Intro
TOTP is a time-based one-time password generation algorithm, which is composed of RFC 6238 Definition. Different from the event based one-time password generation algorithm HOTP TOTP is time-based and has the following relationship with HOTP:
TOTP = HOTP(K, T) HOTP(K,C) = Truncate(HMAC-SHA-1(K,C))
Among them:
- T: T = (Current Unix time - T0) / X, T0 = 0,X = 30
- K: the shared key of the client and the server. The key of different clients is different.
- HOTP: please refer to RFC , also refer to Understand HMAC based one time password algorithm
TOTP algorithm is based on HOTP. For HOTP algorithm, when the input of HOTP is consistent, it always outputs the same value, while TOTP is a value calculated based on time, which can be guaranteed to be fixed for a period of time (official recommendation is 30s) and the same value for a period of time, so as to achieve the one-time password generation algorithm based on time As a whole, it's not bad. There's a small problem. If you need to implement a password, you can only verify it once. You need to implement it in the business logic by yourself. TOTP is only responsible for generation and verification.
C ා implementation of TOTP
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
namespace WeihanLi.Totp
{
public class Totp
{
private readonly OtpHashAlgorithm _hashAlgorithm;
private readonly int _codeSize;
public Totp() : this(OtpHashAlgorithm.SHA1, 6)
{
}
public Totp(OtpHashAlgorithm otpHashAlgorithm, int codeSize)
{
_hashAlgorithm = otpHashAlgorithm;
// valid input parameter
if (codeSize <= 0 || codeSize > 10)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(codeSize), codeSize, "length must between 1 and 9");
}
_codeSize = codeSize;
}
private static readonly Encoding Encoding = new UTF8Encoding(false, true);
public virtual string Compute(string securityToken) => Compute(Encoding.GetBytes(securityToken));
public virtual string Compute(byte[] securityToken) => Compute(securityToken, GetCurrentTimeStepNumber());
private string Compute(byte[] securityToken, long counter)
{
HMAC hmac;
switch (_hashAlgorithm)
{
case OtpHashAlgorithm.SHA1:
hmac = new HMACSHA1(securityToken);
break;
case OtpHashAlgorithm.SHA256:
hmac = new HMACSHA256(securityToken);
break;
case OtpHashAlgorithm.SHA512:
hmac = new HMACSHA512(securityToken);
break;
default:
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(_hashAlgorithm), _hashAlgorithm, null);
}
using (hmac)
{
var stepBytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(counter);
if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian)
{
Array.Reverse(stepBytes); // need BigEndian
}
// See https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4226
var hashResult = hmac.ComputeHash(stepBytes);
var offset = hashResult[hashResult.Length - 1] & 0xf;
var p = "";
for (var i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
p += hashResult[offset + i].ToString("X2");
}
var num = Convert.ToInt64(p, 16) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
//var binaryCode = (hashResult[offset] & 0x7f) << 24
// | (hashResult[offset + 1] & 0xff) << 16
// | (hashResult[offset + 2] & 0xff) << 8
// | (hashResult[offset + 3] & 0xff);
return (num % (int)Math.Pow(10, _codeSize)).ToString();
}
}
public virtual bool Verify(string securityToken, string code) => Verify(Encoding.GetBytes(securityToken), code);
public virtual bool Verify(string securityToken, string code, TimeSpan timeToleration) => Verify(Encoding.GetBytes(securityToken), code, timeToleration);
public virtual bool Verify(byte[] securityToken, string code) => Verify(securityToken, code, TimeSpan.Zero);
public virtual bool Verify(byte[] securityToken, string code, TimeSpan timeToleration)
{
var futureStep = (int)(timeToleration.TotalSeconds / 30);
var step = GetCurrentTimeStepNumber();
for (int i = -futureStep; i <= futureStep; i++)
{
if (step + i < 0)
{
continue;
}
var totp = Compute(securityToken, step + i);
if (totp == code)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static readonly DateTime _unixEpoch = new DateTime(1970, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, DateTimeKind.Utc);
/// <summary>
/// timestep
/// 30s(Recommend)
/// </summary>
private static readonly long _timeStepTicks = TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond * 30;
// More info: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6238#section-4
private static long GetCurrentTimeStepNumber()
{
var delta = DateTime.UtcNow - _unixEpoch;
return delta.Ticks / _timeStepTicks;
}
}
}Usage:
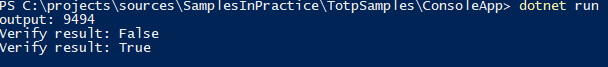
var otp = new Totp(OtpHashAlgorithm.SHA1, 4); // Output 4 bits using SHA1 algorithm
var secretKey = "12345678901234567890";
var output = otp.Compute(secretKey);
Console.WriteLine($"output: {output}");
Thread.Sleep(1000 * 30);
var verifyResult = otp.Verify(secretKey, output); // Use the default verification method, valid within 30s
Console.WriteLine($"Verify result: {verifyResult}");
verifyResult = otp.Verify(secretKey, output, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(60)); // Specify tolerable time difference, valid within 60s
Console.WriteLine($"Verify result: {verifyResult}");Output example: