The wrapper is used. Sort out the data and record it for subsequent review.
Directory ------------ (you can click the corresponding directory to jump directly)
1, Introduction to conditional constructor relationship
Introduction to conditional constructor relationship:
1. Query according to the primary key or simple query criteria
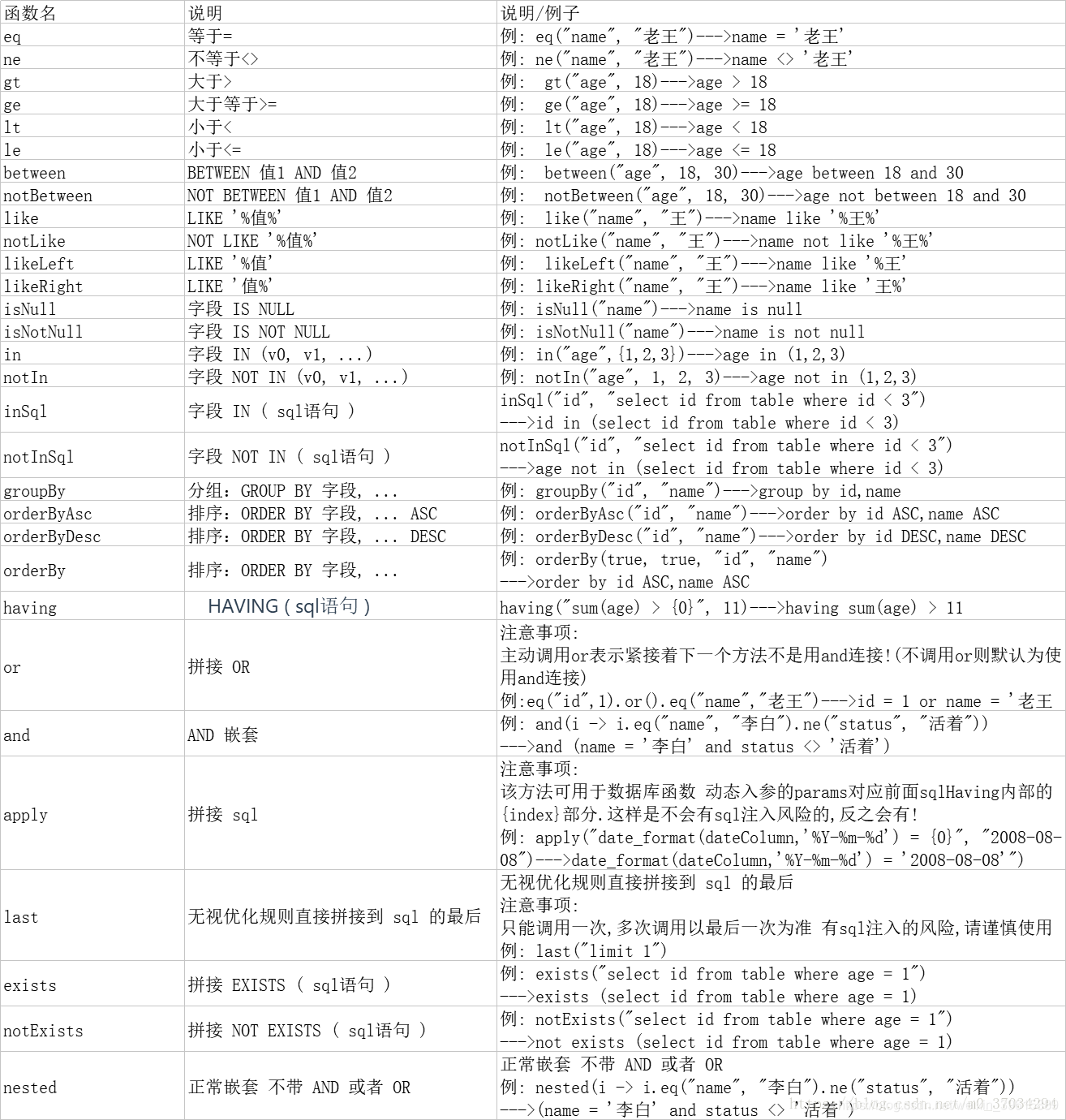
1,ge,gt,le,lt,isNull,isNotNull
5,like,notLike,likeLeft,likeRight
6,in,notIn,inSql,notinSql,exists,notExists
9,orderBy,orderByDesc,orderByAsc
11. Specify the columns to query
1, Introduction to conditional constructor relationship
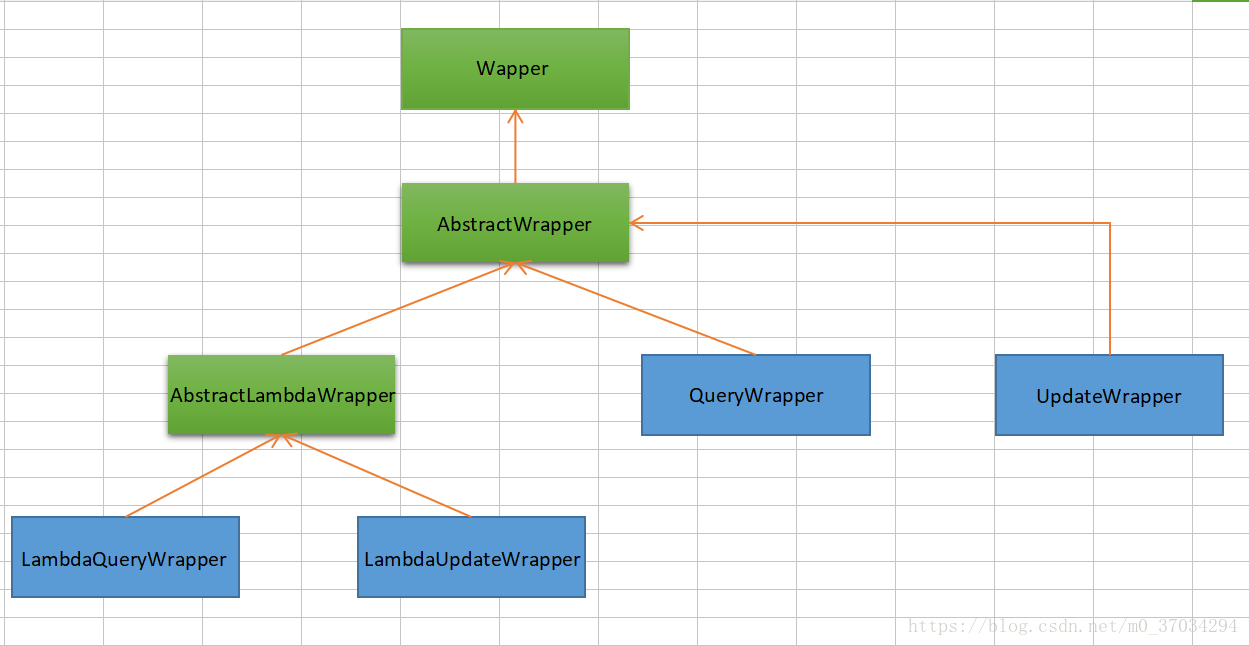
Introduction to conditional constructor relationship:
The green box in the figure above shows the abstract class abstract
The blue box is a normal class class, which can be used as a new object
The yellow arrow points to the parent-child relationship, and the arrow points to the parent class
Introduction to wapper:
Wrapper: conditional construction abstract class, topmost parent class
AbstractWrapper: used to encapsulate query conditions and generate sql where conditions
QueryWrapper: the Entity object encapsulates the operation class instead of using lambda syntax
UpdateWrapper: Update condition encapsulation, used for Entity object Update operation
AbstractLambdaWrapper: lambda syntax uses Wrapper to handle and parse lambda to obtain column.
LambdaQueryWrapper: it can be understood from the name. It is the query Wrapper used for Lambda syntax
Lambda updatewrapper: LambdaUpdateWrapper
2, Project instance
1. Query according to the primary key or simple query criteria
/**
* Query by single ID primary key
*/
@Test
public void selectById() {
User user = userMapper.selectById(1094592041087729666L);
System.out.println(user);
}
/**
* Query by multiple ID primary keys
*/
@Test
public void selectByList() {
List<Long> longs = Arrays.asList(1094592041087729666L, 1094590409767661570L);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(longs);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* Query through Map parameters
*/
@Test
public void selectByMap() {
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("name", "Zhang Yuqi");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(params);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
2. Mybatis plus also provides a Wrapper condition constructor. See the following code for specific use:
/**
* The name contains rain and is less than 40 years old
* <p>
* WHERE name LIKE '%Rain% 'and age < 40
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapperOne() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper();
wrapper.like("name", "rain").lt("age", 40);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* Name includes rain
* Age > 20 < 40
* Mailbox cannot be empty
* <p>
* WHERE name LIKE '%Rain% 'AND age BETWEEN 20 AND 40 AND email IS NOT NULL
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapperTwo() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = Wrappers.query();
wrapper.like("name", "rain").between("age", 20, 40).isNotNull("email");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* The name is Wang Xing
* Or older than or equal to 25
* Sort by age in descending order, and sort by id in ascending order for the same age
* <p>
* WHERE name LIKE 'King% 'or age > = 25 order by age DESC, ID ASC
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapperThree() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = Wrappers.query();
wrapper.likeRight("name", "king").or()
.ge("age", 25).orderByDesc("age").orderByAsc("id");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* The query was created on February 14, 2019
* And the superior leader's surname is Wang
* <p>
* WHERE date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d') = '2019-02-14' AND manager_id IN (select id from user where name like 'Wang% ')
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapperFour() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = Wrappers.query();
wrapper.apply("date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d') = {0}", "2019-02-14")
.inSql("manager_id", "select id from user where name like 'king%'");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* Query surname Wang
* And the age is less than 40 or the mailbox is not empty
* <p>
* WHERE name LIKE 'King% 'and (age < 40 or email is not null)
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapperFive() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = Wrappers.query();
wrapper.likeRight("name", "king").and(qw -> qw.lt("age", 40).or().isNotNull("email"));
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* Query surname Wang
* And the age is greater than 20, the age is less than 40, and the mailbox cannot be empty
* <p>
* WHERE name LIKE ? OR ( age BETWEEN ? AND ? AND email IS NOT NULL )
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapperSix() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = Wrappers.query();
wrapper.likeRight("name", "king").or(
qw -> qw.between("age", 20, 40).isNotNull("email")
);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* (Age less than 40 or email address is not empty) and first name is Wang
* WHERE ( age < 40 OR email IS NOT NULL ) AND name LIKE 'Wang% '
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapperSeven() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = Wrappers.query();
wrapper.nested(qw -> qw.lt("age", 40).or().isNotNull("email"))
.likeRight("name", "king");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* The query age is 30, 31 and 32
* WHERE age IN (?,?,?)
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapperEight() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = Wrappers.query();
wrapper.in("age", Arrays.asList(30, 31, 32));
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* Query a piece of data
* limit 1
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapperNine() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = Wrappers.query();
wrapper.in("age", Arrays.asList(30, 31, 32)).last("limit 1");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3, Specific operation
Note: the method of the following conditional constructor is included in the parameter column All represent database fields
1,ge,gt,le,lt,isNull,isNotNull
@Test
public void testDelete() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper
.isNull("name")
.ge("age", 12)
.isNotNull("email");
int result = userMapper.delete(queryWrapper);
System.out.println("delete return count = " + result);
}
SQL: UPDATE user SET deleted=1 WHERE deleted=0 AND name IS NULL AND age >= ? AND email IS NOT NULL
2,eq,ne
Note: seletOne returns an entity record. If there are multiple records, an error will be reported
@Test
public void testSelectOne() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("name", "Tom");
User user = userMapper.selectOne(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(user);
}
3,between,notBetween
Include size boundary
@Test
public void testSelectCount() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.between("age", 20, 30);
Integer count = userMapper.selectCount(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(count);
}
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND age BETWEEN ? AND ?
4,allEq
@Test
public void testSelectList() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", 2);
map.put("name", "Jack");
map.put("age", 20);9
queryWrapper.allEq(map);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,version FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND name = ? AND id = ? AND age = ?
5,like,notLike,likeLeft,likeRight
selectMaps returns a list of Map collections
@Test
public void testSelectMaps() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper
.notLike("name", "e")
.likeRight("email", "t");
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = userMapper.selectMaps(queryWrapper);//The return value is the Map list
maps.forEach(System.out::println);
}
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,version FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND name NOT LIKE ? AND email LIKE ?
6,in,notIn,inSql,notinSql,exists,notExists
in,notIn:
notIn("age",{1,2,3})--->age not in (1,2,3)
notIn("age", 1, 2, 3)--->age not in (1,2,3)inSql, notinSql: sub query can be implemented
example: inSql("age", "1,2,3,4,5,6")--->age in (1,2,3,4,5,6)
example: inSql("id", "select id from table where id < 3")--->id in (select id from table where id < 3)@Test
public void testSelectObjs() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//queryWrapper.in("id", 1, 2, 3);
queryWrapper.inSql("id", "select id from user where id < 3");
List<Object> objects = userMapper.selectObjs(queryWrapper);//The return value is the Object list
objects.forEach(System.out::println);
}SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,version FROM user WHERE deleted=0 AND id IN (select id from user where id < 3)
7,or,and
Note: UpdateWrapper is used here. If or is not called, and is used by default
@Test
public void testUpdate1() {
//Modify value
User user = new User();
user.setAge(99);
user.setName("Andy");
//modify condition
UpdateWrapper<User> userUpdateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
userUpdateWrapper
.like("name", "h")
.or()
.between("age", 20, 30);
int result = userMapper.update(user, userUpdateWrapper);
System.out.println(result);
}UPDATE user SET name=?, age=?, update_time=? WHERE deleted=0 AND name LIKE ? OR age BETWEEN ? AND ?
8. Nested or, nested and
lambda expressions are used here, and the expressions in or are finally translated into sql with parentheses
@Test
public void testUpdate2() {
//Modify value
User user = new User();
user.setAge(99);
user.setName("Andy");
//modify condition
UpdateWrapper<User> userUpdateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
userUpdateWrapper
.like("name", "h")
.or(i -> i.eq("name", "Li Bai").ne("age", 20));
int result = userMapper.update(user, userUpdateWrapper);
System.out.println(result);
}
UPDATE user SET name=?, age=?, update_time=?
WHERE deleted=0 AND name LIKE ?
OR ( name = ? AND age <> ? )
9,orderBy,orderByDesc,orderByAsc
@Test
public void testSelectListOrderBy() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.orderByDesc("id");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,version
FROM user WHERE deleted=0 ORDER BY id DESC
10,last
Directly spliced to the end of sql
Note: it can only be called once. The last call shall prevail. There is a risk of sql injection. Please use it with caution
@Test
public void testSelectListLast() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.last("limit 1");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
SELECT id,name,age,email,create_time,update_time,deleted,version
FROM user WHERE deleted=0 limit 1
11. Specify the columns to query
@Test
public void testSelectListColumn() {
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.select("id", "name", "age");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}SELECT id,name,age FROM user WHERE deleted=0
12,set,setSql
The final sql will merge user.setAge() and userUpdateWrapper.set() And fields in setSql()
@Test
public void testUpdateSet() {
//Modify value
User user = new User();
user.setAge(99);
//modify condition
UpdateWrapper<User> userUpdateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
userUpdateWrapper
.like("name", "h")
.set("name", "Lao Li Tou")//In addition to querying, you can also use set to set the modified fields
.setSql(" email = '123@qq.com'");//Can have subqueries
int result = userMapper.update(user, userUpdateWrapper);
}
UPDATE user SET age=?, update_time=?, name=?, email = '123@qq.com' WHERE deleted=0 AND name LIKE ?
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------There is no text below-------------------
Reference documents
1,https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37034294/article/details/82917234
2,https://blog.csdn.net/kepengs/article/details/112345870
3,https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39615889/article/details/107086931
4,https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38111957/article/details/91447509