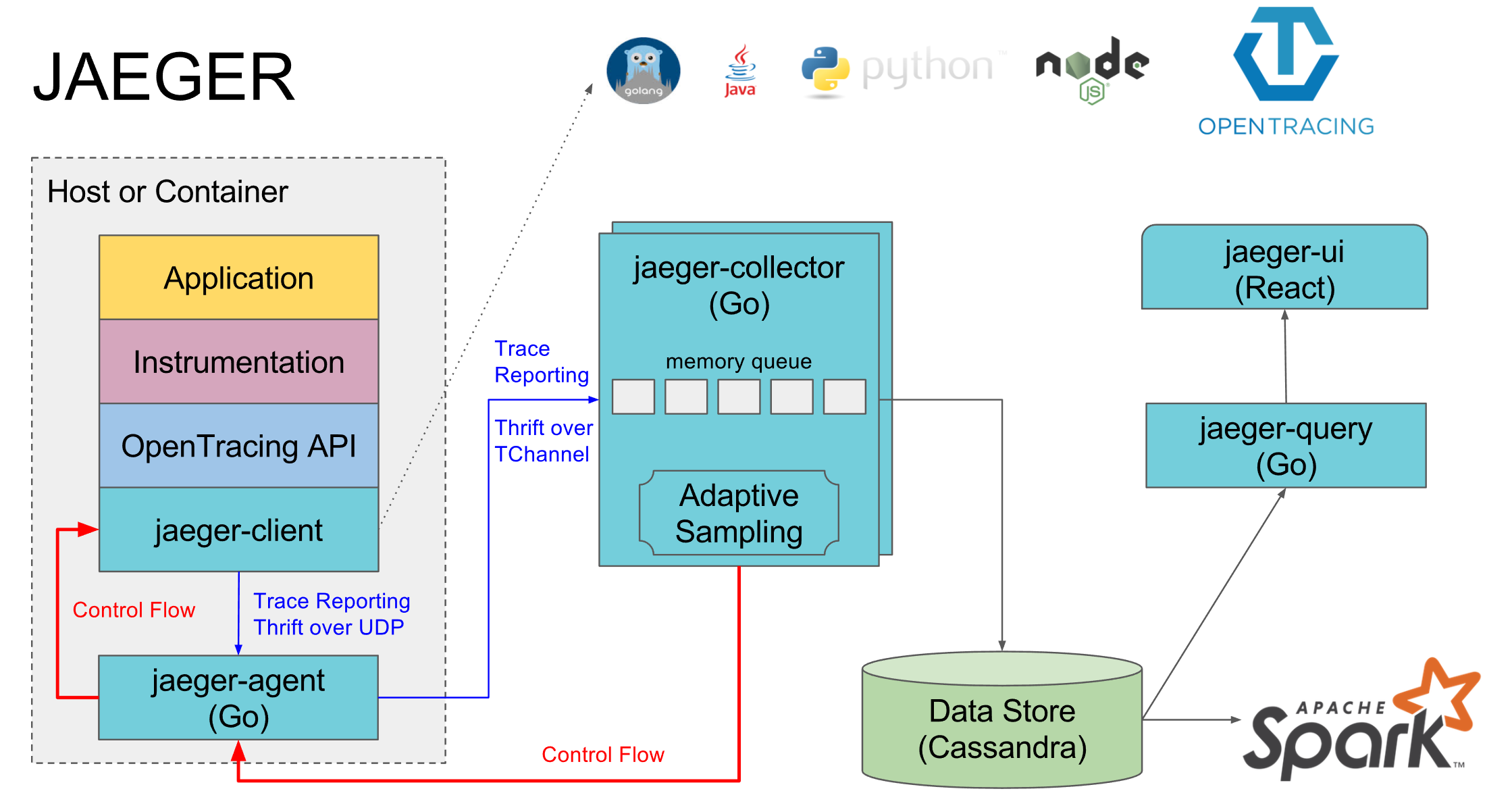
Jaeger-client (the implementation of OpenTracing API in various languages, used to plug in information collection points in applications)
jaeger-agent (responsible for the process of sending, processing and sending spans to collector, monitoring the UDP sending of spans. This layer is designed to be deployed on the host as a basic component, abstracting collector discovery and routing from the client. Note: 1. This layer should be deployed locally in the application; 2. If the endpoint of the configuration report is configured, the spans are sent directly to collector without agent. )
jaeger-collector (collects and tracks spans, and processes tracking data through pipelines). Current pipelines support tracing validation, indexing, transformation, and ultimately data storage)
data store
jaeger-query (retrieving trace information from storage and displaying it through UI)
jaeger-ui (UI display layer, based on React)
Note: jaeger's storage is pluggable and currently supports Cassandra, Elastic Search and Kafka.
Based on the above architecture, this paper focuses on how to implement tracing between services and within services in the jaeger-client section.
Understanding tracking information
Span: Logical units in tracing, such as the execution of a request process/function, including operation name, start time, duration.
SpanContext: Represents Span data that needs to be propagated downstream to Spans and across applications/processes, which can be simply understood as a unified identification object strung across systems.
Baggage: A key-value pair of strings, associated with Span/SpanContext, is propagated across all downstream Spans. (Some powerful functions can be done, such as data entrainment throughout the link, high cost, careful use)
Tracer: Tracking instances in a project, tracking the process of data changes / function execution in a project, can be considered as a set diagram of directed acyclic spans.
Tracer and Span are shown below: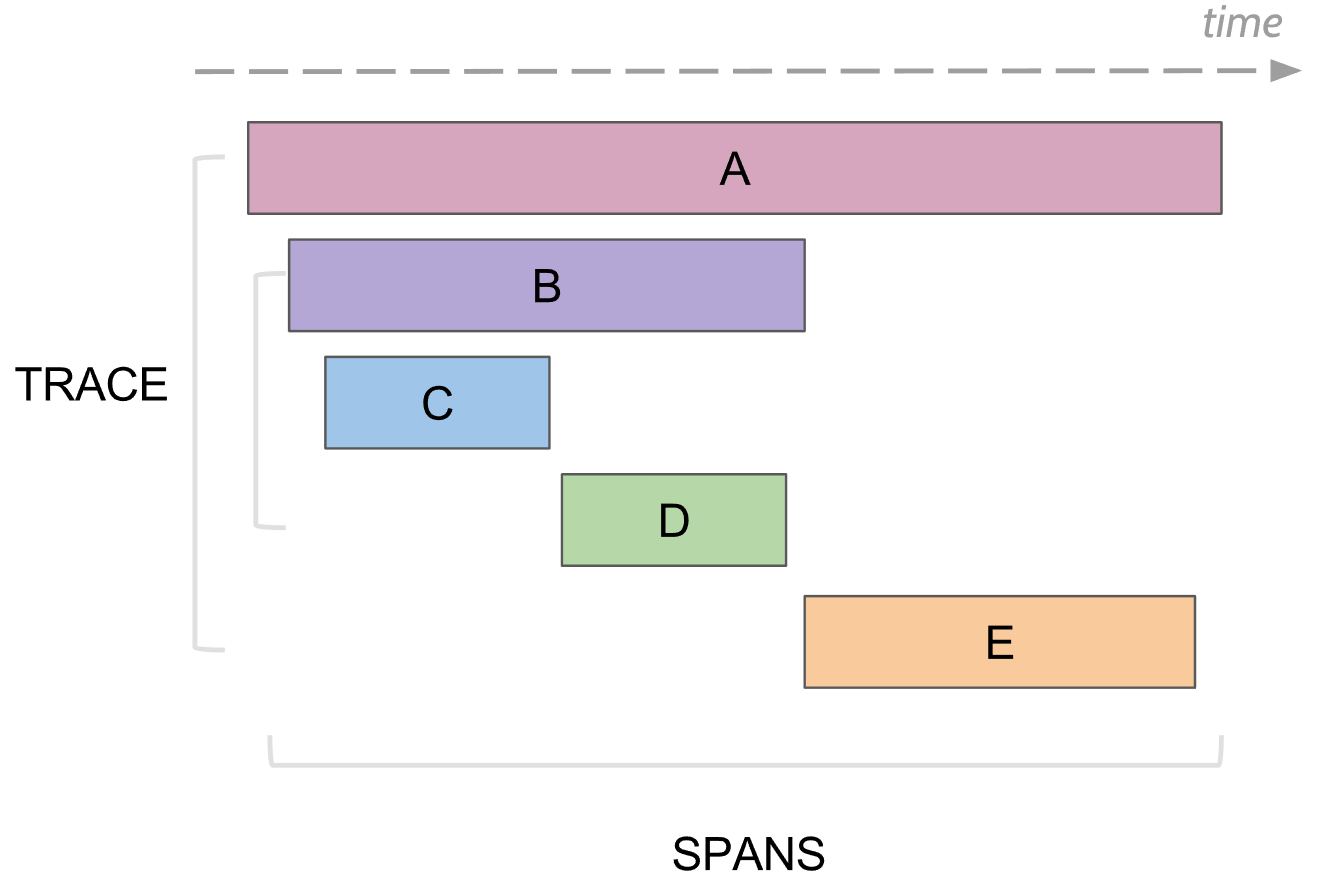
For jaeger-ui, the effect is as follows: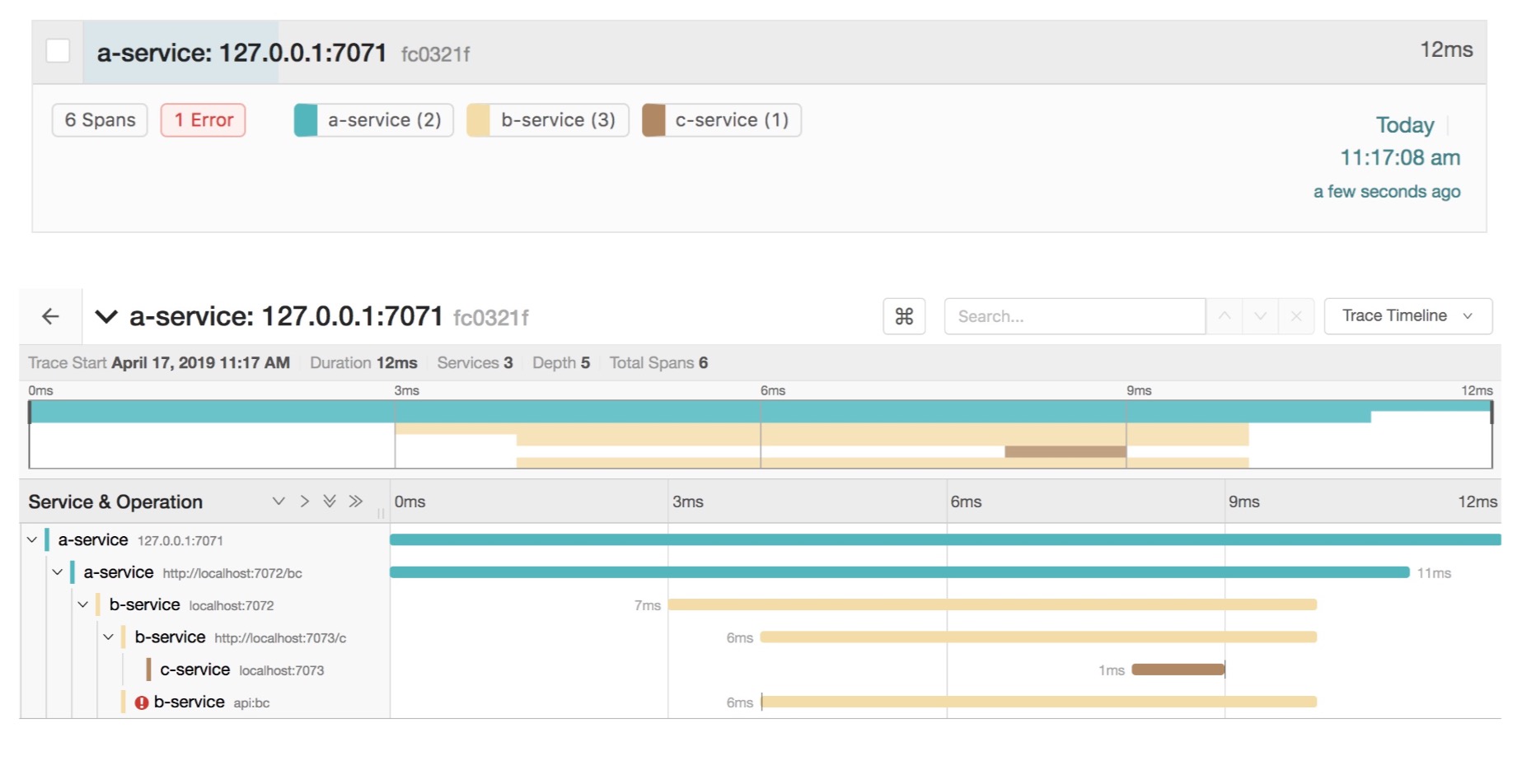
jaeger-client is opentracing The implementation of the jaeger-client api is almost identical to the opentracing api.
Api and configuration reference
In this paper, Nodejs is the main and Go is the supplement (because the current link tracking schemes just involve these two services).
Here's an overview of Configuration/Tracer/Span to implement a basic tracing.
Configuration
{ serviceName: "string", disable: "boolean", sampler: { type: "string", // required param: "number", // required hostPort: "string", host: "string", port: "number", refreshIntervalMs: "number" }, reporter: { logSpans: "boolean", agentHost: "string", agentPort: "number", collectorEndpoint: "string", username: "string", password: "string", flushIntervalMs: "number" }, throttler: { host: "string", port: "number", refreshIntervalMs: "number" } }
Tracer
{ objects: { _tags: "object", // tags information, including jaeger-version/hostname/ip/client-uuid _metrics: "object", // Examples of Metrics metrics _serviceName: "string", // Service name _reporter: "object", // Submit examples _sampler: "object", // Sampler example _logger: "object", // Log instance, default NullLogger _baggageSetter: "object", // Example of Baggage Setter _debugThrottler: "object", // DefaultThrottler configuration example _injectors: "object", // Injector list _extractors: "object", // Extractor list _process: "object" // process information, including serviceName/tags }, // File location. / jaeger-client-node/blob/master/src/tracer.js methods: { _startInternalSpan: "void", // Create a base span for startSpace method calls / params: spanContext (SpanContext) operationName (string) startTime (number) userTags (any) internalTags (any) ntContext? (SpanContext) rpcServer (boolean) references (Array < Reference >) / Sparetuen Span _report: "void", // Initiate data submission to jaeger backend / params: span(Span) registerInjector: "void", // Injecting "How to inject SpanContext content" into tracer / params: format(string) injector(Injector) registerExtractor: "void", // Inject "How to Extract SpanContext Content" into tracer / params: format(string) extractor(Extractor) startSpan: "void", // Create a Span / params: operationName (string) options: {operationName (string) childOf (SpanContext) references (Array < Reference >) tags (object) startTime (number)} inject: "void", // Inject SpanContext into the carrier of the serialized format / params: SpanContext(SpanContext) format(string) carrier(any) extract: "void", // Extract SpanContext / params: format(string) carrier(any) / return SpanContext from the carrier of the serialized format close: "void", // Close tracer, update spans, or execute callback function / params: callback now: "void", // Return the current time _isDebugAllowed: "void" // Returns whether debug is allowed } }
Span
{ objects: { _tracer: "object", // <Tracer> _operationName: "string", // span name _spanContext: "object", // span data, _traceId/_spanId/_parentId/... _startTime: "number", // time stamp _logger: "object", // Log instance, default NullLogger _references: "object", // Reference list _baggageSetter: "object", // Example of Baggage Setter _logs: "object", // span's logs list _tags: "object", // tags list for span _duration: "number" // time consuming }, // File location. / jaeger-client-node/blob/master/src/span.js methods: { _normalizeBaggageKey: "void", // Returns a normalized key / params: key(string) / returns a normalized key, lowercase letters, dashes for underscores setBaggageItem: "void", // Setting baggage value / params: key(string) value(any) / returning the current Span with the associated key getBaggageItem: "void", // Get baggage value / params: key(string) value(any) / return baggage value with the associated key context: "void", // Get the SpanContext of the current Span tracer: "void", // Get Tracer for the current Span _isWriteable: "void", // Returns whether the current Span is writable setOperationName: "void", // Set the operation name / params: operationName(string) / return the current Span finish: "void", // Complete the current Span / params: finishTime?(number) addTags: "void", // Add multiple tag / params: keyValuePairs(object) / return to the current Span setTag: "void", // Add a single tag / params: key(string) value(any) / back to the current Span log: "void", // Add log events to Span or load / params: keyValuePairs(object) timestamp?(number) / Return the current Span logEvent: "void", // Carry the load to record events / params: keyValuePairs(object) timestamp?(number) / Return to the current Span _setSamplingPriority: "void" // If the flag has been successfully updated, return true, otherwise return false / params: priority(number) (0 disables sampling; 1 enables sampling) } }
Span can be divided into span and errorSpan. In the jaeger-ui code, the judgment is:
const isErrorTag = ({ key, value }: KeyValuePair) => key === "error" && (value === true || value === "true");
So the code for setting errorSpan is as follows:
span.setTag("error", true); span.log({ message: err.message }); span.finish();
For data Jaeger is relatively free, you can pull the jaeger-ui code and personalize it according to the KeyValuePair you set up.
Practice/case
Between Nodejs services
For example, there are services [a,b,c], which initiate a request to a, service a calls the interface of service b, and service B calls the interface of service c, and traces it in turn.
request.js
const Request = require("request"); const noop = () => {}; // request const request = (url, options) => { const method = (options && options.method) || "GET"; const headers = (options && options.headers) || {}; const tracer = (options && options.tracer) || { inject: noop, setTag: noop }; const rootSpan = (options && options.rootSpan) || {}; const _config = rootSpan ? { childOf: rootSpan } : {}; const span = tracer.startSpan(`${url}`, _config); span.setTag(Tags.HTTP_URL, url); span.setTag(Tags.HTTP_METHOD, method); tracer.inject(span, FORMAT_HTTP_HEADERS, headers); const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { Request( { url: url, method: method, headers: headers }, (err, res, body) => { span.finish(); if (err) { console.log("request error : ", err); reject(err); } else { resolve(body); } } ); }); return promise; }; export default request
a-service.js
const { initTracer } = require("jaeger-client"); const { FORMAT_HTTP_HEADERS, Tags } = require("opentracing"); // app use trace const jaegerConfig = { serviceName: "a-service", sampler: { type: "const", param: 1 }, reporter: { logSpans: true, collectorEndpoint: "http://localhost:14268/api/traces" } }; const jaegerOptions = { baggagePrefix: "x-b3-" }; const tracer = initTracer(jaegerConfig, jaegerOptions); app.use(async (ctx, next) => { const parent = tracer.extract(FORMAT_HTTP_HEADERS, ctx.headers); const _config = parent ? { childOf: parent } : {}; const span = tracer.startSpan(`${ctx.host}`, _config); span.setTag("route", ctx.path); ctx.tracerRootSpan = span; ctx.tracer = tracer; await next(); span.finish(); }); // app router router.get("/abc", async (ctx, next) => { const result = await request("http://localhost:7072/bc", { tracer: ctx.tracer, rootSpan: ctx.tracerRootSpan }); ctx.body = "get :7071/a , hello a" + "\n" + result; }); app.use(router.routes()); app.listen(7071, () => { console.log("\x1B[32m port : 7071 \x1B[39m"); });
b-service.js
const { initTracer } = require("jaeger-client"); const { FORMAT_HTTP_HEADERS, Tags } = require("opentracing"); // app use trace const jaegerConfig = { serviceName: "b-service", sampler: { type: "const", param: 1 }, reporter: { logSpans: true, collectorEndpoint: "http://localhost:14268/api/traces" } }; const jaegerOptions = { baggagePrefix: "x-b3-" }; const tracer = initTracer(jaegerConfig, jaegerOptions); app.use(async (ctx, next) => { const parent = tracer.extract(FORMAT_HTTP_HEADERS, ctx.headers); const _config = parent ? { childOf: parent } : {}; const span = tracer.startSpan(`${ctx.host}`, _config); span.setTag("route", ctx.path); ctx.tracerRootSpan = span; ctx.tracer = tracer; await next(); span.finish(); }); // app router router.get("/bc", async (ctx, next) => { const span = ctx.tracer.startSpan(`api:bc`, { childOf: ctx.tracerRootSpan }); span.setTag("request:c", ":7073/c"); try { throw Error("err"); } catch (err) { span.setTag("error", true); span.log({ level: "error", message: err.message }); } const result = await request("http://localhost:7073/c", { tracer: ctx.tracer, rootSpan: ctx.tracerRootSpan }); span.finish(); ctx.body = "get :7072/b , hello b" + "\n" + result; }); app.use(router.routes()); app.listen(7072, () => { console.log("\x1B[32m port : 7072 \x1B[39m"); });
c-service.js
const { initTracer } = require("jaeger-client"); const { FORMAT_HTTP_HEADERS } = require("opentracing"); // app use trace const jaegerConfig = { serviceName: "c-service", sampler: { type: "const", param: 1 }, reporter: { logSpans: true, collectorEndpoint: "http://localhost:14268/api/traces" } }; const jaegerOptions = { baggagePrefix: "x-b3-" }; const tracer = initTracer(jaegerConfig, jaegerOptions); app.use(async (ctx, next) => { const parent = tracer.extract(FORMAT_HTTP_HEADERS, ctx.headers); const _config = parent ? { childOf: parent } : {}; const span = tracer.startSpan(`${ctx.host}`, _config); span.setTag("route", ctx.path); ctx.tracerRootSpan = span; ctx.tracer = tracer; span.log({ event: "test-log_1", kk: "kk_1", vv: "vv_1" }); span.log({ event: "test-log_2", kk: "kk_2", vv: "vv_2" }); span.log({ event: "test-log_3", kk: "kk_3", vv: "vv_3" }); span.logEvent("log-event_1", { a: 1, b: 1 }); span.logEvent("log-event_2", { a: 2, b: 2 }); await next(); span.finish(); }); // app router router.get("/c", async (ctx, next) => { ctx.body = "get :7073/c , hello c"; }); app.use(router.routes()); app.listen(7073, () => { console.log("\x1B[32m port : 7073 \x1B[39m"); });
Request address: http://localhost:7071/abc Browser opens address: http://localhost:16686/search
Design sketch: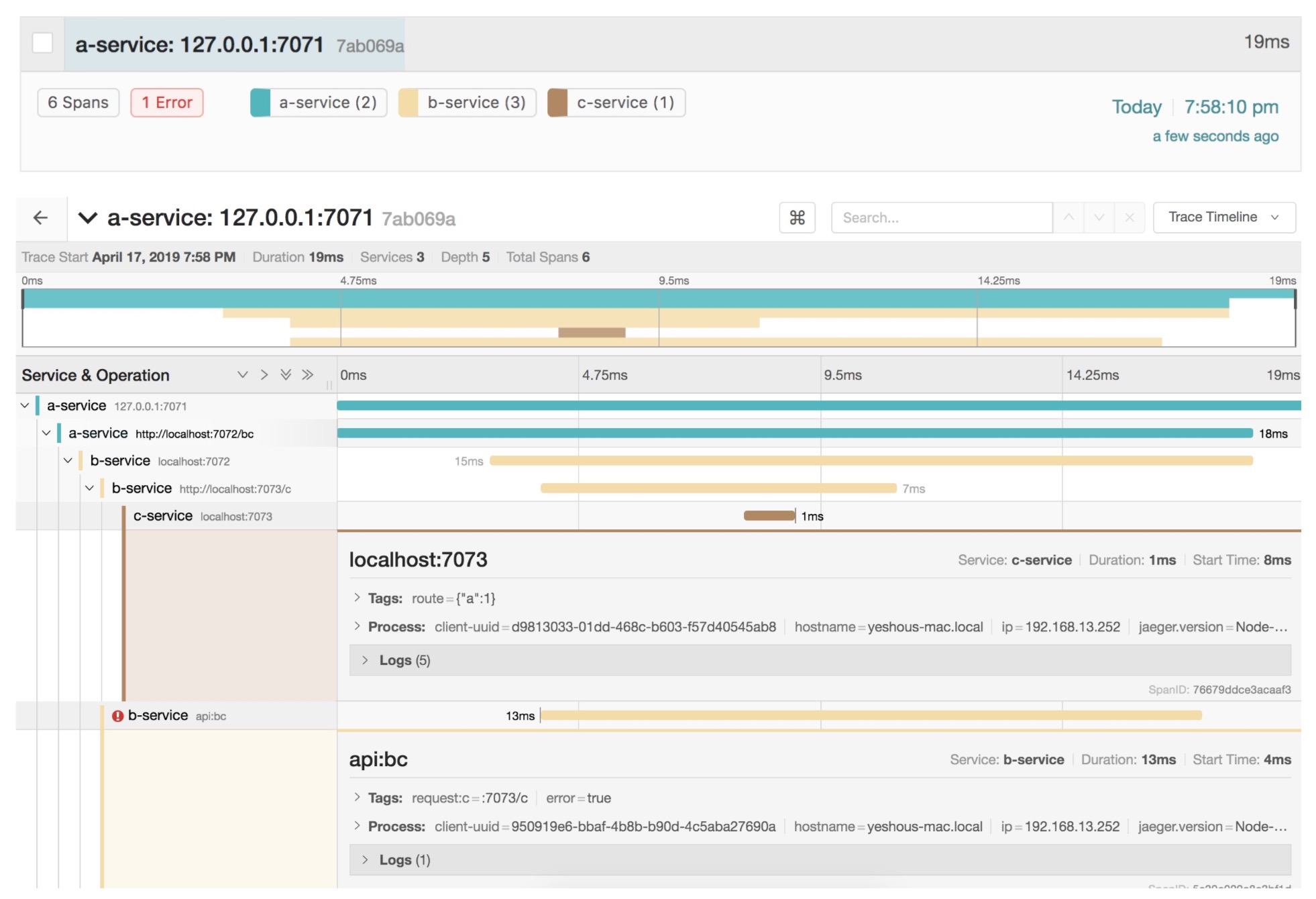
Between Go Services (http & grpc)
Here comes an http service main, port 8081, which requests the method on the service through grpc from the main side. Write go program for the first time, don't spray if you don't like it..... If there is something wrong, thank you for pointing out.
hello.gen.proto
syntax = "proto3"; option go_package = "hello_package"; package hello; message HelloReq { string name = 1; } message HelloRes { string result = 1; } service HelloService { rpc SayHello(HelloReq) returns(HelloRes) {} }
Generating the required files for grpc
protoc -I helloService/ helloService/hello.gen.proto --go_out=plugins=grpc:helloservice
main.go
package main import ( "log" "context" "strings" "net/http" "encoding/json" "google.golang.org/grpc" "google.golang.org/grpc/metadata" pb "goservice/helloService" opentracing "github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go" "github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go/ext" openLog "github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go/log" "github.com/uber/jaeger-client-go" jaegerCfg "github.com/uber/jaeger-client-go/config" ) // metadata read and write type MDReaderWriter struct { metadata.MD } // For opentracing.TextMapReader, refer to the opentracing code func (c MDReaderWriter) ForeachKey(handler func(key, val string) error) error { for k, vs := range c.MD { for _, v := range vs { if err := handler(k, v); err != nil { return err } } } return nil } // For opentracing.TextMapWriter, refer to the opentracing code func (c MDReaderWriter) Set(key, val string) { key = strings.ToLower(key) c.MD[key] = append(c.MD[key], val) } func NewJaegerTracer(serviceName string) (opentracing.Tracer, error) { // Configuration item reference code https://github.com/jaegertracing/jaeger-client-go/blob/master/config/config.go cfg := jaegerCfg.Configuration{ Sampler: &jaegerCfg.SamplerConfig{ Type: "const", Param: 1, }, Reporter: &jaegerCfg.ReporterConfig{ LogSpans: true, CollectorEndpoint: "http://localhost:14268/api/traces", }, } cfg.ServiceName = serviceName tracer, _, err := cfg.NewTracer( jaegerCfg.Logger(jaeger.StdLogger), ) if err != nil { log.Println("tracer error ", err) } return tracer, err } // Refer here to the grpc document https://godoc.org/google.golang.org/grpc#UnaryClientInterceptor func interceptor(tracer opentracing.Tracer) grpc.UnaryClientInterceptor{ return func (ctx context.Context, method string, req, reply interface{}, cc *grpc.ClientConn, invoker grpc.UnaryInvoker, opts ...grpc.CallOption) error { // Create rootSpan var rootCtx opentracing.SpanContext rootSpan := opentracing.SpanFromContext(ctx) if rootSpan != nil { rootCtx = rootSpan.Context() } span := tracer.StartSpan( method, opentracing.ChildOf(rootCtx), opentracing.Tag{"test","hahahahaha"}, ext.SpanKindRPCClient, ) defer span.Finish() md, succ := metadata.FromOutgoingContext(ctx) if !succ { md = metadata.New(nil) } else{ md = md.Copy() } mdWriter := MDReaderWriter{md} // Inject spanContext err := tracer.Inject(span.Context(), opentracing.TextMap, mdWriter) if err != nil { span.LogFields(openLog.String("inject error", err.Error())) } // new ctx and call subsequent operations newCtx := metadata.NewOutgoingContext(ctx, md) err = invoker(newCtx, method, req, reply, cc, opts...) if err != nil { span.LogFields(openLog.String("call error", err.Error())) } return err } } // Method of request execution func hello(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { r.ParseForm(); // new tracer tracer, err := NewJaegerTracer("mainService") if err != nil { log.Fatal("new tracer err ", err) } // dial options dialOpts := []grpc.DialOption{grpc.WithInsecure()} if tracer != nil { dialOpts = append(dialOpts, grpc.WithUnaryInterceptor(interceptor(tracer))) } conn, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:8082", dialOpts...) if err != nil { log.Fatal("connect err ", err) } defer conn.Close() sv := pb.NewHelloServiceClient(conn) var name = "yeshou" if (len(r.Form) > 0 && len(r.Form["name"][0]) > 0) { name = r.Form["name"][0] } res, err := sv.SayHello(context.Background(), &pb.HelloReq{Name: name}) if err != nil { log.Fatal("c.SayHello func error : ", err) } type HelloRes struct{ Result string `json:"result"` } data := HelloRes{ Result: res.Result, } jsonData, err := json.Marshal(data) if err != nil { log.Fatal("server error : ", err) } w.Write(jsonData) } func main() { http.HandleFunc("/get_h", hello) err := http.ListenAndServe(":8081", nil) if err != nil { log.Fatal("Listen server err : ", err) } }
service.go
package main import ( "log" "net" "context" "strings" "google.golang.org/grpc" "google.golang.org/grpc/grpclog" "google.golang.org/grpc/metadata" pb "goservice/helloService" opentracing "github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go" "github.com/opentracing/opentracing-go/ext" "github.com/uber/jaeger-client-go" jaegerCfg "github.com/uber/jaeger-client-go/config" ) // metadata read and write type MDReaderWriter struct { metadata.MD } // For opentracing.TextMapReader, refer to the opentracing code func (c MDReaderWriter) ForeachKey(handler func(key, val string) error) error { for k, vs := range c.MD { for _, v := range vs { if err := handler(k, v); err != nil { return err } } } return nil } // For opentracing.TextMapWriter, refer to the opentracing code func (c MDReaderWriter) Set(key, val string) { key = strings.ToLower(key) c.MD[key] = append(c.MD[key], val) } func NewJaegerTracer(serviceName string) (opentracing.Tracer, error) { cfg := jaegerCfg.Configuration{ Sampler: &jaegerCfg.SamplerConfig{ Type: "const", Param: 1, }, Reporter: &jaegerCfg.ReporterConfig{ LogSpans: true, CollectorEndpoint: "http://localhost:14268/api/traces", }, } cfg.ServiceName = serviceName tracer, _, err := cfg.NewTracer( jaegerCfg.Logger(jaeger.StdLogger), ) if err != nil { log.Println("tracer error ", err) } return tracer, err } // Refer here to the grpc document https://godoc.org/google.golang.org/grpc#WithUnary Interceptor func interceptor(tracer opentracing.Tracer) grpc.UnaryServerInterceptor{ return func (ctx context.Context, req interface{}, info *grpc.UnaryServerInfo, handler grpc.UnaryHandler) (res interface{}, err error) { md, succ := metadata.FromIncomingContext(ctx) if !succ { md = metadata.New(nil) } // Extract spanContext spanContext, err := tracer.Extract(opentracing.TextMap, MDReaderWriter{md}) if err != nil && err != opentracing.ErrSpanContextNotFound { grpclog.Errorf("extract from metadata err: %v", err) } else{ span := tracer.StartSpan( info.FullMethod, ext.RPCServerOption(spanContext), opentracing.Tag{Key: string(ext.Component), Value: "grpc"}, ext.SpanKindRPCServer, ) defer span.Finish() ctx = opentracing.ContextWithSpan(ctx, span) } return handler(ctx, req) } } type server struct{} func (s *server) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *pb.HelloReq) (*pb.HelloRes, error) { return &pb.HelloRes{Result: "Hello " + in.Name}, nil } func main() { var svOpts []grpc.ServerOption tracer, err := NewJaegerTracer("serviceService") if err != nil { log.Fatal("new tracer err ", err) } if tracer != nil { svOpts = append(svOpts, grpc.UnaryInterceptor(interceptor(tracer))) } sv := grpc.NewServer(svOpts...) lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":8082") if err != nil { log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err) } pb.RegisterHelloServiceServer(sv, &server{}) if err := sv.Serve(lis); err != nil { log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err) } }
Request address: http://localhost:8081/get_h Browser opens address: http://localhost:16686/search
Design sketch: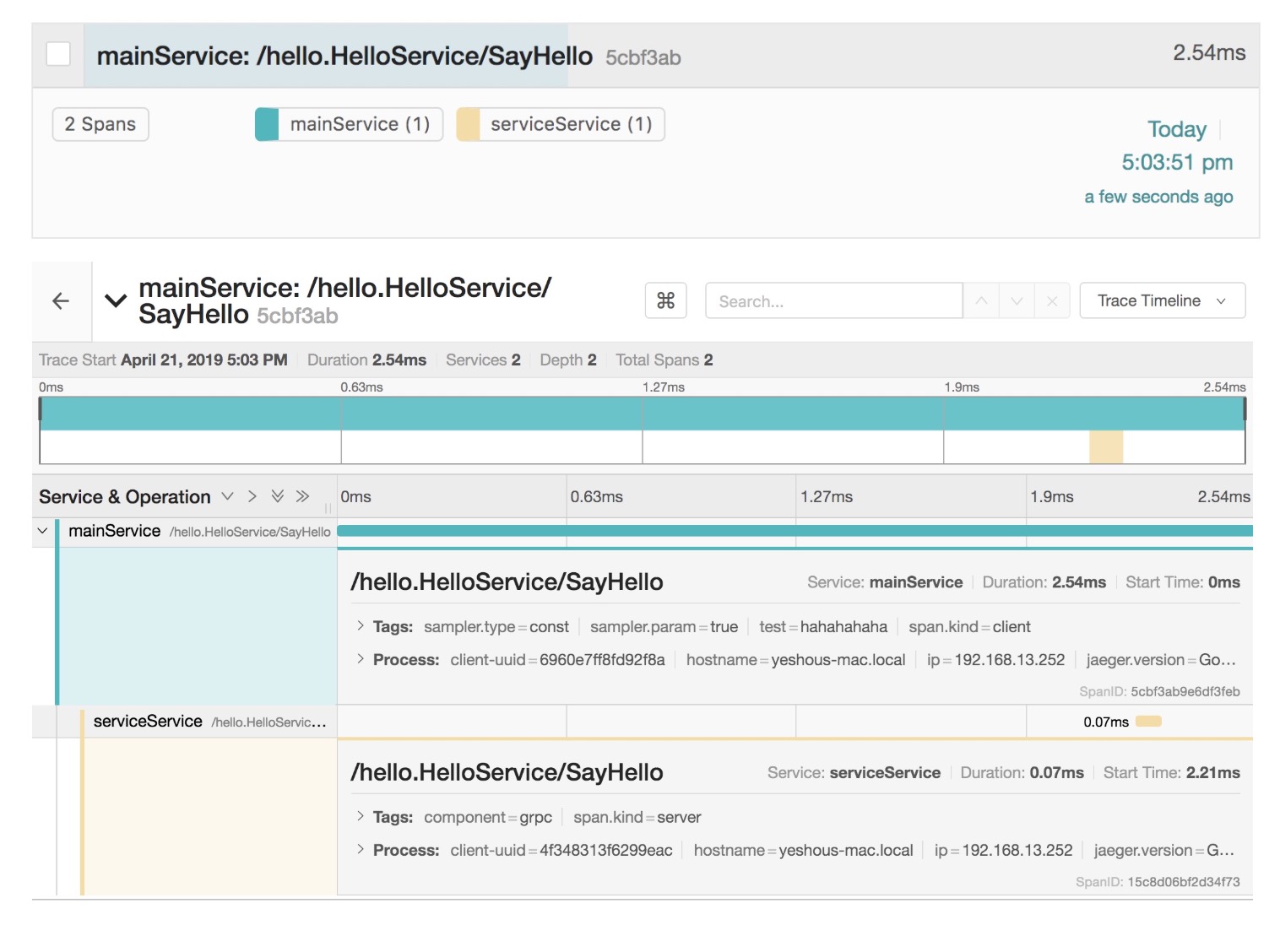
Related links
opentracing-specification
opentracing-javascript
jaegertracing
jaeger-client-node
jaeger-client-go
istio-zh
demo-github
This article is just a simple reference for jaeger. Considering the influence factors of Microservices, Service Mesh, Business Logic Logs and so on, tracing will be more complex and more pitted.