1. What is Selenium?
- Selenium is one of the most widely used open source Web UI (user interface) automation test suites. It was originally developed by Jason Huggins in 2004 as Thought Works Internal tools.
- Selenium supports automation across different browsers, platforms and programming languages.
- Selenium can be easily deployed on Windows, Linux, Solaris, Macintosh and other platforms. In addition, it supports the OS (operating system) of mobile applications such as IOS (IOS, Windows Mobile and Android).
- Selenium supports various programming languages by using drivers specific to each language. Selenium supports languages including C #, Java, Perl, PHP, Python and Ruby.
- Selenium supports browsers including Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome and Safari.
2. What are its characteristics?
- Open source software: open source software can add some functions of tools as needed
- Cross platform: linux, windows, mac
- Core function: automatic testing can be carried out on multiple browsers
- Multilingual: Java, Python, C#, JavaScript, Ruby, etc
- Mature and stable: it has been widely used by google, Baidu, Tencent and other companies
- Powerful: it can realize most of the functions of similar commercial tools. Because of its open source, it can realize customized functions
3. Test tool WebDriver
- Webdriver (selenium 2) is an automatic testing tool for Web applications
- It provides a friendly API
- Webdriver is a complete set of class libraries and does not depend on any test framework except the necessary browser driver
- WebDriver supports Firefox, IE, Opera, Chrome, safari and HtmlUnit
4. Browser related test operations
-
maximize_window
# Maximize browser driver = webdriver.Chrome() driver.maximize_window()
-
refresh
# Refresh browser driver = webdriver.Chrome() driver.refresh()
-
close
# Close a browser window driver = webdriver.Chrome() driver.close()
-
quit
# Close all browser windows driver = webdriver.Chrome() driver.quit()
-
title
# Gets the title of the current browser window driver = webdriver.Chrome() print(driver.title)
-
current_url
# Gets the URL of the browser's current window driver = webdriver.Chrome() print(driver.current_url)
5. Positioning of HTML elements
-
id
# Positioning by element ID attribute driver.find_element_by_id()
-
name
# Locate through the element name attribute driver.find_element_by_name() driver.find_elements_by_name()
-
class_name
# Positioning by element class attribute driver.find_element_by_class_name() driver.find_elements_by_class_name()
-
tag_name
# Positioning by element tag name driver.find_element_by_tag_name() driver.find_elements_by_tag_name()
-
link_text
# Accurately locate the text of the hypertext link element < a > < / a > driver.find_element_by_link_text() driver.find_elements_by_link_text()
-
partial_link_text
# Fuzzy positioning through the text of the hypertext link element < a > < / a > driver.find_element_by_partial_link_text() driver.find_elements_by_partial_link_text()
-
xpath
# Positioning by absolute positioning driver.find_element_by_xpath("/html/body/div/p[2]") # Positioning by relative positioning driver.find_element_by_xpath("//input[@id='username']") # Positioning by element attributes driver.find_element_by_xpath("//*[@name='hobby'] ") # Positioning through the combination of hierarchy and attributes driver.find_element_by_xpath("//*[@id='myfrom']/input") # Positioning through the combination of attributes and logic driver.find_element_by_xpath("//*[@id='password' and @name='password']") -
css
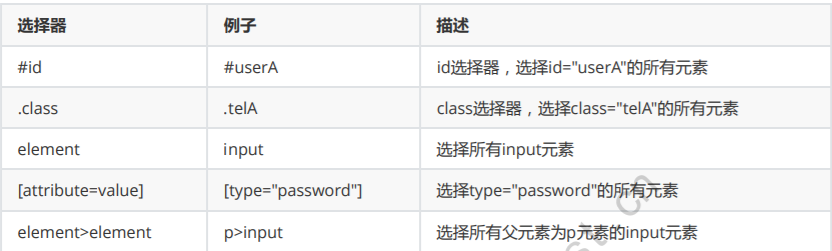
# Locate by id driver.find_element_by_css_selector("#username") # Positioning by clss driver.find_element_by_css_selector(".username") # Positioning by element driver.find_element_by_css_selector("input") # Positioning by attributes driver.find_element_by_css_selector("[type='hidden']") # Positioning through the hierarchy selector driver.find_element_by_css_selector("p>input")
6. Getting HTML elements
-
send_keys
# Enter the text of the element username = driver.find_element_by_id("username") username.send_keys("zhangsan") -
clear
# Clear the text of the element username = driver.find_element_by_id("username") username.clear() -
click
# Click the element button = driver.find_element_by_id("btn") button.click() -
size
# Gets the size of the element username = driver.find_element_by_id("username") print(username.size) -
text
# Gets the text of the element username = driver.find_element_by_id("username") print(username.text) -
get_attribute
# Gets the properties of the element img = driver.find_element_by_id("picture") img.get_attribute("src")
7. Waiting operation of HTML element
When WebDriver locates a page element, if it is not found, it will wait for the specified time
-
Display wait
Explicit wait acts on a single element, and the method is encapsulated in the WebDriverWait class
-
Implicit waiting
Implicit waiting acts on global elements, and the method is called directly through the instantiation object of the browser
- If the positioning of an element fails, an implicit wait valid length is triggered
- If the loading is completed within the specified time, continue
- Otherwise, the NoSuchElementException exception will be thrown. If the element is located for the first time, the implicit waiting time will not be triggered
driver.implicitly_wait(10)
8. Mouse related test operations
-
context_click
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains username = driver.find_element_by_id("username") action = ActionChains(driver) # Right click element = action.context_click(username) # implement element.perform() -
double_click
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains username = driver.find_element_by_id("username") action = ActionChains(driver) # Double click the mouse element = action.double_click(username) # implement element.perform() -
drag_and_drop
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains div1 = driver.find_element_by_id("div1") div2 = driver.find_element_by_id("div2") action = ActionChains(driver) # Mouse drag element = action.drag_and_drop(div1, div2) # implement element.perform() -
move_to_element
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains img = driver.find_element_by_id("picture") action = ActionChains(driver) # Mouse over element = action.move_to_element(img) # implement element.perform()
9. Keyboard related test operations
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys send_keys(Keys.BACK_SPACE) #Delete key (BackSpace) send_keys(Keys.SPACE) #Spacebar (Space) send_keys(Keys.TAB) #Tab send_keys(Keys.ESCAPE) #Back key (Esc) send_keys(Keys.ENTER) #Enter send_keys(Keys.CONTROL,'a') #Select all (Ctrl+A) send_keys(Keys.CONTROL,'c') #Copy (Ctrl+C)