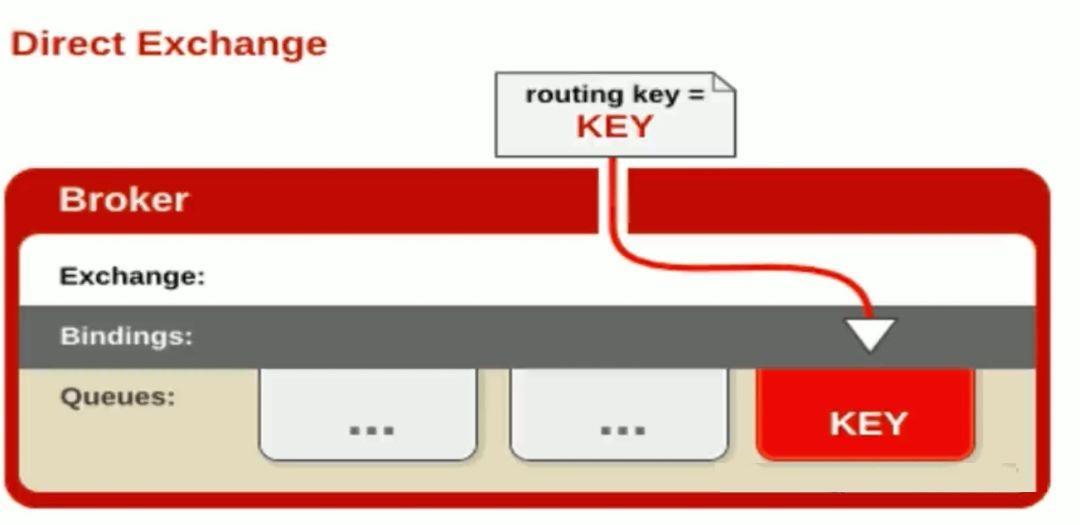
Direct mode
-
All messages sent to Direct Exchange are forwarded to the Queue specified in RouteKey.
-
The Direct mode can use the Exchange: default Exchange provided by RabbitMQ, so there is no need to bind Exchange.
- During message delivery, the RouteKey must match perfectly before it can be received by the queue, otherwise the message will be discarded,
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
public class DirectProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. Create a ConnectionFactory and set it
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
//2. Create a connection through a connection factory
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//3. Create Channel through Connection
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//4. Statement
String exchangeName = "test_direct_exchange";
String routingKey = "item.direct";
//5. Sending
String msg = "this is direct msg";
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey, null, msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("Send message : " + msg);
//6. Close the connection
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DirectConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. Create a ConnectionFactory and set it
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
factory.setAutomaticRecoveryEnabled(true);
factory.setNetworkRecoveryInterval(3000);
//2. Create a connection through a connection factory
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//3. Create Channel through Connection
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//4. Statement
String exchangeName = "test_direct_exchange";
String queueName = "test_direct_queue";
String routingKey = "item.direct";
channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, "direct", true, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
//In general, code binding is not required, but manual binding is required in the management interface
channel.queueBind(queueName, exchangeName, routingKey);
//5. Create consumers and receive messages
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,
AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");
}
};
//6. Set Channel consumer binding queue
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer);
}
}Send message : this is direct msg [x] Received 'this is direct msg' Topic Pattern
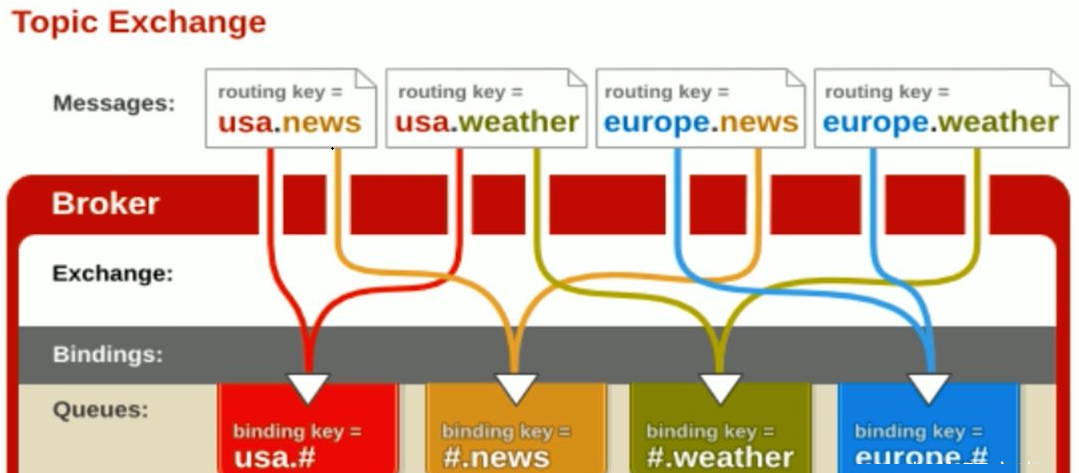
Topic mode
You can use wildcards for fuzzy matching
-
The symbol 'ා' matches one or more words
- The sign "*" doesn't match many words
For example:
-
'log. ා' can match to 'log.info.oa'
- "Log. *" only matches "log.erro"“
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
public class TopicProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. Create a ConnectionFactory and set it
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
//2. Create a connection through a connection factory
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//3. Create Channel through Connection
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//4. Statement
String exchangeName = "test_topic_exchange";
String routingKey1 = "item.update";
String routingKey2 = "item.delete";
String routingKey3 = "user.add";
//5. Sending
String msg = "this is topic msg";
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey1, null, msg.getBytes());
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey2, null, msg.getBytes());
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey3, null, msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("Send message : " + msg);
//6. Close the connection
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TopicConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. Create a ConnectionFactory and set it
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
factory.setAutomaticRecoveryEnabled(true);
factory.setNetworkRecoveryInterval(3000);
//2. Create a connection through a connection factory
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//3. Create Channel through Connection
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//4. Statement
String exchangeName = "test_topic_exchange";
String queueName = "test_topic_queue";
String routingKey = "item.#";
channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, "topic", true, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
//In general, code binding is not required, but manual binding is required in the management interface
channel.queueBind(queueName, exchangeName, routingKey);
//5. Create consumers and receive messages
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,
AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");
}
};
//6. Set Channel consumer binding queue
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer);
}
}Send message : this is topc msg [x] Received 'this is topc msg' [x] Received 'this is topc msg'
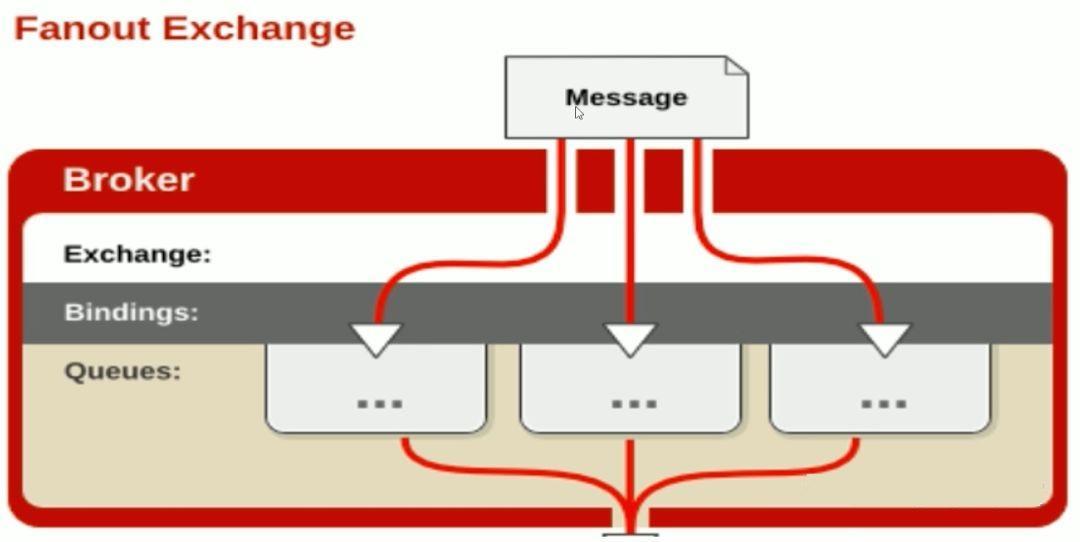
Fanout mode
Without processing the routing key, simply bind the queue to the switch, and messages sent to the switch will be forwarded to all queues bound to the switch.
Fanout switches are the fastest to forward messages.
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FanoutConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. Create a ConnectionFactory and set it
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
factory.setAutomaticRecoveryEnabled(true);
factory.setNetworkRecoveryInterval(3000);
//2. Create a connection through a connection factory
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//3. Create Channel through Connection
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//4. Statement
String exchangeName = "test_fanout_exchange";
String queueName = "test_fanout_queue";
String routingKey = "item.#";
channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, "fanout", true, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
//In general, code binding is not required, but manual binding is required in the management interface
channel.queueBind(queueName, exchangeName, routingKey);
//5. Create consumers and receive messages
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,
AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");
}
};
//6. Set Channel consumer binding queue
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer);
}
}import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
public class FanoutProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. Create a ConnectionFactory and set it
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
//2. Create a connection through a connection factory
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//3. Create Channel through Connection
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//4. Statement
String exchangeName = "test_fanout_exchange";
String routingKey1 = "item.update";
String routingKey2 = "";
String routingKey3 = "ookjkjjkhjhk";//Any routingkey
//5. Sending
String msg = "this is fanout msg";
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey1, null, msg.getBytes());
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey2, null, msg.getBytes());
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey3, null, msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("Send message : " + msg);
//6. Close the connection
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}Send message : this is fanout msg [x] Received 'this is fanout msg' [x] Received 'this is fanout msg' [x] Received 'this is fanout msg'